利用python_matplotlib//numpy//re进行数据处理与分析
本次利用一个最优树问题进行举例,查找最优树的有效算法有Prim和Kruskal两种,分别应用于稀疏图与稠密图上,以下为简单描述:
1).输入:一个加权连通图,其中顶点集合为V,边集合为E;
2).初始化:Vnew = {x},其中x为集合V中的任一节点(起始点),Enew= {},为空;
3).重复下列操作,直到Vnew = V:
a.在集合E中选取权值最小的边<u, v>,其中u为集合Vnew中的元素,而v不在Vnew集合当中,并且v∈V(如果存在有多条满足前述条件即具有相同权值的边,则可任意选取其中之一);
b.将v加入集合Vnew中,将<u, v>边加入集合Enew中;
4).输出:使用集合Vnew和Enew来描述所得到的最小生成树。
本次实现Prim算法(用C++实现):
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef char VertexType; //顶点类型应由用户定义 typedef int EdgeType; //边上的权值类型应由用户定义 #define MAXVEX 100 #define INFINITY 65535 //用65535来代表无穷大 #define DEBUG //邻接矩阵结构 typedef struct { VertexType vexs[MAXVEX]; //顶点表 EdgeType arc[MAXVEX][MAXVEX]; //邻接矩阵,可看作边 int numVertexes, numEdges; //图中当前的顶点数和边数 }Graph; #define MAXEDGE 100 typedef struct { int begin; int end; int weight; }Edge; //定位 int locates(Graph *g, char ch) { int i = 0; for(i = 0; i < g->numVertexes; i++) { if(g->vexs[i] == ch) { break; } } if(i >= g->numVertexes) { return -1; } return i; } //建立一个无向网图的邻接矩阵表示 void CreateGraph(Graph *g) { int i, j, k, w; printf("Enter the Vertexes_number and the Enumber:\n"); scanf("%d,%d", &(g->numVertexes), &(g->numEdges)); #ifdef DEBUG printf("%d %d\n", g->numVertexes, g->numEdges); #endif for(i = 0; i < g->numVertexes; i++) { printf("Enter the vertexs%d:\n", i); g->vexs[i] = getchar(); while(g->vexs[i] == '\n') { g->vexs[i] = getchar(); } } #ifdef DEBUG for(i = 0; i < g->numVertexes; i++) { printf("%c ", g->vexs[i]); } printf("\n"); #endif for(i = 0; i < g->numEdges; i++) { for(j = 0; j < g->numEdges; j++) { g->arc[i][j] = INFINITY; //邻接矩阵初始化 } } for(k = 0; k < g->numEdges; k++) { char p, q; printf("Enter the vertexs and the weight\n"); p = getchar(); while(p == '\n') { p = getchar(); } q = getchar(); while(q == '\n') { q = getchar(); } scanf("%d", &w); int m = -1; int n = -1; m = locates(g, p); n = locates(g, q); if(n == -1 || m == -1) { fprintf(stderr, "there is no this vertex.\n"); return; } //getchar(); g->arc[m][n] = w; g->arc[n][m] = g->arc[m][n]; //因为是无向图,矩阵对称 } } //打印图 void printGraph(Graph g) { int i, j; printf("the builded_marix shows:\n"); for(i = 0; i < g.numVertexes; i++) { for(j = 0; j < g.numVertexes; j++) { printf("%5d ", g.arc[i][j]); } printf("\n"); } } //prime算法最小生成树 void MiniSpanTree_Prime(Graph g) { int min, i, j, k; int adjvex[MAXVEX]; //保存相关顶点下标 int lowcost[MAXVEX]; //保存相关顶点间边的权值 lowcost[0] = 0; //初始化第一个权值为0,即v0加入生成树 adjvex[0] = 0; //初始化第一个顶点下标为0 for(i = 1; i < g.numVertexes; i++) { //循环除下标为0外的全部顶点 lowcost[i] = g.arc[0][i]; //将v0顶点与之有边的权值存入数组 