hadoop分析之二元数据备份方案的机制
1、NameNode启动加载元数据情景分析
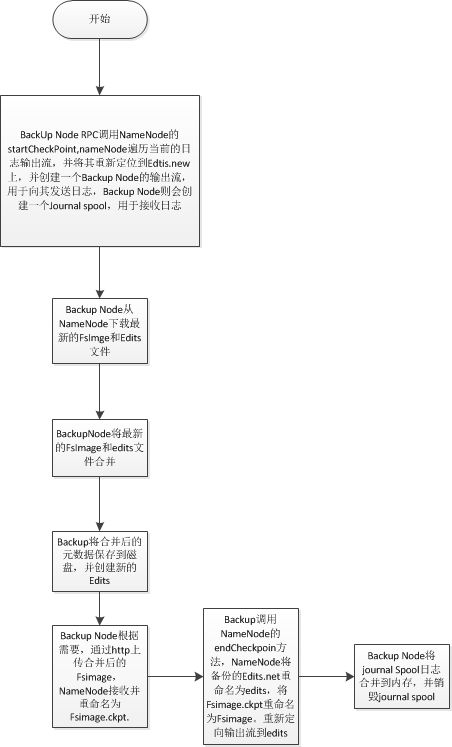
3、Backup Node 的checkpoint的过程分析:
4、元数据可靠性机制。
- NameNode函数里调用FSNamesystemm读取dfs.namenode.name.dir和dfs.namenode.edits.dir构建FSDirectory。
- FSImage类recoverTransitionRead和saveNameSpace分别实现了元数据的检查、加载、内存合并和元数据的持久化存储。
- saveNameSpace将元数据写入到磁盘,具体操作步骤:首先将current目录重命名为lastcheckpoint.tmp;然后在创建新的current目录,并保存文件;最后将lastcheckpoint.tmp重命名为privios.checkpoint.
- checkPoint的过程:Secondary NameNode会通知nameNode产生一个edit log文件edits.new,之后所有的日志操作写入到edits.new文件中。接下来Secondary NameNode会从namenode下载fsimage和edits文件,进行合并产生新的fsimage.ckpt;然后Secondary会将fsimage.ckpt文件上传到namenode。最后namenode会重命名fsimage.ckpt为fsimage,edtis.new为edits;
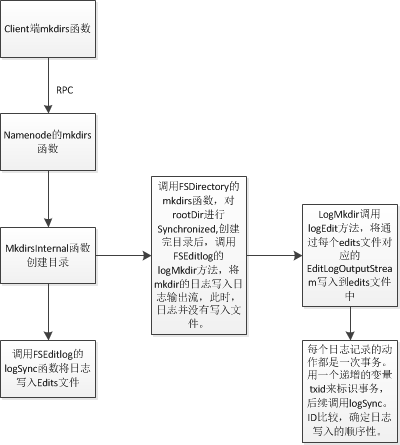
2、元数据更新及日志写入情景分析
以mkdir为例:
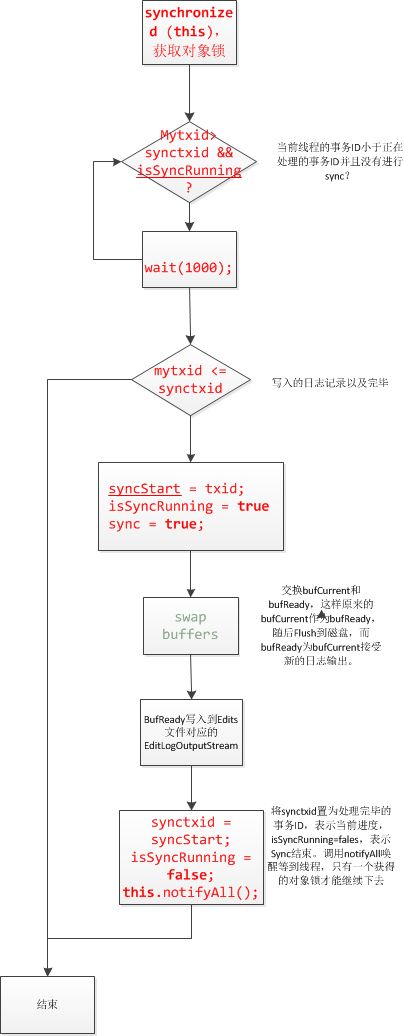
logSync代码分析:
代码:
public void logSync () throws IOException {
ArrayList<EditLogOutputStream > errorStreams = null ;
long syncStart = 0;
// Fetch the transactionId of this thread.
