Compressive Tracking——CT跟踪
感谢香港理工大学的Kaihua Zhang,这是他即将在ECCV 2012上出现的paper:Real-time Compressive Tracking。 这里是他的介绍:
一种简单高效地基于压缩感知的跟踪算法。首先利用符合压缩感知RIP条件的随机感知矩对多尺度图像特征进行降维,然后在降维后的特征上采用简单的朴素贝叶斯分类器进行分类。该跟踪算法非常简单,但是实验结果很鲁棒,速度大概能到达40帧/秒。具体原理分析可参照相关文章。
链接
免积分下载代码:http://download.csdn.net/detail/sangni007/5297374
1.Description: compute Haar features (templates)
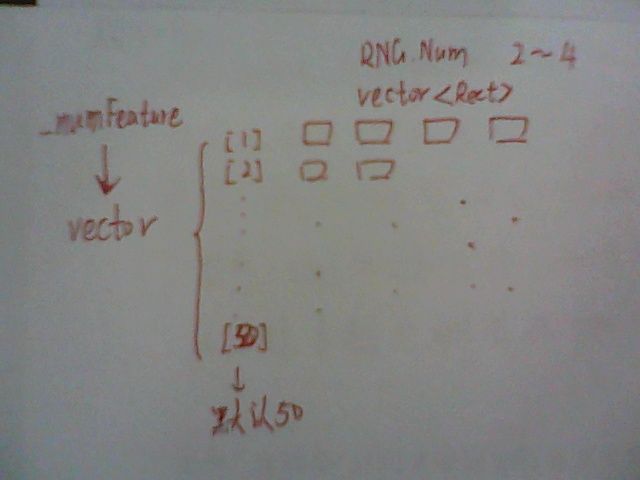
void CompressiveTracker::HaarFeature(Rect& _objectBox, int _numFeature)
在rect内取_numFeature维特征,(rect的宽高与_objectBox一样,与_objectBox.x _objectBox.y无关)
每一维Feature都用若干Rect表示,存在vector<vector<Rect>> feature (_numFeature, vector<Rect>())中,
相应权重 vector<vector<float>>featuresWeight(_numFeature, vector<float>())
2.Description: compute the coordinate of positive and negative sample image templates
void CompressiveTracker::sampleRect(Mat& _image, Rect& _objectBox, float _rInner, float _rOuter, int _maxSampleNum, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox)
随机洒出若干Rect,记录坐标Rect(x,y)
保证sampleRect的(x,y)到_objectBox的(x,y)的dist满足:_rOuter*_rOuter<dist<_rInner*_rInner
取样本:1:正:dist小;2:负:dist大:
存入_sampleBox
void CompressiveTracker::sampleRect(Mat& _image, Rect& _objectBox, float _srw, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox)
这个sampleRect的重载函数是用来,预测位置的
只要满足:dist<_rInner*_rInner
初始化第一帧不运行这个sampleRect的重载函数,只在跟踪时,首先运行它再更新正负样本函数;
3.Compute the features of samples
void CompressiveTracker::getFeatureValue(Mat& _imageIntegral, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox, Mat& _sampleFeatureValue)
计算相应Rect的积分图像的Sum值,存入Mat& _sampleFeatureValue(即特征值)

4.// Update the mean and variance of the gaussian classifier
void CompressiveTracker::classifierUpdate(Mat& _sampleFeatureValue, vector<float>& _mu, vector<float>& _sigma, float _learnRate)
计算每个上一步积分矩阵Mat& _sampleFeatureValue中每一SampleBox的期望和标准差
并Update(具体计算采用文章的公式[6])
5.// Compute the ratio classifier
void CompressiveTracker::radioClassifier(vector<float>& _muPos, vector<float>& _sigmaPos, vector<float>& _muNeg, vector<float>& _sigmaNeg, Mat& _sampleFeatureValue, float& _radioMax, int& _radioMaxIndex)
利用朴素贝叶斯分类(gaussian model)文章公式[4]
计算所有sample的贝叶斯值,用radioMax存储最大值,即为预测位置
Discussion
这篇文章最成功的地方在于简单高效,绝对可以达到实时跟踪的效果,之前实验的粒子滤波就显得太慢了;但是有很多问题需要改进。(个人观点和网友总结,欢迎拍砖~)
1.尺度问题,只能对单尺度操作,当对象远离时跟踪框依然大小不变;
2.关于压缩感知,可以改进,比如选择features pool 像随机森林一样选择最优特征;
3.偏向当前新样本,所以很容易就遗忘以前学习过的样本,一旦偏离,会越偏越远;
4.我也是刚研究tracking by detection不久,拜读了compressive tracking,感觉很有新意,用这么简洁的方法就能实现较好的效果,这篇论文的实验部分很像mil tracking,mil的弱分类器也是假设使用高斯分布,但是我实验的结果是 haar like 特征并不是很好的服从高斯分布,尤其是negative sample,所以在物体的表征变化很大的时候,这种representation不能很好的捕捉到,另外里面有个学习参数 lambda,这个参数的设置也是一个经验值,据我的经验,一般是偏向当前新样本,所以很容易就遗忘以前学习过的样本,TLD的随机森林fern是记录正负样本个数来计算posterior,这种方式在long time tracking比这个要好,另外TLD在每个细节上做得很好,它的更新模型也是有动态系统的理论支持。以上是个人拙见,希望能多交流。——老熊
5.如果在一些跟踪算法上面加些trick,也是可以做 long time tracking的。TLD 的trick就是用了第一帧的信息,其实这个信息很多时候是不太好的。并且这种trick多年前就有人用过了,不是TLD新创的。另外 TLD 的PAMI文章没有说这个trick,CVPR10文章说了。CT这个方法简单,它的侧重点不是说拼什么跟踪效果,主要是在理论方面说明一下问题——
//---------------------------------------------------
class CompressiveTracker
{
public:
CompressiveTracker(void);
~CompressiveTracker(void);
private:
int featureMinNumRect;
int featureMaxNumRect;
int featureNum;
vector<vector<Rect>> features;
vector<vector<float>> featuresWeight;
int rOuterPositive;
vector<Rect> samplePositiveBox;
vector<Rect> sampleNegativeBox;
int rSearchWindow;
Mat imageIntegral;
Mat samplePositiveFeatureValue;
Mat sampleNegativeFeatureValue;
vector<float> muPositive;
