Ethernet的帧格式
局域网包括:以太网、令牌环、光纤分布式数据接口FDDI。
IP数据报必须用数据链路层的报文和报尾封装后才能在物理媒介上发送。数据链路层的报文和报尾提供以下服务:
1. 定界 帧彼此分开。每个帧的开始和结束位置被标出,其有效负载也与报头报尾分开。
2. 协议识别 许多组织使用不同协议套件,如TCP/IP,IPX或AppleTalk,每种协议必须区分开。
3. 寻址 为了共享以太网等局域网技术,必须指出源节点和目标节点。
4.比特级完整性检验 每帧校验和形式检查比特级错误。
同一网段上的所有节点(通过路由器连在一起)必须使用相同的帧格式才能相互通信。
一、Ethernet地址
为了标识以太网上的每台主机,需要给每台主机上的网络适配器(网络接口卡)分配一个唯一的通信地址,即Ethernet地址或称为网卡的物理地址、MAC地址。IEEE负责为网络适配器制造厂商分配Ethernet地址块,各厂商为自己生产的每块网络适配器分配一个唯一的Ethernet地址。因为在每块网络适配器出厂时,其Ethernet地址就已被烧录到网络适配器中。所以,有时我们也将此地址称为烧录地址(Burned-In-Address,BIA)。Ethernet地址长度为48比特,共6个字节,如图所示。其中,前3字节为IEEE分配给厂商的厂商代码,后3字节为网络适配器编号。

二、CSMA/CD
在ISO的OSI参考模型中,数据链路层的功能相对简单。它只负责将数据从一个节点可靠地传输到相邻节点。但在局域网中,多个节点共享传输介质,必须有某种机制来决定下一个时刻,哪个设备占用传输介质传送数据。因此,局域网的数据链路层要有介质访问控制的功能。为此,一般将数据链路层又划分成两个子层:
●逻辑链路控制LLC(Logic Line Control)子层
●介质访问控制MAC(Media Access Control)子层

如图所示。其中,LLC子层负责向其上层提供服务;MAC子层的主要功能包括数据帧的封装/卸装,帧的寻址和识别,帧的接收与发送,链路的管理,帧的差错控制等。MAC子层的存在屏蔽了不同物理链路种类的差异性。
在MAC子层的诸多功能中,非常重要的一项功能是仲裁介质的使用权,即规定站点何时可以使用通信介质。
实际上,局域网技术中是采用具有冲突检测的载波侦听多路访问(Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection,CSMA/CD)这种介质访问方法的。
在这种介质访问方法中规定:在发送数据之前,一个节点必须首先侦听网线上的载波,如果在9.6微秒的时间之内没有检测到载波(说明通信介质空闲),节点才可以发送一帧数据。
如果两个节点同时检测到介质空闲并同时发送出一帧数据,则会导致数据帧的冲突,双方的数据帧均被破坏。一方面,检测到冲突的节点会发送"冲突增强"信号(32比特的"1")通知介质上的每个节点发生了冲突。另一方面,发生冲突的节点在再次发送自己的数据帧之前会各自等待一段随机的时间。
随着以太网上节点数量的增加,冲突的数量也随之增加,而整个网段的有效带宽将随之减少。
|
一。Ethernet帧格式的发展
1980 DEC,Intel,Xerox制订了Ethernet I的标准
1982 DEC,Intel,Xerox又制订了Ehternet II的标准
1982 IEEE开始研究Ethernet的国际标准802.3
1983 迫不及待的Novell基于IEEE的802.3的原始版开发了专用的Ethernet帧格式
1985 IEEE推出IEEE 802.3规范
后来为解决EthernetII与802.3帧格式的兼容问题推出折衷的Ethernet SNAP格式
(其中早期的Ethernet I已经完全被其他帧格式取代了所以现在Ethernet只能见到后面几种Ethernet的帧格式现在大部分的网络设备都支持这几种Ethernet的帧格式如:cisco的路由器再设定Ethernet接口时可以指定不同的以太网的帧格式:arpa,sap,snap,novell-ether)
目前,有四种不同格式的以太网帧在使用,不同厂商有不同的叫法
Frame Type----------------------------------Novell叫法----------------------------Cisco叫法
Ethernet Version 2------------------------Ethernet II------------------------------ARPA
802.3-----------------------------------------Ethernet 802.3 raw------------------Novell-Ether
IEEE 802.3/802.2-------------------------Ethernet 802.2-----------------------SAP
IEEE 802.3/802.2 SNAP-----------------Ethernet SNAP----------------------SNAP
