利用axis2实现WebService(Java)
一.使用axis2构建WebService服务器(POJO方式)。
1.下载所需的包:axis2的二进制包和axis2.war包。
下载地址:http://axis.apache.org/axis2/java/core/download.cgi#a1_5_2
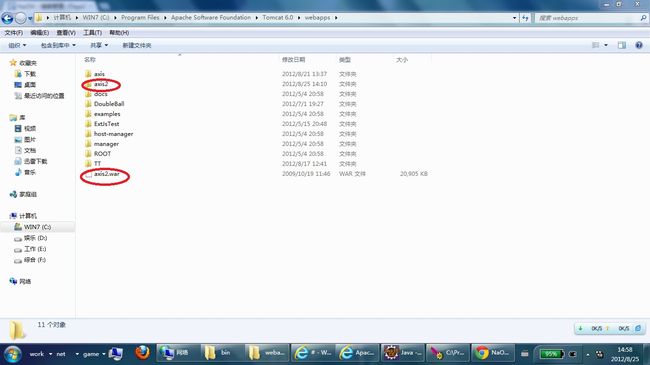
2.将下载的axis2.war放到tomcat的webapps目录下,启动tomcat,此时webapps目录会自动解压出axis2目录,如下图:
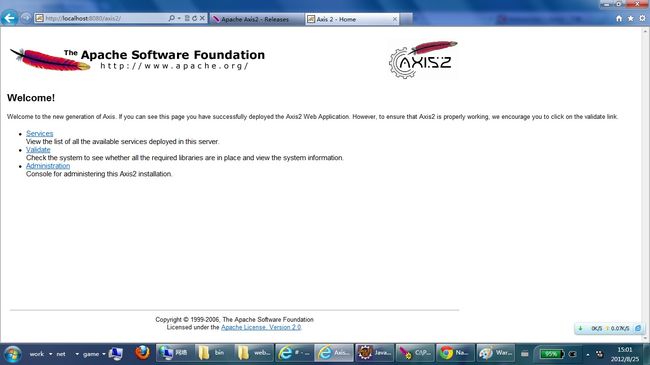
此时在浏览器地址栏中输入: http://localhost:8080/axis2 ,如果一切正常会看到如下页面:
3.编写服务器端代码:
启动Eclipse,选择File---New---Project,找开新建向导,如下图:
4.选择Java Project,点击Next,打开新建项目窗口,为新建项目命名,这里命名为4thWebService,点击Finish完成项目的创建。
5.编写服务器端代码:
选择File---New---Class,新建的类必须是不含任何包名的类,命名为:MyWebService,如下图所示:
6.点击Finish完成创建,并编写该类的代码如下:
public class MyWebService {
public String helloWebService(String name){
System.out.println("client args = "+name) ;
return name + " , this is webService . " ;
}
}
7.将编译后的MyWebService.class文件放置到tomcat的webapps/axis2/WEB-INF/pojo(如果没有pojo文件夹,那么需要手动创建该文件夹)目录下。
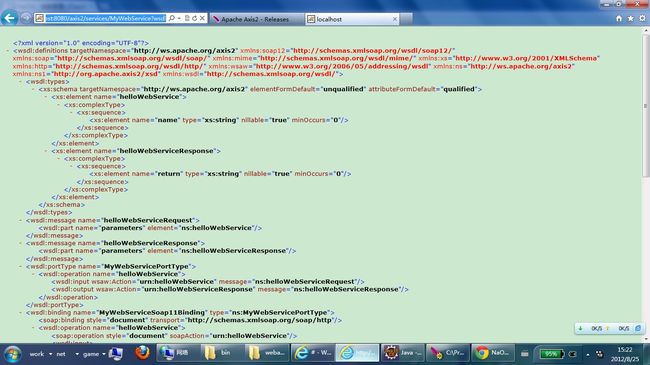
8.在浏览器的地址栏中输入:http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/MyWebService?wsdl
如果创建成功,你会看到如下页面:
使用POJO方式搭建WebService的优缺点:
优点:简单
缺点:服务器端Java类不能含有包名。
二.使用axis2构建WebService客户端.
1.需要把下载的二进制包解压,并把该文件夹下lib中所有的jar包都拷贝到自己的项目中(因为我也不知道具体哪个jar包有用,,所以保险起见,全导入,呵呵).
2. 编写客户端Java类代码如下:
package com.ysj;
import javax.xml.namespace.QName;
import org.apache.axis2.AxisFault;
import org.apache.axis2.addressing.EndpointReference;
import org.apache.axis2.client.Options;
import org.apache.axis2.rpc.client.RPCServiceClient;
public class TestAxis2 {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
new TestAxis2().test();
}
public void test() throws Exception {
// 服务器端WebService的WSDL连接串
String serviceUrl = "http://172.16.225.170:8080/axis2/services/MyWebService?wsdl" ;
RPCServiceClient serviceClient = null;
String resultString = "";
serviceClient = getServiceClient(serviceUrl);
// 服务器端开放的方法名
String wsFunction = "helloWebService";
System.out.println(wsFunction);
// 要传给服务器开放方法的参数.
String jsonString = "你好" ;
resultString = login(serviceUrl,serviceClient, jsonString, wsFunction);
System.out.println("resultString=" + resultString);
}
public RPCServiceClient getServiceClient(String wsdlUrl) {
RPCServiceClient serviceClient = null;
try {
serviceClient = new RPCServiceClient();
Options options = serviceClient.getOptions();
EndpointReference targetEPR = new EndpointReference(wsdlUrl);
options.setTo(targetEPR);
} catch (AxisFault e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return serviceClient;
}
public String login(String serviceUrl,RPCServiceClient serviceClient, String jsonString, String wsFunction) throws AxisFault {
// 在创建QName对象时,QName类的构造方法的第一个参数表示WSDL文件的命名空间名,也就是<wsdl:definitions>元素的targetNamespace属性值
QName opLogin = new QName("http://ws.apache.org/axis2", wsFunction);
// 参数,如果有多个,继续往后面增加即可,不用指定参数的名称
Object[] inputArgs = new Object[] { };
if(jsonString!=null&&!"".equals(jsonString)){
inputArgs = new Object[] { jsonString };
}
/*
返回参数类型,这个和axis1有点区别
invokeBlocking方法有三个参数,其中第一个参数的类型是QName对象,表示要调用的方法名;
第二个参数表示要调用的WebService方法的参数值,参数类型为Object[];
第三个参数表示WebService方法的返回值类型的Class对象,参数类型为Class[]。
当方法没有参数时,invokeBlocking方法的第二个参数值不能是null,而要使用new Object[]{}
如果被调用的WebService方法没有返回值,应使用RPCServiceClient类的invokeRobust方法,
该方法只有两个参数,它们的含义与invokeBlocking方法的前两个参数的含义相同
*/
Class[] returnTypes = new Class[] { String.class };
Object[] response = serviceClient.invokeBlocking(opLogin, inputArgs, returnTypes);
String result = (String) response[0];
// display results
if (result == null) {
System.out.println("result is null!");
} else {
System.out.println(wsFunction+" : " + result);
}
return result;
}
}
输出结果为:
helloWebService
helloWebService : 你好 , this is webService .
resultString=你好 , this is webService .