Gazebo Ros入门
First step with gazebo and ros
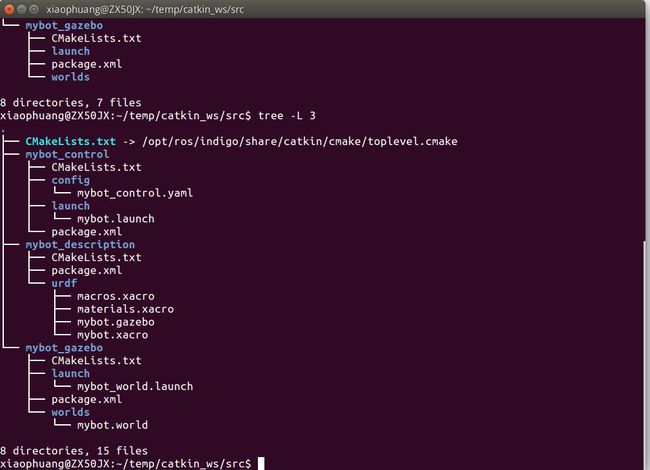
• setup a ROS workspace
• create projects for your simulated robot
• create a Gazebo world
• create your own robot model
• connect your robot model to ROS
• use a teleoperation node to control your robot
• add a camera to your robot
• use Rviz to vizualize all the robot information
Setup a new workspace
mkdir -p ~/catkin_ws/src
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
catkin_init_workspace
cd ..
catkin_make
source ~/catkin_ws/devel/setup.bashCreate projects for your simulated robot
cd ~/catkin_ws/src
catkin_create_pkg mybot_gazebo gazebo_ros
catkin_create_pkg mybot_description
catkin_create_pkg mybot_controlCreating your own World
roscd mybot_gazebo
mkdir launch worlds
cd worlds
vim mybot.worldA basic world file defines at least a name:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<sdf version="1.4">
<world name="myworld">
</world>
</sdf>At first we just want to add some basic objects, like a ground and a basic illumination source inside the world tag.
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://turtlebot</uri>
</include>roscd mybot_gazebo/launch
vim mybot_world.launchmybot_world.launch
<launch>
<include file="$(find gazebo_ros)/launch/empty_world.launch">
<arg name="world_name" value="$(find mybot_gazebo)/worlds/mybot.world"/>
<arg name="gui" value="true"/>
</include>
</launch>make a test
roslaunch mybot_gazebo mybot_world.launchCreating your own Model
roscd mybot_description
mkdir urdf
cd urdf
gedit mybot.xacroXACRO CONCEPTS
• xacro:include: Import the content from other file. We can divide the content in different xacros and merge them using xacro:include.
• property: Useful to define constant values. Use it later using ${property_name}
• xacro:macro: Macro with variable values. Later, we can use this macro from another xacro file, and we specify the required value for the variables. To use a macro, you have to include the file where the macro is, and call it using the macro's name and filling
the required values.
mybot.xacro
This file will be the main description of our robot. Let's put some xacro basic structure:
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="mybot" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<!-- Put here the robot description -->
</robot>Let's define some physical properties for our robot, mainly the dimensions of the chassis, the caster wheel, the wheels and the camera:
<xacro:property name="PI" value="3.1415926535897931"/>
<xacro:property name="chassisHeight" value="0.1"/>
<xacro:property name="chassisLength" value="0.4"/>
<xacro:property name="chassisWidth" value="0.2"/>
<xacro:property name="chassisMass" value="50"/>
<xacro:property name="casterRadius" value="0.05"/>
<xacro:property name="casterMass" value="5"/>
<xacro:property name="wheelWidth" value="0.05"/>
<xacro:property name="wheelRadius" value="0.1"/>
<xacro:property name="wheelPos" value="0.2"/>
<xacro:property name="wheelMass" value="5"/>
<xacro:property name="cameraSize" value="0.05"/>
<xacro:property name="cameraMass" value="0.1"/>We will also include three files :
<xacro:include filename="$(find mybot_description)/urdf/mybot.gazebo" />
<xacro:include filename="$(find mybot_description)/urdf/materials.xacro" />
<xacro:include filename="$(find mybot_description)/urdf/macros.xacro" />These three correspond respectively to:
• all the gazebo-specific aspects of our robot
• definition of the materials used (mostly colors)
• definitions of some macros for easier description of the robot
Add it to mybot.xacro
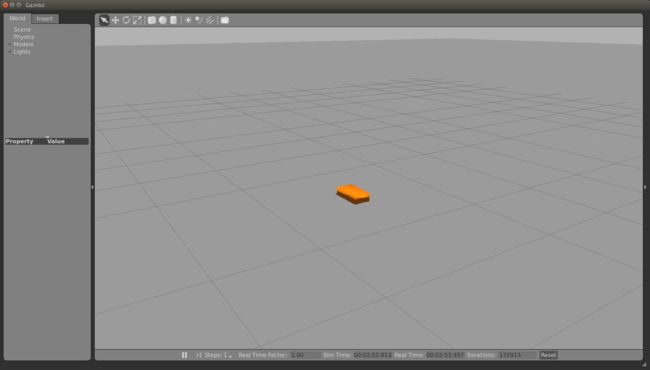
<link name='chassis'>
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 ${wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="${chassisLength} ${chassisWidth} ${chassisHeight}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 ${wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="${chassisLength} ${chassisWidth} ${chassisHeight}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="orange"/>
