第二次编程作业
第二次作业要求
[TOC]
描述
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "robot.h"
using namespace std;
int main(){
Robot myRobot(10, 5);
taskFrame tk1(0, 0, -90), tk2(1, 5, 30);
Vector2d P(5, 5);
myRobot.PTPMove(tk1, P);
cout << "第一个角度" << myRobot.getA() << ',' << "第二个的角度" << myRobot.getB() << endl;
myRobot.PTPMove(tk2, P);
cout << "第一个角度" << myRobot.getA() << ',' << "第二个的角度" << myRobot.getB() << endl;
return 0;
}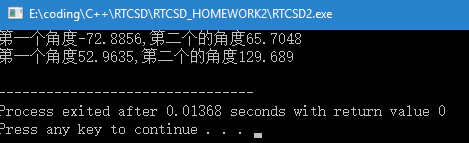
反解的时候有两组解,最终只选择显示了一种,代码注释中有第二种结果
其他代码段
frame.h
#ifndef _Frame_H_
#define _Frame_H_
class worldFrame{
private:
double x, y, angle;
public:
worldFrame();
double getX();
double getY();
double getAngle();
};
class taskFrame{
private:
double x, y, angle;
public:
taskFrame();
taskFrame(double, double, double);
double getX();
double getY();
double getAngle();
};
class jointFrame{
private:
double alpha,beta;
public:
jointFrame();
jointFrame(double, double);
double getAlpha();
double getBeta();
void setAlpha(double);
void setBeta(double);
};
#endifframe.cpp
#include "Frame.h"
worldFrame::worldFrame(){
x = 0;
y = 0;
angle = 0;
}
double worldFrame::getX(){
return x;
}
double worldFrame::getY(){
return y;
}
double worldFrame::getAngle(){
return angle;
}
taskFrame::taskFrame(){
x = 0;
y = 0;
angle = 0;
}
double taskFrame::getX(){
return x;
}
double taskFrame::getY(){
return y;
}
double taskFrame::getAngle(){
return angle;
}
taskFrame::taskFrame(double a, double b, double ang){
x = a;
y = b;
angle = ang;
}
jointFrame::jointFrame(){
alpha = 0;
beta = 0;
}
jointFrame::jointFrame(double ang1, double ang2){
alpha = ang1;
beta = ang2;
}
double jointFrame::getAlpha(){
return alpha;
}
double jointFrame::getBeta(){
return beta;
}
void jointFrame::setAlpha(double a){
alpha = a;
}
void jointFrame::setBeta(double b){
beta = b;
}solver.h
#ifndef _Solver_H_
#define _Solver_H_
#include "Frame.h"
#include <Eigen/Dense>
using Eigen::Vector2d;
using Eigen::Matrix2d;
class Solver{
private:
double la;
double lb;
public:
Vector2d forwardS(Vector2d); //将关节坐标转化为笛卡尔坐标
Vector2d reverseS(Vector2d); //将笛卡尔坐标转化为关节坐标
void setLa(double);
void setLb(double);
double getLa();
double getLb();
Vector2d TF2WF(taskFrame, Vector2d); //将任务坐标系下的点转换到世界坐标系下
};
#endifsolver.cpp
#include "solver.h"
#include <cmath>
Vector2d Solver::forwardS(Vector2d jnt){
Vector2d dkr; //笛卡尔坐标
dkr(0) = la * cos(jnt(0)*180/M_PI) + lb * cos(jnt(1)*180/M_PI);
dkr(1) = la * sin(jnt(0)*180/M_PI) + lb * sin(jnt(1)*180/M_PI);
return dkr;
}
Vector2d Solver::reverseS(Vector2d dkr){
Vector2d jnt; //关节坐标
double delta = 0.00001;
double x = dkr(0);
double y = dkr(1);
double thita = atan(y/x);
double k0 = (x*x + y*y + la*la - lb*lb) / (2*la*sqrt(x*x+y*y));
double fi0 = acos(k0);
jnt(0) = (thita - fi0) * 180 / M_PI;
double k1 = (x*x + y*y + lb*lb - la*la) / (2*lb*sqrt(x*x+y*y));
double fi1 = acos(k1);
jnt(1) = (thita + fi1) * 180 / M_PI;
// 角度值足够小的时候取 0
if (abs(jnt(0))< delta) jnt(0) = 0;
if (abs(jnt(1))< delta) jnt(1) = 0;
return jnt;
// 反解的时候有两组解
// 第一组里jnt(0) = thita - fi
// jnt(1) = fi + thita
// 第二组里jnt(0) = thita + fi
// jnt(1) = fi - thita
}
void Solver::setLa(double l){
la = l;
}
void Solver::setLb(double l){
lb = l;
}
double Solver::getLa(){
return la;
}
double Solver::getLb(){
return lb;
}
Vector2d Solver::TF2WF(taskFrame TF, Vector2d P){
Vector2d T; //距离矢量
Matrix2d R; //旋转矩阵
double angle = TF.getAngle() / 180 * M_PI;
T(0) = TF.getX();
T(1) = TF.getY();
R << cos(angle), -sin(angle),
sin(angle), cos(angle);
return R * P + T;
}robot.h
#ifndef _Robot_H_
#define _Robot_H_
#include "solver.h"
#include "frame.h"
class Robot{
private:
double lengthA, lengthB;
double alpha, beta;
Solver S;
public:
Robot();
Robot(double, double);
void setLa(double);
void setLb(double);
double getLa();
double getLb();
double getA();
double getB();
void PTPMove(jointFrame, Vector2d);
void PTPMove(worldFrame, Vector2d);
void PTPMove(taskFrame, Vector2d);
};
#endifrobot.cpp
#include "robot.h"
Robot::Robot(){
lengthA = 0;
lengthB = 0;
}
Robot::Robot(double l1, double l2){
lengthA = l1;
lengthB = l2;
}
void Robot::setLa(double l){
lengthA = l;
}
void Robot::setLb(double l){
lengthB = l;
}
double Robot::getLa(){
return lengthA;
}
double Robot::getLb(){
return lengthB;
}
double Robot::getA(){
return alpha;
}
double Robot::getB(){
return beta;
}
void Robot::PTPMove(jointFrame JF, Vector2d P){
alpha = P(0);
beta = P(1);
}
void Robot::PTPMove(taskFrame TF, Vector2d P){
Vector2d tmp;
tmp = S.TF2WF(TF, P);
S.setLa(lengthA); //给solver类中的la和lb赋值
S.setLb(lengthB);
tmp = S.reverseS(tmp);
alpha = tmp(0);
beta = tmp(1);
}
void Robot::PTPMove(worldFrame WF, Vector2d P){
Vector2d tmp;
S.setLa(lengthA);
S.setLb(lengthB);
tmp = S.reverseS(P);
alpha = tmp(0);
beta = tmp(1);
}