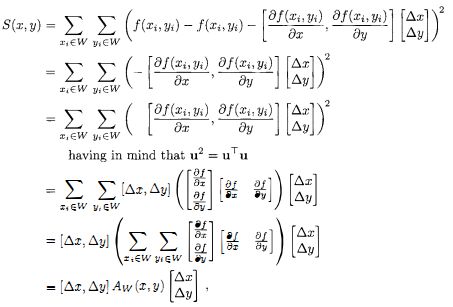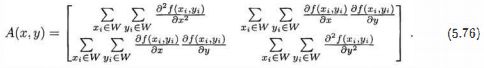Harris角点检测
引言
在上一节我们已介绍Moravec检测器,它仅仅在8个方向(水平、垂直和四个对角方向)计算灰度变化,为了对其扩展,有必要设计一个可以在任何方向对灰度变化进行测度的函数。1988年,Harris和Stephen通过对Moravec算子进行展开,推导得到了Plessey算子,也即Harris算子。即Harris比Moravec有所提升,因它考虑了角评分(平方差的和)的差分。
基本理论
考察一幅二维有灰度图像f,取出一个图像块![]() ,并平移
,并平移![]() 。图像块W内的图像f值与其平移后的图像之差平方和S为:
。图像块W内的图像f值与其平移后的图像之差平方和S为:
角点不受光圈问题的影响,对于所有![]() ,
,![]() 都是高响应。如果平移图像用一阶泰勒展开近似。则可以表示为:
都是高响应。如果平移图像用一阶泰勒展开近似。则可以表示为:
此时,![]() 的最小值有解析解。将式(5.7.5)的近似表达式代入式(5.7.4)后得到:
的最小值有解析解。将式(5.7.5)的近似表达式代入式(5.7.4)后得到:
其中Harris矩阵![]() 是S在点(x, y) = (0, 0)处二阶导数。A为:
是S在点(x, y) = (0, 0)处二阶导数。A为:
通常会使用一个各向同性窗,比如高斯窗,其响应也是各向同性的。局部结构矩阵A代表邻域:Harris矩阵A是半正定对称矩阵。其主要变化模式对应于正交方向的偏微分,并由矩阵A的特征值反映出来。在有关文献中建议,通过计算响应函数![]() ,可避免精确的特征值计算,其中det(M)为局部结构矩阵M的行列式,trace(M)为矩阵M的迹,K是可调参数。一般在0.04-0.15之间。
,可避免精确的特征值计算,其中det(M)为局部结构矩阵M的行列式,trace(M)为矩阵M的迹,K是可调参数。一般在0.04-0.15之间。
算法Harris角点检测
1.对图像进行高斯滤波。 2.对每个像素,估计其垂直两方向的梯度值。使用近似于导数的核做两次一维卷积即可。 3.对于每一个像素和给定的邻域窗口: 1)计算局部结构矩阵A 2)计算响应函数R(A) 4.选取响应函数R(A)的一个阈值,以选择最佳候选角点,并完成非最大化抑制。
Harris角点检测器的优点是对二维平移和旋转,少量光照变化,少量视角变化都不每感,而且其计算其很小。另一方面,当有较大变化,视角变化以及对比鲜明的剧烈变化时,它就失去了原先的不变性。
参考代码
Matlab版Harris.m文件
function [im_out,figs] = buttfilt(im,type,Do,n,padd_opt,fig)
%
% Usage: [im_out,figs] = buttfilt(im,type,Do,n,padd_opt,fig)
% Inputs:
% im [m x n x l] Input image; if it is an RGB image,
% filtering is applied to the intensity part only.
% Outputs:
% im_out [m x n x l] Filtered image of the same size as the input.