●Ethernet II即DIX 2.0:Xerox与DEC、Intel在1982年制定的以太网标准帧格式。Cisco名称为:ARPA。
●Ethernet 802.3 raw:Novell在1983年公布的专用以太网标准帧格式。Cisco名称为:Novell-Ether。
●Ethernet 802.3 SAP:IEEE在1985年公布的Ethernet 802.3的SAP版本以太网帧格式。Cisco名称为:SAP。
●Ethernet 802.3 SNAP:IEEE在1985年公布的Ethernet 802.3的SNAP版本以太网帧格式。Cisco名称为:SNAP。
在每种格式的以太网帧的开始处都有64比特(8字节)的前导字符,如图所示。其中,前7个字节称为前同步码(Preamble),内容是16进制数0xAA,最后1字节为帧起始标志符0xAB,它标识着以太网帧的开始。前导字符的作用是使接收节点进行同步并做好接收数据帧的准备
二.各种不同的帧格式
下面介绍一下各个帧格式
Ethernet II
就是DIX以太网联盟推出的,它由6个字节的目的MAC地址,6个字节的源MAC地址,2个字节的类型域(用于标示封装在这个Frame、里面数据的类型)以上为Frame Header,接下来是46--1500 字节的数据,和4字节的帧校验)
Novell Ethernet
它的帧头与Ethernet有所不同其中EthernetII帧头中的类型域变成了长度域,后面接着的两个字节为0xFFFF
用于标示这个帧是Novell Ether类型的Frame 由于前面的0xFFFF站掉了两个字节所以数据域缩小为44-1498个字节,帧校验不变。
IEEE 802.3/802.2
802.3的Frame Header和Ethernet II的帧头有所不同EthernetII类型域变成了长度域。其中又引入802.2协议(LLC)在802.3帧头后面添加了一个LLC首部,由DSAP(Destination Service Access Point)
1 byte,SSAP(Source SAP),一个控制域--1 byte!
SAP用于标示帧的上层协议
Ethernet SNAP
SNAP Frame与802.3/802.2 Frame的最大区别是增加了一个5 Bytes的SNAP ID其中前面3个byte通常与源mac地址的前三个bytes相同为厂商代码!有时也可设为0,后2 bytes 与Ethernet II的类型域相同。。。
三.如何区分不同的帧格式
Ethernet中存在这四种Frame那些网络设备又是如何识别的呢? 如何区分EthernetII与其他三种格式的Frame 如果帧头跟随source mac地址的2 bytes的值大于1500 则此Frame为EthernetII格式的。
接着比较紧接着的两bytes如果为0xFFFF则为Novell Ether 类型的Frame
如果为0xAAAA则为Ethernet SNAP格式的Frame ,如果都不是则为Ethernet 802.3/802.2格式的帧
Distinguishing Between Frame Types 1) Receive good frame.
2) Analyze frame. Perform the following steps, in order:
- If the EtherType/Length value is greater than 0x05-DC (decimal 1500), then process the frame as Ethernet II. Any EtherType value greater than 0x05-DC (such as 0x0800 for IP or 0x81-37 for NetWare IPX/SPX) will be interpreted as an Ethernet II frame.
- If the IPX header (0xFF-FF) follows the Length field, the frame is interpreted as a 802.3 (Raw) frame with Netware IPX/SPX traffic. Standard SSAP and DSAP values do not include hexadecimal FF, so the 802.3 (Raw) frame can be distinguished from LLC frames (Ethernet SNAP, 802.2).
- Next, the byte following the length field (DSAP) is examined. If the value is 0xAA, the frame is interpreted as a SNAP frame. Otherwise, it is interpreted as a 802.2 frame.
