BloomFilter算法概述
一. 实例
为了说明Bloom Filter存在的重要意义,举一个实例:
假设要你写一个网络蜘蛛(web crawler)。由于网络间的链接错综复杂,蜘蛛在网络间爬行很可能会形成“环”。为了避免形成“环”,就需要知道蜘蛛已经访问过那些URL。给一个URL,怎样知道蜘蛛是否已经访问过呢?稍微想想,就会有如下几种方案:
- 将访问过的URL保存到数据库。
- 用HashSet将访问过的URL保存起来。那只需接近O(1)的代价就可以查到一个URL是否被访问过了。
- URL经过MD5或SHA-1等单向哈希后再保存到HashSet或数据库。
- Bit-Map方法。建立一个BitSet,将每个URL经过一个哈希函数映射到某一位。
以上方法在数据量较小的情况下都能完美解决问题,但是当数据量变得非常庞大时问题就来了。
方法1的缺点:数据量变得非常庞大后关系型数据库查询的效率会变得很低。而且每来一个URL就启动一次数据库查询是不是太小题大做了?
方法2的缺点:太消耗内存。随着URL的增多,占用的内存会越来越多。就算只有1亿个URL,每个URL只算50个字符,就需要5GB内存。
方法3:由于字符串经过MD5处理后的信息摘要长度只有128Bit,SHA-1处理后也只有160Bit,因此方法3比方法2节省了好几倍的内存。
方法4消耗内存是相对较少的,但缺点是单一哈希函数发生冲突的概率太高。还记得数据结构课上学过的Hash表冲突的各种解决方法么?若要降低冲突发生的概率到1%,就要将BitSet的长度设置为URL个数的100倍。
实质上上面的算法都忽略了一个重要的隐含条件:允许小概率的出错,不一定要100%准确!也就是说少量url实际上没有没网络蜘蛛访问,而将它们错判为已访问的代价是很小的——大不了少抓几个网页呗。
二. Bloom Filter的算法
废话说到这里,下面引入本篇的主角——Bloom Filter。其实上面方法4的思想已经很接近Bloom Filter了。方法四的致命缺点是冲突概率高,为了降低冲突的概念,Bloom Filter使用了多个哈希函数,而不是一个。
Bloom Filter算法如下:
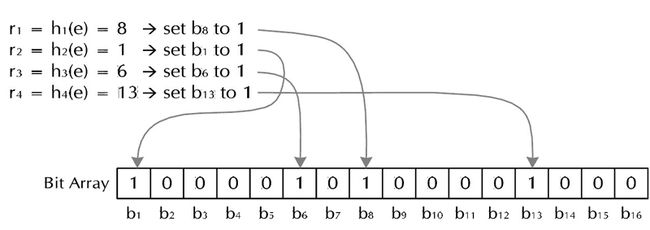
创建一个m位BitSet,先将所有位初始化为0,然后选择k个不同的哈希函数。第i个哈希函数对字符串str哈希的结果记为h(i,str),且h(i,str)的范围是0到m-1 。
(1) 加入字符串过程
下面是每个字符串处理的过程,首先是将字符串str“记录”到BitSet中的过程:
对于字符串str,分别计算h(1,str),h(2,str)…… h(k,str)。然后将BitSet的第h(1,str)、h(2,str)…… h(k,str)位设为1。
很简单吧?这样就将字符串str映射到BitSet中的k个二进制位了。
(2) 检查字符串是否存在的过程
下面是检查字符串str是否被BitSet记录过的过程:
对于字符串str,分别计算h(1,str),h(2,str)…… h(k,str)。然后检查BitSet的第h(1,str)、h(2,str)…… h(k,str)位是否为1,若其中任何一位不为1则可以判定str一定没有被记录过。若全部位都是1,则“认为”字符串str存在。
若一个字符串对应的Bit不全为1,则可以肯定该字符串一定没有被Bloom Filter记录过。(这是显然的,因为字符串被记录过,其对应的二进制位肯定全部被设为1了)
但是若一个字符串对应的Bit全为1,实际上是不能100%的肯定该字符串被Bloom Filter记录过的。(因为有可能该字符串的所有位都刚好是被其他字符串所对应)这种将该字符串划分错的情况,称为false positive 。
(3) 删除字符串过程
字符串加入了就被不能删除了,因为删除会影响到其他字符串。实在需要删除字符串的可以使用Counting bloomfilter(CBF),这是一种基本Bloom Filter的变体,CBF将基本 Bloom Filter每一个Bit改为一个计数器,这样就可以实现删除字符串的功能了。count占用4位即可,详细参考:深入解析Bloom Filter(上)
Bloom Filter跟单哈希函数Bit-Map不同之处在于:Bloom Filter使用了k个哈希函数,每个字符串跟k个bit对应。从而降低了冲突的概率。
三. Bloom Filter参数选择
(1)哈希函数选择
哈希函数的选择对性能的影响应该是很大的,一个好的哈希函数要能近似等概率的将字符串映射到各个Bit。选择k个不同的哈希函数比较麻烦,一种简单的方法是选择一个哈希函数,然后送入k个不同的参数。
(2)Bit数组大小选择
哈希函数个数k、位数组大小m、加入的字符串数量n的关系可以参考参考文献1。该文献证明了对于给定的m、n,当 k = ln(2)* m/n 时出错的概率是最小的。
同时该文献还给出特定的k,m,n的出错概率。例如:根据参考文献1,哈希函数个数k取10,位数组大小m设为字符串个数n的20倍时,false positive发生的概率是0.0000889 ,这个概率基本能满足网络爬虫的需求了。
四. Bloom Filter实现代码
下面给出一个简单的Bloom Filter的Java实现代码:
package algorithm;
import java.util.BitSet;
public class BloomFilter
{
/* BitSet初始分配2^24个bit */
private static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 1 << 25;
/* 不同哈希函数的种子,一般应取质数 */
private static final int[] seeds = new int[]{ 5, 7, 11, 13, 31, 37, 61 };
private BitSet bits = new BitSet(DEFAULT_SIZE);
/* 哈希函数对象 */
private SimpleHash[] func = new SimpleHash[seeds.length];
public BloomFilter()
{
for (int i = 0; i < seeds.length; i++)
{
func[i] = new SimpleHash(DEFAULT_SIZE, seeds[i]);
}
}
// 将字符串标记到bits中
public void add(String value)
{
for (SimpleHash f : func)
{
bits.set(f.hash(value), true);
}
}
// 判断字符串是否已经被bits标记
public boolean contains(String value)
{
if (value == null)
{
return false;
}
boolean ret = true;
for (SimpleHash f : func)
{
ret = ret && bits.get(f.hash(value));
}
return ret;
}
/* 哈希函数类 */
public static class SimpleHash
{
private int cap;
private int seed;
public SimpleHash(int cap, int seed)
{
this.cap = cap;
this.seed = seed;
}
// hash函数,采用简单的加权和hash
public int hash(String value)
{
int result = 0;
int len = value.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
result = seed * result + value.charAt(i);
}
return (cap - 1) & result;
}
}
}原文地址: 点击打开链接
参考文章:
- 深入解析Bloom Filter(上)