20135327郭皓——信息安全系统设计基础第十周学习总结
第十周(11.09-11.15):
| 学习计时:共6小时 读书: 代码: 作业: 博客: |
| 一、学习目标 |
| 1 理解I/O代码 |
实践代码
cp1.c
这是一个将目标文件复制到目的文件的程序,具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h>////Unix类系统定义符号常量 4 #include <fcntl.h>//定义了很多宏和open,fcntl函数原型 5 6 #define BUFFERSIZE 4096//存储器容量 7 #define COPYMODE 0644//复制的长度 8 9 void oops(char *, char *); 10 11 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 12 //argc记录了用户在运行程序的命令行中输入的参数的个数;argv[]是argc个参数,其中第0个参数是程序的全名,以后的参数 命令行后面跟的用户输入的参数 13 { 14 int in_fd, out_fd, n_chars;//三个描述符 15 char buf[BUFFERSIZE];//存储器 16 /* 17 检查参数是否为三,不是则返回标准错误 18 */ 19 if (argc != 3) { 20 fprintf(stderr, "usage: %s source destination\n", *argv); 21 exit(1); 22 } 23 /* 24 打开目的文件,若返回描述符为-1,则打开失败 25 */ 26 27 if ((in_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY)) == -1) 28 oops("Cannot open ", argv[1]); 29 /* 30 创建目的文件,若返回描述符为-1,则创建失败 31 */ 32 33 if ((out_fd = creat(argv[2], COPYMODE)) == -1) 34 oops("Cannot creat", argv[2]); 35 /* 36 当文件复制成功后,判断写入的字符个数是否等于原来的数,若不等,则返回写错误;若无法读取,则为读错误 37 */ 38 while ((n_chars = read(in_fd, buf, BUFFERSIZE)) > 0) 39 if (write(out_fd, buf, n_chars) != n_chars) 40 oops("Write error to ", argv[2]); 41 if (n_chars == -1) 42 oops("Read error from ", argv[1]); 43 /* 44 若关闭文件描述符为-1,则返回关闭错误 45 */ 46 47 if (close(in_fd) == -1 || close(out_fd) == -1) 48 oops("Error closing files", ""); 49 } 50 /* 51 输出错误信息和 52 */ 53 void oops(char *s1, char *s2) 54 { 55 fprintf(stderr, "Error: %s ", s1); 56 perror(s2);//用来将上一个函数发生错误的原因输出到标准设备(stderr) 57 exit(1); 58 }
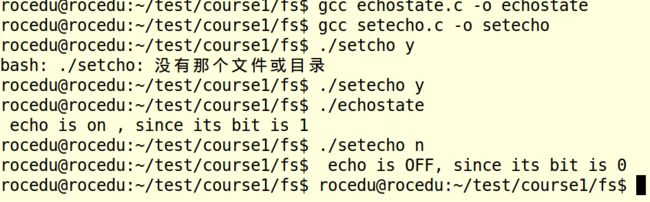
setecho.c/echostate.c
setecho:本函数是设置命令符是否显示,具体如下:
echostate:本函数是显示命令符是否显示状态,具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <termios.h> 4 5 #define oops(s,x) { perror(s); exit(x); } 6 /* 7 设置命令符是否显示 8 */ 9 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 10 { 11 struct termios info; 12 13 if ( argc == 1 ) 14 exit(0); 15 16 if ( tcgetattr(0,&info) == -1 ) /* get attribs */ 17 oops("tcgettattr", 1); 18 19 if ( argv[1][0] == 'y' ) 20 info.c_lflag |= ECHO ; /* turn on bit */ 21 else 22 info.c_lflag &= ~ECHO ; /* turn off bit */ 23 24 if ( tcsetattr(0,TCSANOW,&info) == -1 ) /* set attribs */ 25 oops("tcsetattr",2); 26 27 return 0; 28 }