Hexadecimal Assignment Description ----------- --------------------------------- 0200 Xerox PUP 0201 Xerox PUP Address Translation 0600 Xerox NS IDP 0800 Internetworking Protocol (IP) 0801 X.75 0802 NBS 0803 ECMA 0804 Chaosnet 0805 X.25 Packet (Level 3) 0806 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) 0807 XNS Compatibility 1000 Berkeley Trailer 5208 BBN Simnet 6001 DEC MOP (Dump/Load) 6002 DEC MOP (Remote Console) 6003 DECNET Phase 4 6004 DEC LAT 6005 DEC 6006 DEC 8005 HP Probe 8010 Excelan 8035 Reverse ARP 8038 DEC LANBridge 809B AppleTalk 80F3 AppleTalk ARP 8137 NetWare IPX/SPX Sources:
Layered Protocols for Data Communications, Uyless Black, Information Engineering Institute NetWare LAN Analysis, Laura Chappell, Novell Press
1 Ethernet II
Ethernet Version 2------------------------Ethernet II------------------------------ARPA
1.1 Ethernet II协议简介
以太网是当今现有局域网采用的最通用的通信协议标准。该标准定义了在局域网中采用的电缆类型和信号处理方法。Ethernet II由DEC,Intel和Xerox在1982年公布其标准,Etherent II主要更改了Ethernet I的电气特性和物理接口,在帧格式上并无变化。Etherent II采用CSMA/CD的媒体接入和广播机制。
1.2 Ethernet II报头详解
Ethernet II协议报头结构
每个字段的详细解释如下:
?目标地址:此数据包的目标MAC地址。
?源地址:此数据包的源MAC地址。
?协议类型:上层协议,表示网络层使用的协议。
?数据:高层协议、数据和填充符,范围在46~1500字节。
?FCS:数据帧校验序列,用于确定数据包在传输过程中是否损坏。
1.3 数据包解码
下面我们就通过实际解码来学习Ethernet II协议。

以下是对该数据包解码的详细介绍:
?目标地址:00:00:59:AA:93:0D。
?源地址:00:00:41:26:3F:9E。
?协议类型:0x0800表示网络层使用的是IP协议。
?数据:传输层和应用层的数据(UDP和QQ)。
?FCS:数据帧校验序列。
2 Ethernet 802.2
IEEE 802.3/802.2-------------------------Ethernet 802.2-----------------------SAP
2.1 Ethernet 802.2协议简介
Ethernet 802.2协议是IEEE正式的802.3标准,它由Ethernet II发展而来。Ethernet 802.2将Ethernet II帧头的协议类型字段替换为帧长度字段,并加入LLC-802.2头,用以标记上层协议。LLC头包含目的服务访问点(DSAP)、源服务访问点(SSAP)和控制(Control)字段。
This frame includes fields from 802.3 and 802.2 (Logical Link Control) and can support the Novell IPX/SPX and FTAM (File Transfer, Access, and Management) protocols.
Preamble : 8 bytes Destination Address : 6 bytes Source Address : 6 bytes Length Field : 2 bytes Data Field : Between 46 and 1500 bytes (including LLC) Pad Characters : Variable, stuffs data field up to 46 bytes Frame Check Sequence: 4 bytes Min Frame Length : 64 bytes Max Frame Length : 1518 bytes (not including Preamble)
The LLC field consists of:
Destination Service Access Point (DSAP): 1 byte (NetWare 0xE0) Source Service Access Point (SSAP) : 1 byte (NetWare 0xE0) Control Field : 1 byte (NetWare 0x03)
NetWare IPX/SPX packets will assign a hexadecimal value of E0 to the DSAP and SSAP fields and a hexadecimal value of 03 to the Control field. The "03" Control value indicates an unnumbered 802.2 layer.
