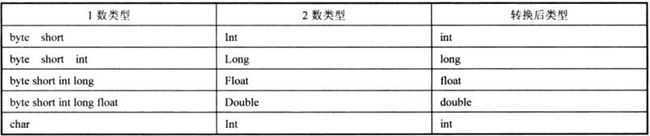
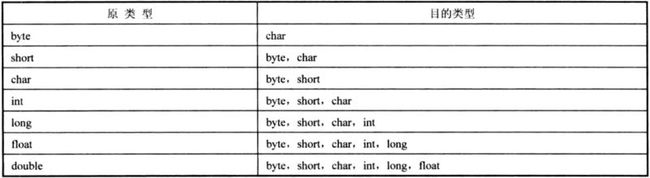
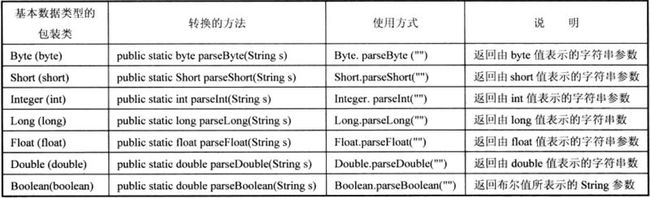
数据类型的转换方式主要可以分为3种:自动类型转换、强制类型转换、包装类过渡类型转换。其中强制类型转换在实际开发中运用的比较多。
1.自动类型转换
public class Conversion_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
short s = 10;
byte b = 5;
char c = 'A';
int i = 6;
System.out.println("short -> int " + (s - i));
System.out.println("byte -> int " + (b * i));
System.out.println("char -> int " + (c + i));
}
}
运行结果:
short -> int 4
byte -> int 30
char -> int 71
2.强制类型转换
public class Conversion_2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a = 123.4567890123456789;
float f = 2.65f;
int i = 56;
System.out.println("int -> byte " + (byte) i);
System.out.println("float -> int " + (int) f);
System.out.println("double -> int " + (double) a);
System.out.println("int -> char " + (char) i);
}
}
运行结果:
int -> byte 56
float -> int 2
double -> int 123.45678901234568
int -> char 8
3.包装类过渡类型转换
在进行简单数据类型之间的强制转换时,也可以利用包装类进行中间过渡。
在一般情况下,首先声明一个变量,再将其转换成与其相对应的包装类的一个实例化对象,然后用这个对象调用包装类中的XXValue()方法进行类型转换。
例如,当把int型转换为short型时,代码如下:
int i = 67; Integer it = new Integer(i); short s = it.shortValue(); // it.shortValue()以short类型返回该Integer的值
当希望把double型转换为int型时,代码如下所示:
double d1 = 100.00; Double d2 = new Double(d1); int i1 = d2.intValue();
String类型转换成数据类型
public class StringType_1
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String n = Integer.toString(12);
String f = Float.toString(12.3f);
String d = Double.toString(12.6);
String l = Long.toString(123L);
String s = Short.toString((short) 12);
System.out.println("The StringType of int is " + n);
System.out.println("The StringType of float is " + f);
System.out.println("The StringType of double is " + d);
System.out.println("The StringType of long is " + l);
System.out.println("The StringType of short is " + s);
}
}
运行结果:
The StringType of int is 12
The StringType of float is 12.3
The StringType of double is 12.6
The StringType of long is 123
The StringType of short is 12
代码示例2:
public class StringType_2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String n = "123";
String f = "45.6f";
String d = "12.3456789";
String l = "15555555666";
String b = "12";
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(n);
float f1 = Float.parseFloat(f);
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(d);
long l1 = Long.parseLong(l);
byte b1 = Byte.parseByte(b);
System.out.println("The intType of String is " + n1);
System.out.println("The floatType of String is " + f1);
System.out.println("The doubleType of String is " + d1);
System.out.println("The longType of String is " + l1);
System.out.println("The byteType of String is " + b1);
}
}
运行结果:
The intType of String is 123
The floatType of String is 45.6
The doubleType of String is 12.3456789
The longType of String is 15555555666
The byteType of String is 12