figs = [];
if size(im,3)==3, % rgb image assumed
im_hsv = rgb2hsv(im);
imval = im_hsv(:,:,3);
else % gray scale image assumed
imval = im;
end
[im_height,im_width] = size(imval);
if strcmp( padd_opt, 'none' )
ps = [im_height im_width];
else
ps = paddedsize( [im_height im_width], padd_opt );
end
D = rc2d( ps, 'euclidean' );
Do = Do*ps(2)/im_width;
F = fftshift( fft2(double(imval),ps(1),ps(2)) );
H = 1 ./ ( 1+(D./(Do+eps)).^n );
if strcmp( lower(type), 'hp' )
H = 1-H;
end
G = F .* H;
g = real( ifft2(fftshift(G)) );
g = g( 1:im_height, 1:im_width );
if size(im,3)==3 % rgb image assumed
im_out = im_hsv;
im_out(:,:,3) = g;
im_out = hsv2rgb(im_out);
else
im_out = g;
im_out(im_out>255) = 255;
im_out(im_out<0) = 0;
im_out = uint8(im_out);
end
if fig
figs(1).h = figure(fig); clf
imagesc(log(abs(F)+1));
colormap(jet(256)), axis on, axis image, colorbar
title('Shifted log(abs(FFT)) of the original image');
figs(1).fname = sprintf('%s_fft_original.eps',type);
figs(2).h = figure(fig+1); clf
mesh(H(1:end,1:end));
title(sprintf('%s Butt filter n=%d, Do=%d',type, n, Do))
rotate3d on
figs(2).fname = sprintf('%s_butt.eps',type);
figs(3).h = figure(fig+2); clf
imagesc(log(abs(G)+1));
colormap(jet(256)), axis on, axis image, colorbar
title('Shifted log(abs(FFT)) of the filtered image');
figs(3).fname = sprintf('%s_fft_filtered.eps',type);
end
return; % end of the buttfilt
OpenCV版Harris类
#ifndef _HARRIS_H
#define _HARRIS_H
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
class harris
{
private:
cv::Mat cornerStrength;
cv::Mat cornerTh;
cv::Mat localMax;
int neighbourhood;
int aperture;
double k;
double maxStrength;
double threshold;
int nonMaxSize;
cv::Mat kernel;
public:
harris():neighbourhood(3),aperture(3),k(0.01),maxStrength(0.0),
threshold(0.01),nonMaxSize(3){
};
void setLocalMaxWindowsize(int nonMaxSize){
this->nonMaxSize = nonMaxSize;
};
void detect(const cv::Mat &image){
cv::cornerHarris (image,cornerStrength,neighbourhood,aperture,k);
double minStrength;
cv::minMaxLoc (cornerStrength,&minStrength,&maxStrength);
cv::Mat dilated;
cv::dilate (cornerStrength,dilated,cv::Mat());
cv::compare(cornerStrength,dilated,localMax,cv::CMP_EQ);
}
cv::Mat getCornerMap(double qualityLevel) {
cv::Mat cornerMap;
threshold= qualityLevel*maxStrength;
cv::threshold(cornerStrength,cornerTh,
threshold,255,cv::THRESH_BINARY);
cornerTh.convertTo(cornerMap,CV_8U);
cv::bitwise_and(cornerMap,localMax,cornerMap);
return cornerMap;
}
void getCorners(std::vector<cv::Point> &points,
double qualityLevel) {
cv::Mat cornerMap= getCornerMap(qualityLevel);
getCorners(points, cornerMap);
}
void getCorners(std::vector<cv::Point> &points,
const cv::Mat& cornerMap) {
for( int y = 0; y < cornerMap.rows; y++ ) {
const uchar* rowPtr = cornerMap.ptr<uchar>(y);
for( int x = 0; x < cornerMap.cols; x++ ) {
if (rowPtr[x]) {
points.push_back(cv::Point(x,y));
}
}
}
}
void drawOnImage(cv::Mat &image,
const std::vector<cv::Point> &points,
cv::Scalar color= cv::Scalar(255,255,255),
int radius=3, int thickness=2) {
std::vector<cv::Point>::const_iterator it=points.begin();
while (it!=points.end()) {
cv::circle(image,*it,radius,color,thickness);
++it;
}
}
};
#endif // _HARRIS_H
OpenCV版HarrisCorner
cv::Mat image, image1 = cv::imread ("test.jpg");
cv::cvtColor (image1,image,CV_BGR2GRAY);
harris Harris;
Harris.detect(image);
std::vector<cv::Point> pts;
Harris.getCorners(pts,0.01);
Harris.drawOnImage(image,pts);
cv::namedWindow ("harris");
cv::imshow ("harris",image);
cv::waitKey (0);
相关测试结果:
从经典的Harris角点检测方法不难看出,该算法的稳定性和k有关,而k是个经验值,不好把握,浮动也有可能较大。鉴于此,改进的Harris方法()直接计算出两个特征值,通过比较两个特征值直接分类,这样就不用计算Harris响应函数了。另一方面,我们不再用非极大值抑制了,而选取容忍距离:容忍距离内只有一个特征点。
该算法首先选取一个具有最大 最小特征值的点(即:max(min(e1,e2)),e1,e2是harris矩阵的特征值)作为角点,然后依次按照最大最小特征值顺序寻找余下的角点,当然和前一角点距离在容忍距离内的新角点呗忽略。
OpenCV版改进的HarrisCorner
cv::Mat image, image1 = cv::imread ("test.jpg");
cv::cvtColor (image1,image,CV_BGR2GRAY);
std::vector<cv::Point> corners;
cv::goodFeaturesToTrack(image,corners,300,0.01,10);
harris().drawOnImage(image,corners);
测试结果如下:

OpenCV-Python版HarrisCorner
import cv2
import numpy as np
filename = 'Test.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(filename)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = np.float32(gray)
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray,2,3,0.04)
#result is dilated for marking the corners, not important
dst = cv2.dilate(dst,None)