long mytxid = myTransactionId .get (). txid;
EditLogOutputStream streams[] = null;
boolean sync = false;
try {
synchronized (this) {
assert editStreams. size() > 0 : "no editlog streams" ;
printStatistics (false);
// if somebody is already syncing, then wait
while (mytxid > synctxid && isSyncRunning) {
try {
wait (1000 );
} catch (InterruptedException ie ) {
}
}
//
// If this transaction was already flushed, then nothing to do
//
if (mytxid <= synctxid ) {
numTransactionsBatchedInSync ++;
if (metrics != null) // Metrics is non-null only when used inside name node
metrics .transactionsBatchedInSync .inc ();
return;
}
// now, this thread will do the sync
syncStart = txid ;
isSyncRunning = true;
sync = true;
// swap buffers
for( EditLogOutputStream eStream : editStreams ) {
eStream .setReadyToFlush ();
}
streams =
editStreams .toArray (new EditLogOutputStream[editStreams. size()]) ;
}
// do the sync
long start = FSNamesystem.now();
for (int idx = 0; idx < streams. length; idx++ ) {
EditLogOutputStream eStream = streams [idx ];
try {
eStream .flush ();
} catch (IOException ie ) {
FSNamesystem .LOG .error ("Unable to sync edit log." , ie );
//
// remember the streams that encountered an error.
//
if (errorStreams == null) {
errorStreams = new ArrayList <EditLogOutputStream >( 1) ;
}
errorStreams .add (eStream );
}
}
long elapsed = FSNamesystem.now() - start ;
processIOError (errorStreams , true);
if (metrics != null) // Metrics non-null only when used inside name node
metrics .syncs .inc (elapsed );
} finally {
synchronized (this) {
synctxid = syncStart ;
if (sync ) {
isSyncRunning = false;
}
this.notifyAll ();
}
}
}
3、Backup Node 的checkpoint的过程分析:
/**
* Create a new checkpoint
*/
void doCheckpoint() throws IOException {
long startTime = FSNamesystem.now ();
NamenodeCommand cmd =
getNamenode().startCheckpoint( backupNode. getRegistration());
CheckpointCommand cpCmd = null;
switch( cmd. getAction()) {
case NamenodeProtocol .ACT_SHUTDOWN :
shutdown() ;
throw new IOException ("Name-node " + backupNode .nnRpcAddress
+ " requested shutdown.");
case NamenodeProtocol .ACT_CHECKPOINT :
cpCmd = (CheckpointCommand )cmd ;
break;
default:
throw new IOException ("Unsupported NamenodeCommand: "+cmd.getAction()) ;
}
CheckpointSignature sig = cpCmd. getSignature();
assert FSConstants.LAYOUT_VERSION == sig .getLayoutVersion () :
"Signature should have current layout version. Expected: "
+ FSConstants.LAYOUT_VERSION + " actual " + sig. getLayoutVersion();
assert !backupNode .isRole (NamenodeRole .CHECKPOINT ) ||
cpCmd. isImageObsolete() : "checkpoint node should always download image.";
backupNode. setCheckpointState(CheckpointStates .UPLOAD_START );
if( cpCmd. isImageObsolete()) {
// First reset storage on disk and memory state
backupNode. resetNamespace();
downloadCheckpoint(sig);
}
BackupStorage bnImage = getFSImage() ;
bnImage. loadCheckpoint(sig);
sig.validateStorageInfo( bnImage) ;
bnImage. saveCheckpoint();
if( cpCmd. needToReturnImage())
uploadCheckpoint(sig);
getNamenode() .endCheckpoint (backupNode .getRegistration (), sig );
bnImage. convergeJournalSpool();
backupNode. setRegistration(); // keep registration up to date
if( backupNode. isRole( NamenodeRole.CHECKPOINT ))
getFSImage() .getEditLog (). close() ;
LOG. info( "Checkpoint completed in "
+ (FSNamesystem .now() - startTime )/ 1000 + " seconds."
+ " New Image Size: " + bnImage .getFsImageName (). length()) ;
}
}
4、元数据可靠性机制。
- 配置多个备份路径。NameNode在更新日志或进行Checkpoint的过程,会将元数据放在多个目录下。
- 对于没一个需要保存的元数据文件,都创建一个输出流,对访问过程中出现的异常输出流进行处理,将其移除。并再合适的时机再次检查移除的数据量是否恢复正常。有效的保证了备份输出流的异常问题。
- 采用了多种机制来保证元数据的可靠性。例如在checkpoint的过程中,分为几个阶段,通过不同的文件名来标识当前所处的状态。为存储失败后进行恢复提供了可能。
5、元数据的一致性机制。
- 首先从NameNode启动时,对每个备份目录是否格式化、目录元数据文件名是否正确等进行检查,确保元数据文件间的状态一致性,然后选取最新的加载到内存,这样可以确保HDFS当前状态和最后一次关闭时的状态一致性。
- 其次,通过异常输出流的处理,可以确保正常输出流数据的一致性。
- 运用同步机制,确保了输出流一致性问题。