vector<float> sigmaPositive;
vector<float> muNegative;
vector<float> sigmaNegative;
float learnRate;
vector<Rect> detectBox;
Mat detectFeatureValue;
RNG rng;
private:
void HaarFeature(Rect& _objectBox, int _numFeature);
void sampleRect(Mat& _image, Rect& _objectBox, float _rInner, float _rOuter, int _maxSampleNum, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox);
void sampleRect(Mat& _image, Rect& _objectBox, float _srw, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox);
void getFeatureValue(Mat& _imageIntegral, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox, Mat& _sampleFeatureValue);
void classifierUpdate(Mat& _sampleFeatureValue, vector<float>& _mu, vector<float>& _sigma, float _learnRate);
void radioClassifier(vector<float>& _muPos, vector<float>& _sigmaPos, vector<float>& _muNeg, vector<float>& _sigmaNeg,
Mat& _sampleFeatureValue, float& _radioMax, int& _radioMaxIndex);
public:
void processFrame(Mat& _frame, Rect& _objectBox);
void init(Mat& _frame, Rect& _objectBox);
};
#include "CompressiveTracker.h"
#include <math.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
//------------------------------------------------
CompressiveTracker::CompressiveTracker(void)
{
featureMinNumRect = 2;
featureMaxNumRect = 4; // number of rectangle from 2 to 4
featureNum = 50; // number of all weaker classifiers, i.e,feature pool
rOuterPositive = 4; // radical scope of positive samples
rSearchWindow = 25; // size of search window
muPositive = vector<float>(featureNum, 0.0f);
muNegative = vector<float>(featureNum, 0.0f);
sigmaPositive = vector<float>(featureNum, 1.0f);
sigmaNegative = vector<float>(featureNum, 1.0f);
learnRate = 0.85f; // Learning rate parameter
}
CompressiveTracker::~CompressiveTracker(void)
{
}
void CompressiveTracker::HaarFeature(Rect& _objectBox, int _numFeature)
/*Description: compute Haar features
Arguments:
-_objectBox: [x y width height] object rectangle
-_numFeature: total number of features.The default is 50.
*/
{
features = vector<vector<Rect>>(_numFeature, vector<Rect>());
featuresWeight = vector<vector<float>>(_numFeature, vector<float>());
int numRect;
Rect rectTemp;
float weightTemp;
for (int i=0; i<_numFeature; i++)
{
//每一个特征生成一个平均分布的随机数, 这个特征用几个Rect表示;
numRect = cvFloor(rng.uniform((double)featureMinNumRect, (double)featureMaxNumRect));
for (int j=0; j<numRect; j++)
{
//在Rcet(x,y,w,h)内画随机rectTemp,事实上,只用到了_objectBox的w和h,原则上在rect(0,0,w,h)内均匀分布;
rectTemp.x = cvFloor(rng.uniform(0.0, (double)(_objectBox.width - 3)));
rectTemp.y = cvFloor(rng.uniform(0.0, (double)(_objectBox.height - 3)));
rectTemp.width = cvCeil(rng.uniform(0.0, (double)(_objectBox.width - rectTemp.x - 2)));
rectTemp.height = cvCeil(rng.uniform(0.0, (double)(_objectBox.height - rectTemp.y - 2)));
features[i].push_back(rectTemp);
weightTemp = (float)pow(-1.0, cvFloor(rng.uniform(0.0, 2.0))) / sqrt(float(numRect));
featuresWeight[i].push_back(weightTemp);
}
}
}
void CompressiveTracker::sampleRect(Mat& _image, Rect& _objectBox, float _rInner,
float _rOuter, int _maxSampleNum, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox)
/* Description: compute the coordinate of positive and negative sample image templates
Arguments:
-_image: processing frame
-_objectBox: recent object position
-_rInner: inner sampling radius
-_rOuter: Outer sampling radius
-_maxSampleNum: maximal number of sampled images
-_sampleBox: Storing the rectangle coordinates of the sampled images.
