16、从头学Android之Service初步一
今天偶门外汉也来学习下Service,嘿嘿
Service概述
由于手机屏幕的限制,通常情况下在同一时刻仅有一个应用程序牌激活状态,并能够显示在手机屏幕上,因此,应用程序需要一种机制,在没有用户界面的情况下,合其能够长时间在后台运行,实现应用程序的特定功能,并能够处理事件或更新数据,Android系统提供了(Service)服务组件,它不直接与用户进行交互,却能够长期在后台运行。有很多情况需要使用Service,典型的例子就是:MP3播放器。
Service非常适用于无需用户干预,且需要长期运行的后台功能。Service没有用户界面,有利于降低系统资源。而且Service比Activity具有更高的优先级,因此在系统资源紧张的时候,Service不会轻易被Android系统终止。即使Service被系统终止了,在系统资源恢复后Service也将自动恢复运行状态,因此可以认为Service是在系统中永久运行的组件。Service除了实现后台服务功能,还可以用于进程间通信,解决两个不同Activity应用程序进程之间的调用和通信问题。
Service概览:
类结构图:
Service生命周期:
三个生命周期函数:
onCreate()
onStart()
onDestory
生命周期图:
不相信?那就让我们用实例说话吧!
启动Service的两种方式:startService 和bindService
一、startService启动Service
示例:
1、 先创建一个类继承于Service然后重写onBind()[且这个方法必须实现],onCreate()、onStart()、onDestory()方法
2、 在AndroidMainfest.xml中注册刚才写的这个Service
<service android:name=".MyService" >
<intent-filter >
<action android:name="com.jiahui.myservice" />
</intent-filter>
</service>
3、 通过在Activty中启动Service
startServiceDemo:
MyService继承于Service类
package com.jiahui.serviceDemo;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
public class MyService extends Service {
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
System.out.println("----onCreate-----");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
System.out.println("----onDestory-----");
super.onDestroy();
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
System.out.println("----onStart-----");
super.onStart(intent, startId);
}
}
MainActivty:
package com.jiahui.serviceDemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
Button btnStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStart);
Button btnStop = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStop);
final Intent service = new Intent();
service.setAction("com.jiahui.myservice");
btnStart.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 启动Service
MainActivity.this.startService(service);
}
});
btnStop.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// 停止Service
MainActivity.this.stopService(service);
}
});
}
}
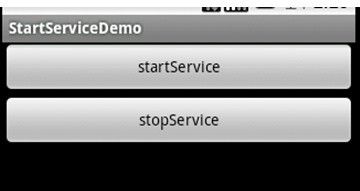
实现效果:
点击startService按钮:
再点startSerivce
点击stopService:
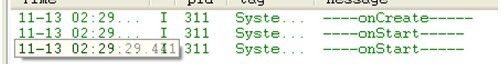
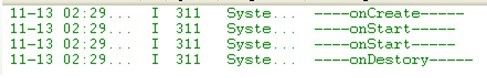
所以我们可以知道通过startService()方法启动Service的Service生命周期
从图可以看到startService的生命周期为:onCreate()-->onStart-->onDestory()。当第一次启动Service如果Service未创建,将调用onCreate()周期函数,之后再startService如果Service已创建则只会调用onStart()方法,stopService将调用onDestory()方法
除了通过startService来启动Service外我们还可以通过bindService()方法启动Service,也正好我们可以来好好比较这两种方式的区别。
由于篇幅过长,bindService方法将在下一篇中介绍
如需转载引用请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/jiahui524