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <termios.h>//UNIX的可移植的操作系统接口规范中定义的标准接口 4 /* 5 显示命令符是否显示状态 6 */ 7 int main() 8 { 9 struct termios info; 10 int rv; 11 12 rv = tcgetattr( 0, &info ); /* read values from driver */ 13 14 if ( rv == -1 ){ 15 perror( "tcgetattr"); 16 exit(1); 17 } 18 if ( info.c_lflag & ECHO ) 19 printf(" echo is on , since its bit is 1\n"); 20 else 21 printf(" echo is OFF, since its bit is 0\n"); 22 23 return 0; 24 }
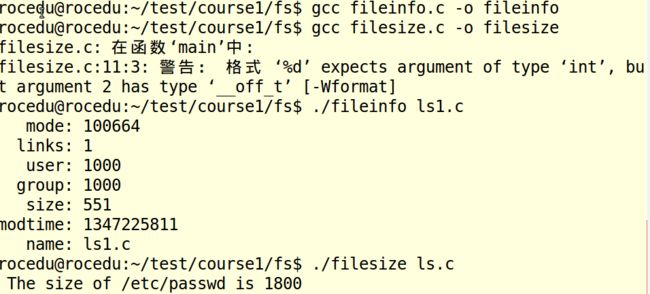
fileinfo.c/filesize.c
fileinfo:显示当前文件具体信息,具体如下:
filesize:计算文件的字节数大小,具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/types.h> 3 #include <sys/stat.h> 4 5 void show_stat_info(char *, struct stat *); 6 /* 7 显示当前文件具体信息 8 */ 9 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 10 { 11 struct stat info; 12 13 if (argc>1) 14 { 15 16 if( stat(argv[1], &info) != -1 ){ 17 show_stat_info( argv[1], &info ); 18 return 0; 19 } 20 else 21 perror(argv[1]); 22 } 23 return 1; 24 } 25 void show_stat_info(char *fname, struct stat *buf) 26 { 27 printf(" mode: %o\n", buf->st_mode); 28 printf(" links: %d\n", buf->st_nlink); 29 printf(" user: %d\n", buf->st_uid); 30 printf(" group: %d\n", buf->st_gid); 31 printf(" size: %d\n", (int)buf->st_size); 32 printf("modtime: %d\n", (int)buf->st_mtime); 33 printf(" name: %s\n", fname ); 34 }
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/stat.h> 3 /* 4 计算文件的字节数大小 5 */ 6 int main() 7 { 8 struct stat infobuf; 9 10 if ( stat( "/etc/passwd", &infobuf) == -1 ) 11 perror("/etc/passwd"); 12 else 13 printf(" The size of /etc/passwd is %d\n", infobuf.st_size ); 14 }
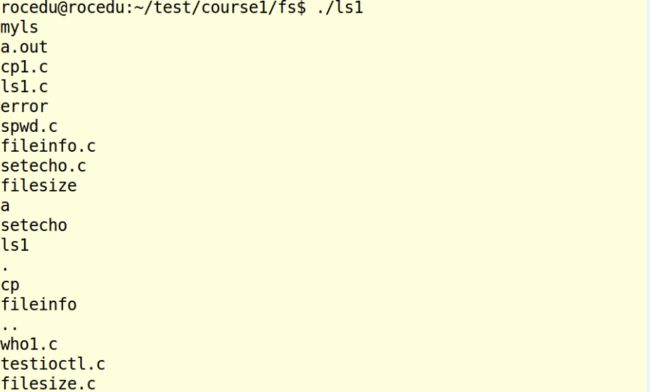
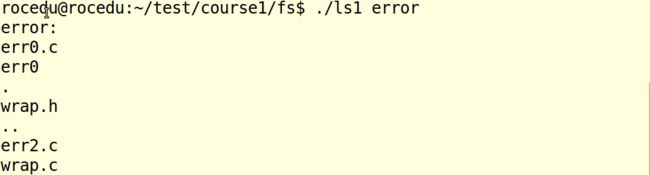
ls1.c/ls2.c
ls1:显示当前目录下文件或目标文件下目录(ls的功能),具体如下:
ls2:ls1的加强版,增加文件属性(ls -l的功能),具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <sys/types.h> 3 #include <dirent.h> 4 5 void do_ls(char []); 6 /* 7 显示当前目录下文件或目标文件下目录(ls的功能) 8 */ 9 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 10 { 11 /* 12 如果ls后没有参数,则打印当前目录;如果有则打印目录 13 */ 14 if ( argc == 1 ) 15 do_ls( "." ); 16 else 17 while ( --argc ){ 18 printf("%s:\n", *++argv ); 19 do_ls( *argv ); 20 } 21 22 return 0; 23 } 24 25 void do_ls( char dirname[] ) 26 { 27 /* 28 使用dir命令功能 29 */ 30 DIR *dir_ptr; 31 struct dirent *direntp; 32 /* 33 判断地址是否正确。