*/
{
int rowsz = _image.rows - _objectBox.height - 1;
int colsz = _image.cols - _objectBox.width - 1;
float inradsq = _rInner*_rInner;//4*4
float outradsq = _rOuter*_rOuter;//0*0
int dist;
int minrow = max(0,(int)_objectBox.y-(int)_rInner);//起始位置最小坐标处;
int maxrow = min((int)rowsz-1,(int)_objectBox.y+(int)_rInner);//起始位置最大坐标处;
int mincol = max(0,(int)_objectBox.x-(int)_rInner);
int maxcol = min((int)colsz-1,(int)_objectBox.x+(int)_rInner);
int i = 0;
float prob = ((float)(_maxSampleNum))/(maxrow-minrow+1)/(maxcol-mincol+1);
int r;
int c;
_sampleBox.clear();//important
Rect rec(0,0,0,0);
for( r=minrow; r<=(int)maxrow; r++ )
for( c=mincol; c<=(int)maxcol; c++ ){
//保证sampleRect的(x,y)到_objectBox的(x,y)的dist满足:_rOuter*_rOuter<dist<_rInner*_rInner
dist = (_objectBox.y-r)*(_objectBox.y-r) + (_objectBox.x-c)*(_objectBox.x-c);
if( rng.uniform(0.,1.)<prob && dist < inradsq && dist >= outradsq ){
rec.x = c;
rec.y = r;
rec.width = _objectBox.width;
rec.height= _objectBox.height;
_sampleBox.push_back(rec);
i++;
}
}
_sampleBox.resize(i);
}
void CompressiveTracker::sampleRect(Mat& _image, Rect& _objectBox, float _srw, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox)
/* Description: Compute the coordinate of samples when detecting the object.*/
{
int rowsz = _image.rows - _objectBox.height - 1;
int colsz = _image.cols - _objectBox.width - 1;
float inradsq = _srw*_srw;
int dist;
int minrow = max(0,(int)_objectBox.y-(int)_srw);
int maxrow = min((int)rowsz-1,(int)_objectBox.y+(int)_srw);
int mincol = max(0,(int)_objectBox.x-(int)_srw);
int maxcol = min((int)colsz-1,(int)_objectBox.x+(int)_srw);
int i = 0;
int r;
int c;
Rect rec(0,0,0,0);
_sampleBox.clear();//important
for( r=minrow; r<=(int)maxrow; r++ )
for( c=mincol; c<=(int)maxcol; c++ ){
dist = (_objectBox.y-r)*(_objectBox.y-r) + (_objectBox.x-c)*(_objectBox.x-c);
if( dist < inradsq ){
rec.x = c;
rec.y = r;
rec.width = _objectBox.width;
rec.height= _objectBox.height;
_sampleBox.push_back(rec);
i++;
}
}
_sampleBox.resize(i);
}
// Compute the features of samples
void CompressiveTracker::getFeatureValue(Mat& _imageIntegral, vector<Rect>& _sampleBox, Mat& _sampleFeatureValue)
{
int sampleBoxSize = _sampleBox.size();
_sampleFeatureValue.create(featureNum, sampleBoxSize, CV_32F);
float tempValue;
int xMin;
int xMax;
int yMin;
int yMax;
for (int i=0; i<featureNum; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<sampleBoxSize; j++)
{
tempValue = 0.0f;
for (size_t k=0; k<features[i].size(); k++)
{
xMin = _sampleBox[j].x + features[i][k].x;
xMax = _sampleBox[j].x + features[i][k].x + features[i][k].width;
yMin = _sampleBox[j].y + features[i][k].y;
yMax = _sampleBox[j].y + features[i][k].y + features[i][k].height;
tempValue += featuresWeight[i][k] *
(_imageIntegral.at<float>(yMin, xMin) + //计算指定区域的积分图像的sum值;
_imageIntegral.at<float>(yMax, xMax) -
_imageIntegral.at<float>(yMin, xMax) -
_imageIntegral.at<float>(yMax, xMin));
}
_sampleFeatureValue.at<float>(i,j) = tempValue; //计算指定区域的积分图像的sum值,作为特征;
}
}
}
// Update the mean and variance of the gaussian classifier
void CompressiveTracker::classifierUpdate(Mat& _sampleFeatureValue, vector<float>& _mu, vector<float>& _sigma, float _learnRate)