</visual>
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 ${wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="${chassisMass}"/>
<box_inertia m="${chassisMass}" x="${chassisLength}" y="${chassisWidth}" z="${chassisHeight}"/>
</inertial>
</link>Add it to mybot.gazebo
<gazebo reference="chassis">
<material>Gazebo/Orange</material>
</gazebo>Add this in the “materials.xacro” :
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot>
<material name="black">
<color rgba="0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="blue">
<color rgba="0.0 0.0 0.8 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="green">
<color rgba="0.0 0.8 0.0 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="grey">
<color rgba="0.2 0.2 0.2 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="orange">
<color rgba="${255/255} ${108/255} ${10/255} 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="brown">
<color rgba="${222/255} ${207/255} ${195/255} 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="red">
<color rgba="0.8 0.0 0.0 1.0"/>
</material>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1.0 1.0 1.0 1.0"/>
</material>
</robot>Add this in the
macros.xacrofile, within the robot tag
<?xml version="1.0" ?>
<robot name="mybot" xmlns:xacro="http://www.ros.org/wiki/xacro">
<macro name="cylinder_inertia" params="m r h">
<inertia ixx="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(3*r*r+h*h)/12}" iyz = "0"
izz="${m*r*r/2}"
/>
</macro>
<macro name="box_inertia" params="m x y z">
<inertia ixx="${m*(y*y+z*z)/12}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${m*(x*x+z*z)/12}" iyz = "0"
izz="${m*(x*x+z*z)/12}"
/>
</macro>
<macro name="sphere_inertia" params="m r">
<inertia ixx="${2*m*r*r/5}" ixy = "0" ixz = "0"
iyy="${2*m*r*r/5}" iyz = "0"
izz="${2*m*r*r/5}"
/>
</macro>
</robot>Add this before the chassis link in the mybot.xacro file :
<link name="footprint" />
<joint name="base_joint" type="fixed">
<parent link="footprint"/>
<child link="chassis"/>
</joint>mybot_world.launch by adding the following two tags in the launch tag:
<!-- urdf xml robot description loaded on the Parameter Server, converting the xacro into a proper urdf file-->
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py '$(find mybot_description)/urdf/mybot.xacro'" />
<!-- push robot_description to factory and spawn robot in gazebo -->
<node name="mybot_spawn" pkg="gazebo_ros" type="spawn_model" output="screen"
args="-urdf -param robot_description -model mybot" />make a test
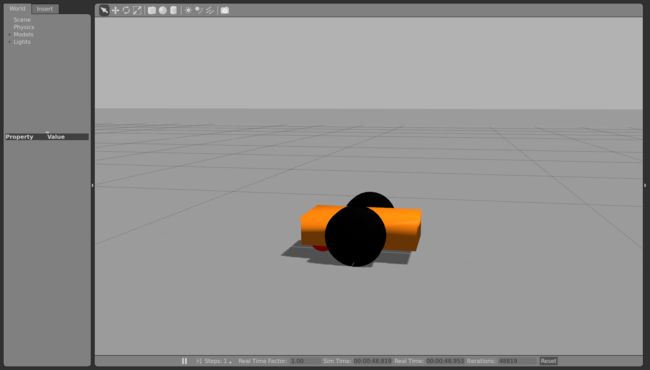
roslaunch mybot_gazebo mybot_world.launch mybot.xacro As a next step we add a caster wheel to the robot. This is the simplest wheel as we have no axis and no friction
<joint name="fixed" type="fixed">
<parent link="chassis"/>
<child link="caster_wheel"/>
</joint>
<link name="caster_wheel">
<collision>
<origin xyz="${casterRadius-chassisLength/2} 0 ${casterRadius-chassisHeight+wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${casterRadius}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual>
<origin xyz="${casterRadius-chassisLength/2} 0 ${casterRadius-chassisHeight+wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<sphere radius="${casterRadius}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="red"/>
</visual>
<inertial>
<origin xyz="${casterRadius-chassisLength/2} 0 ${casterRadius-chassisHeight+wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<mass value="${casterMass}"/>
<sphere_inertia m="${casterMass}" r="${casterRadius}"/>
</inertial>
</link>mybot.gazebo Add a gazebo tag in the gazebo file for this link :
<gazebo reference="caster_wheel">
<mu1>0.0</mu1>
<mu2>0.0</mu2>
<material>Gazebo/Red</material>
</gazebo>As usual, we specify the color used in material. We also added mu1 and mu2, with value 0 to remove the friction.