否则返回打开失败,正确则依次打印文件名 34 */ 35 if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL ) 36 fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open %s\n", dirname); 37 else 38 { 39 while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ) 40 printf("%s\n", direntp->d_name ); 41 closedir(dir_ptr); 42 } 43 }
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 #include <sys/types.h> 4 #include <dirent.h> 5 #include <sys/stat.h> 6 7 void do_ls(char[]); 8 void dostat(char *); 9 void show_file_info( char *, struct stat *); 10 void mode_to_letters( int , char [] ); 11 char *uid_to_name( uid_t ); 12 char *gid_to_name( gid_t ); 13 14 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) 15 { 16 if ( argc == 1 ) 17 do_ls( "." ); 18 else 19 while ( --argc ){ 20 printf("%s:\n", *++argv ); 21 do_ls( *argv ); 22 } 23 24 return 0; 25 } 26 27 void do_ls( char dirname[] ) 28 { 29 DIR *dir_ptr; 30 struct dirent *direntp; 31 32 if ( ( dir_ptr = opendir( dirname ) ) == NULL ) 33 fprintf(stderr,"ls1: cannot open %s\n", dirname); 34 else 35 { 36 while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ) 37 dostat( direntp->d_name ); 38 closedir(dir_ptr); 39 } 40 } 41 42 void dostat( char *filename ) 43 { 44 struct stat info; 45 46 if ( stat(filename, &info) == -1 ) 47 perror( filename ); 48 else 49 show_file_info( filename, &info ); 50 } 51 52 void show_file_info( char *filename, struct stat *info_p ) 53 { 54 char *uid_to_name(), *ctime(), *gid_to_name(), *filemode(); 55 void mode_to_letters(); 56 char modestr[11]; 57 58 mode_to_letters( info_p->st_mode, modestr ); 59 60 printf( "%s" , modestr ); 61 printf( "%4d " , (int) info_p->st_nlink); 62 printf( "%-8s " , uid_to_name(info_p->st_uid) ); 63 printf( "%-8s " , gid_to_name(info_p->st_gid) ); 64 printf( "%8ld " , (long)info_p->st_size); 65 printf( "%.12s ", 4+ctime(&info_p->st_mtime)); 66 printf( "%s\n" , filename ); 67 68 } 69 70 void mode_to_letters( int mode, char str[] ) 71 { 72 strcpy( str, "----------" ); 73 74 if ( S_ISDIR(mode) ) str[0] = 'd'; 75 if ( S_ISCHR(mode) ) str[0] = 'c'; 76 if ( S_ISBLK(mode) ) str[0] = 'b'; 77 78 if ( mode & S_IRUSR ) str[1] = 'r'; 79 if ( mode & S_IWUSR ) str[2] = 'w'; 80 if ( mode & S_IXUSR ) str[3] = 'x'; 81 82 if ( mode & S_IRGRP ) str[4] = 'r'; 83 if ( mode & S_IWGRP ) str[5] = 'w'; 84 if ( mode & S_IXGRP ) str[6] = 'x'; 85 86 if ( mode & S_IROTH ) str[7] = 'r'; 87 if ( mode & S_IWOTH ) str[8] = 'w'; 88 if ( mode & S_IXOTH ) str[9] = 'x'; 89 } 90 91 #include <pwd.h> 92 93 char *uid_to_name( uid_t uid ) 94 { 95 struct passwd *getpwuid(), *pw_ptr; 96 static char numstr[10]; 97 98 if ( ( pw_ptr = getpwuid( uid ) ) == NULL ){ 99 sprintf(numstr,"%d", uid); 100 return numstr; 101 } 102 else 103 return pw_ptr->pw_name ; 104 } 105 106 #include <grp.h> 107 108 char *gid_to_name( gid_t gid ) 109 { 110 struct group *getgrgid(), *grp_ptr; 111 static char numstr[10]; 112 113 if ( ( grp_ptr = getgrgid(gid) ) == NULL ){ 114 sprintf(numstr,"%d", gid); 115 return numstr; 116 } 117 else 118 return grp_ptr->gr_name; 119 }
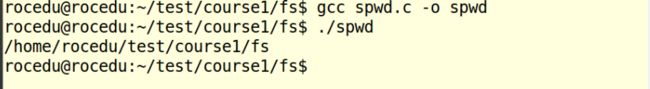
spwd.c
本函数功能为打印当前文件目录,具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <string.h> 4 #include <sys/types.h>//基本系统数据类型 5 #include <sys/stat.h>//unix/linux系统定义文件状态所在的伪标准头文件 6 #include <dirent.h>//unix类目录操作的头文件 7 8 ino_t get_inode(char *); 9 void printpathto(ino_t); 10 void inum_to_name(ino_t , char *, int ); 11 12 /* 13 打印当前文件目录 14 */ 15 int main() 16 { 17 printpathto( get_inode( "." ) ); 18 putchar('\n'); 19 return 0; 20 } 21 /* 22 打印路径 23 */ 24 void printpathto( ino_t this_inode ) 25 { 26 ino_t my_inode ; 27 char its_name[BUFSIZ]; 28 29 if ( get_inode("..") != this_inode ) 30 { 31 chdir( ".." ); 32 33 inum_to_name(this_inode,its_name,BUFSIZ); 34 35 my_inode = get_inode( "." ); 36 printpathto( my_inode ); 37 printf("/%s", its_name ); 38 39 } 40 } 41 /* 42 打开目录 43 */ 44 void inum_to_name(ino_t inode_to_find , char *namebuf, int buflen) 45 { 46 DIR *dir_ptr; 47 struct dirent *direntp; 48 49 dir_ptr = opendir( "." ); 50 if ( dir_ptr == NULL ){ 51 perror( "." ); 52 exit(1); 53 } 54 55 56 while ( ( direntp = readdir( dir_ptr ) ) != NULL ) 57 if ( direntp->d_ino == inode_to_find ) 58 { 59 strncpy( namebuf, direntp->d_name, buflen); 60 namebuf[buflen-1] = '\0'; 61 closedir( dir_ptr ); 62 return; 63 } 64 fprintf(stderr, "error looking for inum %d\n", (int) inode_to_find); 65 exit(1); 66 } 67 68 ino_t get_inode( char *fname ) 69 { 70 struct stat info; 71 72 if ( stat( fname , &info ) == -1 ){ 73 fprintf(stderr, "Cannot stat "); 74 perror(fname); 75 exit(1); 76 } 77 return info.st_ino; 78 }