adjvex[i] = 0; //初始化都为v0下标 } for(i = 1; i < g.numVertexes; i++) { min = INFINITY; //初始化最小权值为无穷大 j = 1; k = 0; while(j < g.numVertexes) //循环全部顶点 { //如果权值不为0,且权值小于min if(lowcost[j] != 0 && lowcost[j] < min) { min = lowcost[j]; //则让当前权值成为最小值 k = j; //将当前最小值的下标存入k } j++; } //printf("(%d,%d)", adjvex[k], k); //打印当前顶点边中权值最小边 lowcost[k] = 0; //将当前顶点的权值设置为0,表示此顶点已经完成任务 for(j = 1; j < g.numVertexes; j++)//循环所有顶点 { if(lowcost[j] != 0 && g.arc[k][j] < lowcost[j]) { //若下标为k的顶点各边权值小于此前这些顶点未被加入的生成树权值 lowcost[j] = g.arc[k][j]; adjvex[j] = k; //将下标为k的顶点存入adjvex } } } printf("\n"); } //查找连线顶点的尾部 int Find(int *parent, int f) { while(parent[f] > 0) { f = parent[f]; } return f; } //直接插入排序 void InsertSort(Edge edges[], int k) { int i, j; Edge ss; for(i = 1; i <= k; i++) { if(edges[i].weight < edges[i - 1].weight) { ss = edges[i]; for(j = i - 1; edges[j].weight > ss.weight; j--) { edges[j + 1] = edges[j]; } edges[j + 1] = ss; } } } void Convert(Graph g, Edge edges[]) { int i; int j; int k; k = 0; for(i = 0; i < g.numVertexes; i++) { for(j = i; j < g.numVertexes; j++) { if(g.arc[i][j] < 65535) { edges[k].begin = i; edges[k].end = j; edges[k].weight = g.arc[i][j]; k++; } } } k--; InsertSort(edges, k); } //克鲁斯卡尔算法实现 void MiniSpanTree_Kruskal(Graph g) { FILE* fp; int i, n, m; Edge edges[MAXEDGE]; //定义边集数组 int parent[MAXVEX]; //定义一数组用来判断边与边是否形成环 //此处为将邻接矩阵转化为边集数组edges并按权值由小到大排序 Convert(g, edges); fp=fopen("out.txt","w"); for(i = 0; i < g.numVertexes; i++) { parent[i] = 0; //初始化数组值为0 } for(i = 0; i < g.numEdges; i++) //循环每一条边 { n = Find(parent, edges[i].begin); m = Find(parent, edges[i].end); if(n != m) { parent[n] = m; //将此边的结尾顶点放入下标为起点的parent中 //表示此顶点已经在生成树集合中 printf("(%d,%d) %d ", edges[i].begin, edges[i].end, edges[i].weight); fprintf(fp, "(%d,%d) %d ", edges[i].begin, edges[i].end, edges[i].weight); } } printf("\n"); } int main(int argc, char **argv) { //测试文件简单K3 in.txt,自构造的in2.txt freopen("in1.txt","r",stdin); Graph g;//邻接矩阵创建图 CreateGraph(&g);//打印网图 printGraph(g);//普里姆算法求最小生成树 // MiniSpanTree_Prime(g);//克鲁斯卡尔算法求最小生成树 MiniSpanTree_Kruskal(g); return 0; }
上述代码实现了一个Prim算法寻找最小生成树,其输入是我自己构造的一个用于验证可行性的图,输出结果为(A,B) w格式,即最小生成树的边+权值,
输出结果保存于out.txt中。
输入为
5,7 A B C D E A B 17 A E 8 A D 4 A C 13 B C 7 B D 12 C E 4
输出结果为:
(0,3) 4 (2,4) 4 (1,2) 7 (0,4) 8
接下来利用python的matplotlib//numpy等库进行数据的处理与分析,对输出结果文件“out.txt“进行处理
#draw the picture
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numpy import *
import re
fp=open("out.txt","r")
txt=fp.readline()
p=re.compile(r'(.,.)')