macros.xacro .We could add the two links in the main file, but let's make one macro to make it simple.
<macro name="wheel" params="lr tY">
<link name="${lr}_wheel">
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 ${PI/2} ${PI/2}" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${wheelWidth}" radius="${wheelRadius}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 ${PI/2} ${PI/2}" />
<geometry>
<cylinder length="${wheelWidth}" radius="${wheelRadius}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="black"/>
</visual>
<inertial>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 ${PI/2} ${PI/2}" />
<mass value="${wheelMass}"/>
<cylinder_inertia m="${wheelMass}" r="${wheelRadius}" h="${wheelWidth}"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<gazebo reference="${lr}_wheel">
<mu1 value="1.0"/>
<mu2 value="1.0"/>
<kp value="10000000.0" />
<kd value="1.0" />
<fdir1 value="1 0 0"/>
<material>Gazebo/Black</material>
</gazebo>
<joint name="${lr}_wheel_hinge" type="continuous">
<parent link="chassis"/>
<child link="${lr}_wheel"/>
<origin xyz="${-wheelPos+chassisLength/2} ${tY*wheelWidth/2+tY*chassisWidth/2} ${wheelRadius}" rpy="0 0 0" />
<axis xyz="0 1 0" rpy="0 0 0" />
<limit effort="100" velocity="100"/>
<joint_properties damping="0.0" friction="0.0"/>
</joint>
<transmission name="${lr}_trans">
<type>transmission_interface/SimpleTransmission</type>
<joint name="${lr}_wheel_hinge">
<hardwareInterface>EffortJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
</joint>
<actuator name="${lr}Motor">
<hardwareInterface>EffortJointInterface</hardwareInterface>
<mechanicalReduction>10</mechanicalReduction>
</actuator>
</transmission>
</macro>mybot.xacro
<wheel lr="left" tY="1"/>
<wheel lr="right" tY="-1"/>Connect your robot to ROS
Alright, our robot is all nice and has this new car smell, but we can't do anything with it yet as it has no connection with
ROS In order to add this connection we need to add gazebeo plugins to our model. There are different kinds of plugins:
- World: Dynamic changes to the world, e.g. Physics, like illumination or gravity, inserting models
- Model: Manipulation of models (robots), e.g. move the robots
- Sensor: Feedback from virtual sensor, like camera, laser scanner
- System: Plugins that are loaded by the GUI, like saving images
First of all we'll use a plugin to provide access to the joints of the wheels. The transmission tags in our URDF will be used by this plugin the define how to link the joints to controllers. To activate the plugin, add the following to
mybot.gazebo:
<gazebo>
<plugin name="gazebo_ros_control" filename="libgazebo_ros_control.so">
<robotNamespace>/mybot</robotNamespace>
</plugin>
</gazebo>With this plugin, we will be able to control the joints, however we need to provide some extra configuration and explicitely
start controllers for the joints. In order to do so, we'll use the package mybot_control that we have defined before. Let's first create the configuration file:
roscd mybot_control
mkdir config
cd config
vim mybot_control.yamlThis file will define three controllers: one for each wheel, connections to the joint by the transmission tag, one for
publishing the joint states. It also defined the PID gains to use for this controller:
mybot:
# Publish all joint states -----------------------------------
joint_state_controller:
type: joint_state_controller/JointStateController
publish_rate: 50
# Effort Controllers ---------------------------------------
leftWheel_effort_controller:
type: effort_controllers/JointEffortController
joint: left_wheel_hinge
pid: {p: 100.0, i: 0.1, d: 10.0}
rightWheel_effort_controller:
type: effort_controllers/JointEffortController