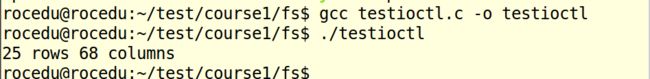
testioctl.c
本函数主要功能为:查看终端窗口大小,具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <unistd.h> 4 #include <sys/ioctl.h> 5 /* 6 查看终端窗口大小 7 */ 8 int main() 9 { 10 struct winsize size; 11 if( isatty(STDOUT_FILENO) == 0) 12 exit(1); 13 if (ioctl(STDOUT_FILENO, TIOCGWINSZ, &size) < 0) { 14 perror("ioctl TIOCGWINSZ error"); 15 exit(1); 16 } 17 18 printf("%d rows %d columns\n", size.ws_row, size.ws_col); 19 return 0; 20 }
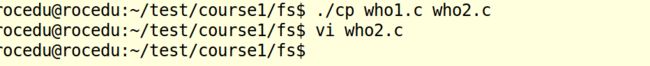
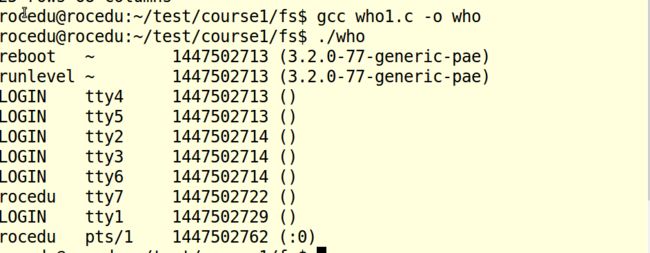
who1.c
本函数实际是实现who功能的函数,用于显示包含在结构体utmp中的用户的用户名,用户的登录时间等相关信息。具体如下:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <utmp.h> 4 #include <fcntl.h> 5 #include <unistd.h> 6 7 #define SHOWHOST 8 9 /* 10 实现who功能的函数,用于显示包含在结构体utmp中的用户的用户名,用户的登录时间等相关信息 11 */ 12 int show_info( struct utmp *utbufp ) 13 { 14 printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_name);//用户名 15 printf(" "); 16 /*tty:tty是Teletype的缩写。Teletype是最早出现的一种终端设备 17 终端是一种字符型设备,它有多种类型,通常使用tty来简称各种类型的终端设备。 18 */ 19 printf("%-8.8s", utbufp->ut_line);//tty 20 printf(" "); 21 printf("%10ld", utbufp->ut_time);//时间 22 printf(" "); 23 #ifdef SHOWHOST 24 printf("(%s)", utbufp->ut_host);//主机 25 #endif 26 printf("\n"); 27 28 return 0; 29 } 30 int main() 31 { 32 struct utmp current_record; 33 int utmpfd; 34 int reclen = sizeof(current_record); 35 /* 36 打开UTMP_FILE文件,如果打开则读取文件并打印在屏幕上,失败则返回失败 37 */ 38 if ( (utmpfd = open(UTMP_FILE, O_RDONLY)) == -1 ){ 39 perror( UTMP_FILE ); 40 exit(1); 41 } 42 while ( read(utmpfd, ¤t_record, reclen) == reclen ) 43 show_info(¤t_record); 44 close(utmpfd); 45 return 0; 46 }
PS:who1.c实际与who2.c是一个函数,故只写who1.c
参考资料:baidu,闫佳欣同学的博客,《深入理解计算机系统》
总结
这次实践代码大多是实现Linux的一些命令,在学习这些代码时,首先,我对几个未知的头文件进行了查阅,例如:4 #include <sys/types.h>//基本系统数据类型 5 #include <sys/stat.h>//unix/linux系统定义文件状态所在的伪标准头文件 6 #include <dirent.h>//unix类目录操作的头文件
同时,在研究函数功能时,有许多函数都不知道他的具体用法和定义,一部分是通过grep -nr xxx /usr/include,一部分是上网查找参考资料。对于具体一些函数的理解不是很明白,例如:ioctl,isatty等,对于这些还要继续询问查找。这次学习加大了我对代码的认识,同时也反映了我功底并不牢固,有一些代码并不能直接读懂,还要先编译运行后反推具体功能,这个方面还需继续加强,对书上的代码要多读多想多查。