.Net插件编程模型:MEF和MAF
.Net插件编程模型:MEF和MAF
MEF和MAF都是C#下的插件编程框架,我们通过它们只需简单的配置下源代码就能轻松的实现插件编程概念,设计出可扩展的程序。这真是件美妙的事情!
MEF(Managed Extensibility Framework)
MEF的工作原理大概是这样的:首先定义一个接口,用这个接口来约束插件需要具备的职责;然后在实现接口的程序方法上面添加反射标记“[Export()]”将实现的内容导出;最后在接口的调用程序中通过属性将插件加载进来。我们还是用代码来描述吧:
1. 定义一个接口:
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
简介:该节主要学习.net下的插件编程框架MEF(managed extensibility framework)
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows;
namespace chapter28_simplecontract
{
public interface ICalculator
{
IList<IOperation> GetOperations();
double Operate(IOperation operation, double[] operands);
}
public interface IOperation
{
string Name { get; }
int NumberOperands { get; }
}
public interface ICaculatorExtension
{
string Title { get; }
string Description { get; }
FrameworkElement GetUI();
}
}
2. 实现定义的接口(部分一)
/* 作者:GhostBear 博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear */
[Export(typeof(ICalculator))]
public class Caculator:ICalculator
{
public IList<IOperation> GetOperations()
{
return new List<IOperation>(){
new Operation{ Name="+",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="-",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="*",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="/",NumberOperands=2}
};
}
public double Operate(IOperation operation, double[] operands)
{
double result=0;
switch (operation.Name)
{
case "+":
result = operands[0] + operands[1];
break;
case "-":
result = operands[0] - operands[1];
break;
case "*":
result = operands[0] * operands[1];
break;
case "/":
result = operands[0] / operands[1];
break;
default:
throw new Exception("not provide this method");
}
return result;
}
}
public class Operation:IOperation
{
public string Name
{
get;
internal set;
}
public int NumberOperands
{
get;
internal set;
}
}
实现定义的接口(部分二)
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
*/
[Export(typeof(ICalculator))]
public class Caculator : ICalculator
{
public IList<IOperation> GetOperations()
{
return new List<IOperation>(){
new Operation{ Name="+",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="-",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="*",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="/",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="%",NumberOperands=2},
new Operation{Name="**",NumberOperands=1},
};
}
public double Operate(IOperation operation, double[] operands)
{
double result = 0;
switch (operation.Name)
{
case "+":
result = operands[0] + operands[1];
break;
case "-":
result = operands[0] - operands[1];
break;
case "*":
result = operands[0] * operands[1];
break;
case "/":
result = operands[0] / operands[1];
break;
case "%":
result=operands[0]%operands[1];
break;
case "**":
result=operands[0]*operands[0];
break;
default:
throw new Exception("not provide this method");
}
return result;
}
}
public class Operation : IOperation
{
public string Name
{
get;
internal set;
}
public int NumberOperands
{
get;
internal set;
}
}
分析:
标记“[Export(typeof(ICalculator))]”声明表达的意思是:这个类可以编译为插件,并能放入插件容器“ICalculator”中。这里需要注意的是:部分一和部分二的代码分布在不同的程序集中。导出的插件不一定必须是以类的形式,也可以是方法。
通过导出方法来生成插件:
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
*/
public class Bomb
{
[Export("Bomb")]
public void Fire()
{
Console.WriteLine("you are dead!!!");
}
}
插件的调用者:
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
* 简介:该节主要学习.net下的插件编程框架MEF(managed extensibility framework)
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.ComponentModel.Composition;
using System.ComponentModel.Composition.Hosting;
using chapter28_simplecontract;
namespace chapter28
{
class Program
{
[ImportMany(typeof(ICalculator))]
public IEnumerable<ICalculator> Calculators { get; set; }
[Import("Bomb")]
public Action Bomb { get; set; }
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Program pro = new Program();
pro.Run();
pro.Run2();
}
public void Run()