# Threshold for an optimal value, it may vary depending on the image.
img[dst>0.01*dst.max()]=[0,0,255]
cv2.imshow('dst',img)
if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xff == 27:
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
相应测试输出结果如下:
OpenCV-Python版HarrisCorner带SubPixel Accuracy
import cv2
import numpy as np
filename = 'Test.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(filename)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# find Harris corners
gray = np.float32(gray)
dst = cv2.cornerHarris(gray,2,3,0.04)
dst = cv2.dilate(dst,None)
ret, dst = cv2.threshold(dst,0.01*dst.max(),255,0)
dst = np.uint8(dst)
# find centroids
ret, labels, stats, centroids = cv2.connectedComponentsWithStats(dst)
# define the criteria to stop and refine the corners
criteria = (cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS + cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_MAX_ITER, 100, 0.001)
corners = cv2.cornerSubPix(gray,np.float32(centroids),(5,5),(-1,-1),criteria)
# Now draw them
res = np.hstack((centroids,corners))
res = np.int0(res)
img[res[:,1],res[:,0]]=[0,0,255]
img[res[:,3],res[:,2]] = [0,255,0]
cv2.imwrite('Testsubpixel.jpg',img)
由测试结果,我们所知,Harris算子针对Moravec算子的不足进行了改进,提高了特征点的检测率以及Repeatability。但是,Harris算子计算量大,对尺度很敏感,不具有尺度不变形;Harris对特征点的定位也不是很精确,而且Harris也是各向异性的,对噪声敏感。
补充
(2013年11月4日)
#coding=utf-8
import cv2
image = cv2.imread("test.jpg", 0)
origin = cv2.imread("test.jpg")
#构造5×5的结构元素,分别为十字形、菱形、方形和X型
cross = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_CROSS,(5,5))
#菱形结构元素的定义稍麻烦一些
diamond = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(5,5))
diamond[0, 0] = 0
diamond[0, 1] = 0
diamond[1, 0] = 0
diamond[4, 4] = 0
diamond[4, 3] = 0
diamond[3, 4] = 0
diamond[4, 0] = 0
diamond[4, 1] = 0
diamond[3, 0] = 0
diamond[0, 3] = 0
diamond[0, 4] = 0
diamond[1, 4] = 0
square = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT,(5, 5))
x = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_CROSS,(5, 5))
#使用cross膨胀图像
result1 = cv2.dilate(image,cross)
#使用菱形腐蚀图像
result1 = cv2.erode(result1, diamond)
#使用X膨胀原图像
result2 = cv2.dilate(image, x)
#使用方形腐蚀图像
result2 = cv2.erode(result2,square)
#result = result1.copy()
#将两幅闭运算的图像相减获得角
result = cv2.absdiff(result2, result1)
#使用阈值获得二值图
retval, result = cv2.threshold(result, 40, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
#在原图上用半径为5的圆圈将点标出。
for j in range(result.size):
y = j / result.shape[0]
x = j % result.shape[0]
if result[x, y] == 255:
cv2.circle(image, (y, x), 5, (255,0,0))
cv2.imshow("Result", image)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
输出灰度图像结果:
参考文献
[1] Svoboda T.nKybic J., and Hlavac V. "Image Processing Analysis and Machine Vision". Thomson Engineering 2008.
[2] C. Harris and M.J. Stephens, "A combined corner and edge detector" Alvey Vision Conference, pp. 147–152, 1988.
[3] J. Shi and C. Tomasi, "Good features to track", Int. Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp. 593-600, 1994.
[4] K. Mikolajczyk and C. Schmid, "Scale and Affine invariant interest point detectors", International Journal of Computer Vision, vol 60, no 1, pp. 63-86, 2004,
[5] E. Rosten and T. Drummond, "Machine learning for high-speed corner detection", in In European Conference on Computer Vision, pp. 430-443, 2006.
关于Image Engineering & Computer Vision的更多讨论与交流,敬请关注本博和新浪微博songzi_tea.