{
Scalar muTemp;
Scalar sigmaTemp;
for (int i=0; i<featureNum; i++)
{
meanStdDev(_sampleFeatureValue.row(i), muTemp, sigmaTemp);
_sigma[i] = (float)sqrt( _learnRate*_sigma[i]*_sigma[i] + (1.0f-_learnRate)*sigmaTemp.val[0]*sigmaTemp.val[0]
+ _learnRate*(1.0f-_learnRate)*(_mu[i]-muTemp.val[0])*(_mu[i]-muTemp.val[0])); // equation 6 in paper
_mu[i] = _mu[i]*_learnRate + (1.0f-_learnRate)*muTemp.val[0]; // equation 6 in paper
}
}
// Compute the ratio classifier
void CompressiveTracker::radioClassifier(vector<float>& _muPos, vector<float>& _sigmaPos, vector<float>& _muNeg, vector<float>& _sigmaNeg,
Mat& _sampleFeatureValue, float& _radioMax, int& _radioMaxIndex)
{
float sumRadio;
_radioMax = -FLT_MAX;
_radioMaxIndex = 0;
float pPos;
float pNeg;
int sampleBoxNum = _sampleFeatureValue.cols;
for (int j=0; j<sampleBoxNum; j++)
{
sumRadio = 0.0f;
for (int i=0; i<featureNum; i++)
{
pPos = exp( (_sampleFeatureValue.at<float>(i,j)-_muPos[i])*(_sampleFeatureValue.at<float>(i,j)-_muPos[i]) / -(2.0f*_sigmaPos[i]*_sigmaPos[i]+1e-30) ) / (_sigmaPos[i]+1e-30);
pNeg = exp( (_sampleFeatureValue.at<float>(i,j)-_muNeg[i])*(_sampleFeatureValue.at<float>(i,j)-_muNeg[i]) / -(2.0f*_sigmaNeg[i]*_sigmaNeg[i]+1e-30) ) / (_sigmaNeg[i]+1e-30);
sumRadio += log(pPos+1e-30) - log(pNeg+1e-30); // equation 4
}
if (_radioMax < sumRadio)
{
_radioMax = sumRadio;
_radioMaxIndex = j;
}
}
}
void CompressiveTracker::init(Mat& _frame, Rect& _objectBox)
{
// compute feature template
HaarFeature(_objectBox, featureNum);
// compute sample templates
sampleRect(_frame, _objectBox, rOuterPositive, 0, 1000000, samplePositiveBox);
sampleRect(_frame, _objectBox, rSearchWindow*1.5, rOuterPositive+4.0, 100, sampleNegativeBox);
integral(_frame, imageIntegral, CV_32F);//计算积分图像;
getFeatureValue(imageIntegral, samplePositiveBox, samplePositiveFeatureValue);
getFeatureValue(imageIntegral, sampleNegativeBox, sampleNegativeFeatureValue);
classifierUpdate(samplePositiveFeatureValue, muPositive, sigmaPositive, learnRate);
classifierUpdate(sampleNegativeFeatureValue, muNegative, sigmaNegative, learnRate);
}
void CompressiveTracker::processFrame(Mat& _frame, Rect& _objectBox)
{
// predict
sampleRect(_frame, _objectBox, rSearchWindow,detectBox);
integral(_frame, imageIntegral, CV_32F);
getFeatureValue(imageIntegral, detectBox, detectFeatureValue);
int radioMaxIndex;
float radioMax;
radioClassifier(muPositive, sigmaPositive, muNegative, sigmaNegative, detectFeatureValue, radioMax, radioMaxIndex);
_objectBox = detectBox[radioMaxIndex];
// update
sampleRect(_frame, _objectBox, rOuterPositive, 0.0, 1000000, samplePositiveBox);
sampleRect(_frame, _objectBox, rSearchWindow*1.5, rOuterPositive+4.0, 100, sampleNegativeBox);
getFeatureValue(imageIntegral, samplePositiveBox, samplePositiveFeatureValue);
getFeatureValue(imageIntegral, sampleNegativeBox, sampleNegativeFeatureValue);
classifierUpdate(samplePositiveFeatureValue, muPositive, sigmaPositive, learnRate);
classifierUpdate(sampleNegativeFeatureValue, muNegative, sigmaNegative, learnRate);
}
参考文献:
增强视觉:http://www.cvchina.info/2012/07/31/real-time-compressive-tracking/