{
var catalog = new DirectoryCatalog("c:\\plugins");
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
try
{
container.ComposeParts(this);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
return;
}
ICalculator myCalculator = Calculators.ToList<ICalculator>()[1];
var operations = myCalculator.GetOperations();
var operationsDict = new SortedList<string, IOperation>();
foreach(IOperation item in operations)
{
Console.WriteLine("Name:{0},number operands:{1}"
, item.Name, item.NumberOperands);
operationsDict.Add(item.Name, item);
}
Console.WriteLine();
string selectedOp = null;
do
{
try
{
Console.Write("Operation?");
selectedOp = Console.ReadLine();
if (selectedOp.ToLower() == "exit"
|| !operationsDict.ContainsKey(selectedOp))
{
continue;
}
var operation = operationsDict[selectedOp];
double[] operands = new double[operation.NumberOperands];
for (int i = 0; i < operation.NumberOperands; i++)
{
Console.WriteLine("\t operand {0}?", i + 1);
string selectedOperand = Console.ReadLine();
operands[i] = double.Parse(selectedOperand);
}
Console.WriteLine("calling calculator");
double result = myCalculator.Operate(operation, operands);
Console.WriteLine("result:{0}", result);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
Console.WriteLine();
continue;
}
} while (selectedOp != "exit");
}
public void Run2()
{
var catalog = new DirectoryCatalog("c:\\plugins");
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
container.ComposeParts(this);
Bomb.Invoke();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
分析:
标记“[ImportMany(typeof(ICalculator))]”,该声明表达的意图是:将所有声明了标记“[Export(typeof(ICalculator))]”的程序集加载进容器。这里“[ImportMany]和”[Import]”的区别就是:前者的容器可以存放多个插件,而后者只能存放一个。
光声明“[Import()]”和”[Export()]”标记是不行的,还必须通过下面的代码将这两个标记的功能联合起来:
//DirectoryCatalog表示这类插件会存放在系统的哪个文件夹下
var catalog = new DirectoryCatalog("c:\\plugins");
var container = new CompositionContainer(catalog);
try
{
//将存放在目录中的插件按“[Export()]和[Import()]”规则装载进当前
//类中。
container.ComposeParts(this);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine(ex.Message);
return;
}
执行结果
Name:+,number operands:2 Name:-,number operands:2 Name:*,number operands:2 Name:/,number operands:2
Operation?+ operand 1? 1 operand 2? 1 calling calculator result:2 Operation?exit
you are dead!!! |
MAF(Managed Addin Framework)
MAF也是.Net为我们提供的一个“插件编程”解决方案。它比MEF复杂,需要配置很多元素。但它也有些优点:1.宿主程序和插件程序可以进行隔离,以此降低运行插件所带来的风险;2。MAF的设计是基于7个程序集组成的管道,这些管道部分可以单独更换,这些管道的详细情况见下图。
图1
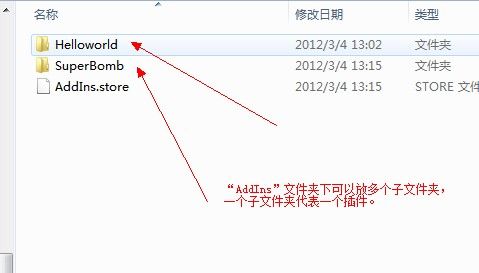
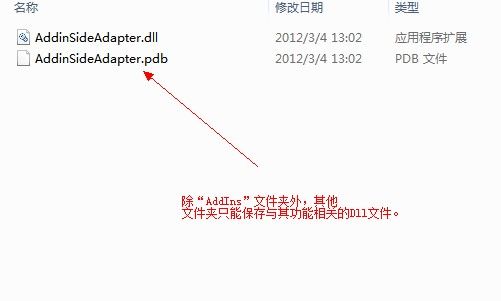
使用MAF是需要有些细节需要注意:组成管道的7个程序集在系统中的保存路径有格式要求,并且没个保存它的文件夹内只运行同时出现一个程序集。具体情况如下图所示:
图2
图3
图4
图5
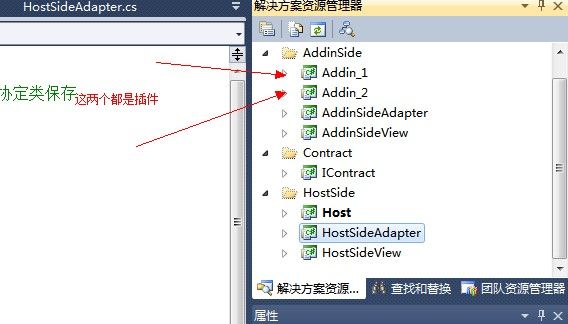
下面我们来看一个小Demo吧,这个demo一共有7个项目,它们分别对应图1描述的管道中的7个部分。具体情况见下图。
图6
插件:Addin_1,Addin_2 插件视图:AddinSideView 插件适配器:AddinSideAdapter 协定:IContract 宿主视图:HostSideView 宿主适配器:HostSideAdapter 宿主程序:Host |
程序代码
Addin_1
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
简介:测试MAF,这段代码是用来定义一个插件的。这个插件可以在宿主程序
中动态加载。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.AddIn;
using System.AddIn.Pipeline;
namespace Addin_1
{
[AddIn("Helloworld",Description="this is helloworld addin"
,Publisher="GhostBear",Version="1.0")]
public class Addin_1:AddinSideView.AddinSideView
{
public string Say()
{
return "Helloworld";
}
}
}
Addin_2
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.AddIn;
namespace Addin_2
{
[AddIn("SuperBomb",Description="This is a bigger bomb"
,Publisher="SuperWorker",Version="1.0.0.0")]
public class Addin_2:AddinSideView.AddinSideView
{
public string Say()
{
return "B--O--M--B";
}
}
}
AddinSideView
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
* 简介:测试MAF,这段代码是定义插件端的视图类,该视图类的方法和属性必须与协定一致。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.AddIn.Pipeline;
namespace AddinSideView
{
[AddInBase()]
public interface AddinSideView
{
string Say();
}
}
AddinSideAdapter
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