plist=re.findall(p,txt)
xlist=[]
ylist=[]
#A\B\C\D\E\的初始坐标
gridlist=array([[30.0,30.0],[20.0,40.0],[60.0,50.0],[20.0,10.0],[37.0,6.0]])
for i in range(4):
x0=gridlist[ord(plist[i][0])-48][0]
y0=gridlist[ord(plist[i][0])-48][1]
x1=gridlist[ord(plist[i][2])-48][0]
y1=gridlist[ord(plist[i][2])-48][1]
if(x0<=x1):
x=arange(x0,x1,0.01)
y=((y0-y1)/(x0-x1))*x+(y0-(y0-y1)/(x0-x1)*x0)
else:
x=arange(x1,x0,0.01)
y=((y0-y1)/(x0-x1))*x+(y0-(y0-y1)/(x0-x1)*x0)
xlist.append(x)
ylist.append(y)
#plt.grid(True)
print plist
print xlist
plt.annotate('A', xy = (30, 30), xytext = (30,30), \
arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
plt.annotate('B', xy = (20, 40), xytext = (20,40), \
arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
plt.annotate('C', xy = (60, 50), xytext = (60,50), \
arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
plt.annotate('D', xy = (20, 10), xytext = (20,10), \
arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
plt.annotate('E', xy = (37, 6), xytext = (37,6), \
arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
plt.plot(xlist[0],ylist[0],xlist[1],ylist[1],xlist[2],ylist[2],xlist[3],ylist[3])
plt.show()
先将out.txt的内容通过文件操作读取出来,利用正则匹配,p=re.compile(r'(.,.)') plist=re.findall(p,txt)将out.txt保存在txt的内容中的括号中的
结果读取出来并保存即为将要做处理的数据。
gridlist=array([[30.0,30.0],[20.0,40.0],[60.0,50.0],[20.0,10.0],[37.0,6.0]])
规定ABCDE的初始坐标(为了作出直观的最小生成树图)。
for i in range(4): x0=gridlist[ord(plist[i][0])-48][0] y0=gridlist[ord(plist[i][0])-48][1] x1=gridlist[ord(plist[i][2])-48][0] y1=gridlist[ord(plist[i][2])-48][1] if(x0<=x1): x=arange(x0,x1,0.01) y=((y0-y1)/(x0-x1))*x+(y0-(y0-y1)/(x0-x1)*x0) else: x=arange(x1,x0,0.01) y=((y0-y1)/(x0-x1))*x+(y0-(y0-y1)/(x0-x1)*x0) xlist.append(x) ylist.append(y)
对所有(a,b)这样的边进行求x,y,保存在xlist和ylist中
将各个点标记
plt.annotate('A', xy = (30, 30), xytext = (30,30), \ arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1)) plt.annotate('B', xy = (20, 40), xytext = (20,40), \ arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1)) plt.annotate('C', xy = (60, 50), xytext = (60,50), \ arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1)) plt.annotate('D', xy = (20, 10), xytext = (20,10), \ arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1)) plt.annotate('E', xy = (37, 6), xytext = (37,6), \ arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
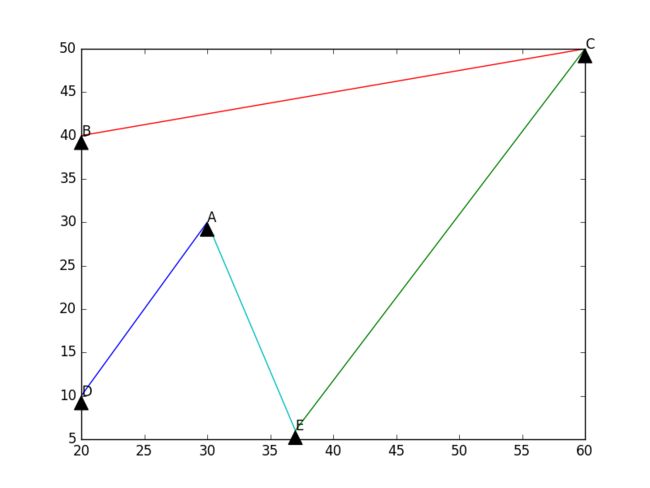
最终将其画出:
plt.plot(xlist[0],ylist[0],xlist[1],ylist[1],xlist[2],ylist[2],xlist[3],ylist[3]) plt.show()
其结果为:
生成了与原图(根据输入与点位置确定的)最小生成树的直观结果,数据处理完成。