joint: right_wheel_hinge
pid: {p: 100.0, i: 0.1, d: 10.0}Now we need to create a launch file to start the controllers. For this let's do:
roscd mybot_control
mkdir launch
cd launch
vim mybot_control.launchIn this file we'll put two things. First we'll load the configuration and the controllers, and we'll also start a node that will
provide 3D transforms (tf) of our robot. This is not mandatory but that makes the simulation more complete
<launch>
<!-- Load joint controller configurations from YAML file to parameter server -->
<rosparam file="$(find mybot_control)/config/mybot_control.yaml" command="load"/>
<!-- load the controllers -->
<node name="controller_spawner"
pkg="controller_manager"
type="spawner" respawn="false"
output="screen" ns="/mybot"
args="joint_state_controller
rightWheel_effort_controller
leftWheel_effort_controller"/>
<!-- convert joint states to TF transforms for rviz, etc -->
<node name="robot_state_publisher" pkg="robot_state_publisher" type="robot_state_publisher" respawn="false" output="screen">
<param name="robot_description" command="$(find xacro)/xacro.py '$(find mybot_description)/urdf/mybot.xacro'" />
<remap from="/joint_states" to="/mybot/joint_states" />
</node>
</launch>make a test
roslaunch mybot_gazebo mybot_world.launch
roslaunch mybot_control mybot.launch
rostopic listWe could launch our model on gazebo and then launch the controller, but to save some time (and terminals), we'll start the controllers automatically by adding a line to the mybot_world.launch in the mybot_gazebo package :
<!-- ros_control mybot launch file -->
<include file="$(find mybot_control)/launch/mybot_control.launch" />rostopic pub -1 /mybot/leftWheel_effort_controller/command std_msgs/Float64 "data: 1.5"
rostopic pub -1 /mybot/rightWheel_effort_controller/command std_msgs/Float64 "data: 1.0"
rostopic echo /mybot/joint_statesTeleoperation of your robot
Adding a camera
<joint name="camera_joint" type="fixed">
<axis xyz="0 1 0" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0.2" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="footprint"/>
<child link="camera"/>
</joint>
<link name="camera">
<collision>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="${cameraSize} ${cameraSize} ${cameraSize}"/>
</geometry>
</collision>
<visual>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<geometry>
<box size="${cameraSize} ${cameraSize} ${cameraSize}"/>
</geometry>
<material name="blue"/>
</visual>
<inertial>
<mass value="${cameraMass}" />
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<box_inertia m="${cameraMass}" x="${cameraSize}" y="${cameraSize}" z="${cameraSize}" />
</inertial>
</link>Add the plugin to gazebo file
<gazebo reference="camera">
<material>Gazebo/Blue</material>
<sensor type="camera" name="camera1">
<update_rate>30.0</update_rate>
<camera name="head">
<horizontal_fov>1.3962634</horizontal_fov>
<image>
<width>800</width>
<height>800</height>
<format>R8G8B8</format>
</image>
<clip>
<near>0.02</near>
<far>300</far>
</clip>
</camera>
<plugin name="camera_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_camera.so">
<alwaysOn>true</alwaysOn>
<updateRate>0.0</updateRate>
<cameraName>mybot/camera1</cameraName>
<imageTopicName>image_raw</imageTopicName>
<cameraInfoTopicName>camera_info</cameraInfoTopicName>
<frameName>camera_link</frameName>
<hackBaseline>0.07</hackBaseline>
<distortionK1>0.0</distortionK1>
<distortionK2>0.0</distortionK2>
<distortionK3>0.0</distortionK3>
<distortionT1>0.0</distortionT1>
<distortionT2>0.0</distortionT2>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>rosrun image_view image_view image:=/mybot/camera1/image_rawVisualisation with RViz
rosrun rviz rviz