* 简介:测试MAF,这段代码是插件端的适配器类,它用来实现插件端视图类。
* 并组合协定。这样就能让插件和协定解耦,如果插件有所修改就换掉
* 该适配器类就可以了。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.AddIn.Pipeline;
namespace AddinSideAdapter
{
[AddInAdapter]
public class AddinSideAdapter : ContractBase,IContract.IMyContract
{
private AddinSideView.AddinSideView _handler;
public AddinSideAdapter(AddinSideView.AddinSideView handler)
{
this._handler = handler;
}
public string Say()
{
return this._handler.Say();
}
}
}
IContract
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
简介:测试MAF,这段代码是定义协定。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.AddIn.Pipeline;
using System.AddIn.Contract;
namespace IContract
{
[AddInContract]
public interface IMyContract:System.AddIn.Contract.IContract
{
string Say();
}
}
HostSideView
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
简介:测试MAF,这段代码用来定义宿主段的视图类,该类的所有方法和属性需与协定类一致。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
namespace HostSideView
{
public interface HostSideView
{
string Say();
}
}
HostSideAdapter
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
简介:测试MAF,这段代码用来定义宿主端的适配器类。该类实现宿主端的
视图类并组合协定。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.AddIn.Pipeline;
namespace HostSideAdapter
{
[HostAdapter()]
public class HostSideAdapter:HostSideView.HostSideView
{
private IContract.IMyContract _contract;
//这行代码重要
private System.AddIn.Pipeline.ContractHandle _handle;
public HostSideAdapter(IContract.IMyContract contract)
{
this._contract = contract;
this._handle = new ContractHandle(contract);
}
public string Say()
{
return this._contract.Say();
}
}
}
Host
/*
作者:GhostBear
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/ghostbear
简介:测试MAF,这段代码是宿主程序。该程序可以针对保存在某个目录下的插件来进行选择性调用。
*/
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.ObjectModel;
using System.AddIn.Hosting;
using HostSideView;
namespace Host
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string path = @"D:\学习文档\c#\c#高级编程7\MAF\MAF";
string[] warnings = AddInStore.Update(path);
foreach (var tmp in warnings)
{
Console.WriteLine(tmp);
}
//发现
var tokens = AddInStore.FindAddIns(typeof(HostSideView.HostSideView), path);
Console.WriteLine("当前共有{0}个插件可以选择。它们分别为:",tokens.Count);
var index = 1;
foreach (var tmp in tokens)
{
Console.WriteLine(string.Format("[{4}]名称:{0},描述:{1},版本:{2},发布者:{3}", tmp.Name, tmp.Description, tmp.Version, tmp.Publisher,index++));
}
var token = ChooseCalculator(tokens);
//隔离和激活插件
AddInProcess process=new AddInProcess(Platform.X64);
process.Start();
var addin = token.Activate<HostSideView.HostSideView>(process, AddInSecurityLevel.FullTrust);
Console.WriteLine("PID:{0}",process.ProcessId);
//调用插件
Console.WriteLine(addin.Say());
Console.ReadKey();
}
private static AddInToken ChooseCalculator(Collection<AddInToken> tokens)
{
if (tokens.Count == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("No calculators are available");
return null;
}
Console.WriteLine("Available Calculators: ");
// Show the token properties for each token in the AddInToken collection
// (tokens), preceded by the add-in number in [] brackets.
int tokNumber = 1;
foreach (AddInToken tok in tokens)
{
Console.WriteLine(String.Format("\t[{0}]: {1} - {2}\n\t{3}\n\t\t {4}\n\t\t {5} - {6}",
tokNumber.ToString(),
tok.Name,
tok.AddInFullName,
tok.AssemblyName,
tok.Description,
tok.Version,
tok.Publisher));
tokNumber++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Which calculator do you want to use?");
String line = Console.ReadLine();
int selection;
if (Int32.TryParse(line, out selection))
{
if (selection <= tokens.Count)
{
return tokens[selection - 1];
}
}
Console.WriteLine("Invalid selection: {0}. Please choose again.", line);
return ChooseCalculator(tokens);
}
}
}
分析
在上面的7个程序集,起解耦作用的关键还是2个适配器类。调用程序不直接调用协定,而是通过通过调用这2个适配器来间接调用协定。
小结
MEF和MAF为我们实现“插件编程”提供了2中选择,它们设计的出发点也是完全不同的。在使用它们的时候还是需要更加具体需求来权衡使用。