2.2 Ethernet 802.2协议报详解
Ethernet 802.2协议报头结构
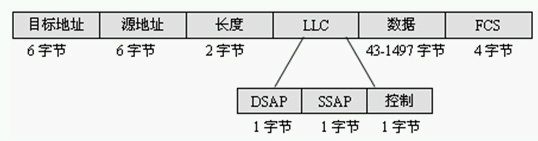
每个字段的详细解释如下:
?目标地址:此数据包的目标mac地址;
?源地址:此数据包的源mac地址;
?长度:帧包含的数据量必须小于或等于1500(16进制的05DC);
?DSAP:目标服务存取点(Destination Service Access Point);
?SSAP:源服务存取点(Source Service Access Point);
?控制:无连接或面向连接的LLC;
?数据:高层协议、数据和填充符;
?FCS:数据帧校验序列,用于确定数据包在传输过程中是否损坏。
2.3 Ethernet 802.2协议解码
Ethernet 802.2协议的解码视图:

以下是对该数据包解码的详细介绍:
?目标地址:01:80:C2:00:00:00;
?源地址:00:04:0C:38:CD:C9;
?长度:数包含的数量为38;
?目标服务存取点:0x42;
?源服务存取点:0x42;
?控制:3;
注意:服务存取点标识的功能类似于以太网类型或TCP/IP传输协议中的端口号,为高协议提供相应的接口。
3 Ethernet 802.3
802.3-----------------------------------------Ethernet 802.3 raw------------------Novell-Ether
3.1 Ethernet 802.3协议简介
Ethernet 802.3是1983年Novell发布其Netware/86网络套件时采用的私有以太网帧格式,该格式以当时尚未正式发布的IEEE802.3标准为基础;但是当两年以后IEEE正式发布802.3标准时情况发生了变化(IEEE在802.3帧头中又加入了802.2 LLC头),这使得Novell的Ethernet 802.3协议与正式的IEEE 802.3标准互不兼容;Ethernet 802.3
只支持IPX/SPX协议,是目前所用的最普通的一种帧格式,在802.2之前是IPX网络事实上的标准帧类型。
This is the original (and default) frame type used by NetWare. IT CAN ONLY SUPPORT NOVELL IPX/SPX TRAFFIC!
3.2 Ethernet 802.3协议报详解
Ethernet 802.3协议报头结构
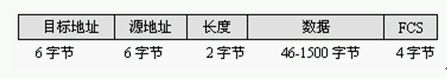
每个字段的详细解释如下:
?目标地址:此数据包的目标MAC地址。
?源地址:此数据包的源MAC地址。
?长度:帧包含的数量必须或等于1500。
?数据:高层协议(IPX/SPX)、数据和填充符,范围在46~1500字节。
?FCS:数据帧校验序列,用于确定数据包在传输过程中是否损坏。
有关IPX/SPX协议可参看http://hi.baidu.com/embedtec/blog/item/bc76924e342c320db3de05f8 .html
3.3 Ethernet 802.3协议解码
下面我们就通过实际解码来学习Ethernet 802.3协议.

下面我们对Ethernet 802.3的解码进行详细的介绍:
?目标地址:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF;
?源地址:00:E0:4C:50:6B:2E;
?长度:协议长度为40;
?数据:Ethernet 802.3只支持IPX/SPX协议;
?FCS:数据帧校验序列,用于确定数据包在传输过程中是否损坏。
注意:从这里就能看出Etherent II和Ethernet 802.3的区别,即协议类型和协议长度。
4 Ethernet SNAP
IEEE 802.3/802.2 SNAP-----------------Ethernet SNAP----------------------SNAP
4.1 Ethernet SNAP协议简介
Ethernet SNAP协议是IEEE为保证在802.2 LLC上支持更多的上层协议的同时更好地支持IP协议而发布的标准,与802.3/802.2 LLC一样802.3/802.2 SNAP也带有LLC头,但是扩展了LLC属性,新添加了一个2字节的协议类型域(同时将SAP的值置为AA),从而使其可以标识更多的上层协议类型;另外添加了一个3字节的厂商代码字段用于标记不同的组织。RFC 1042定义了IP报文在802.2网络中的封装方法和ARP协议在802.2 SANP中的实现方法。
Sub-Network Access Protocol (SNAP) is similar to 802.2, with LLC parameters, but with expanded LLC capabilities. Ethernet SNAP can support IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, and AppleTalk Phase 2 protocols.
Preamble : 8 bytes Destination Address : 6 bytes Source Address : 6 bytes Length Field : 2 bytes Data Field : Between 46 and 1500 bytes (including LLC) Pad Characters : Variable, stuffs data field up to 46 bytes Frame Check Sequence: 4 bytes Min Frame Length : 64 bytes Max Frame Length : 1518 bytes (not including Preamble)
The LLC field (the first eight bytes in the data field) consists of:
Destination Service Access Point (DSAP): 1 byte (0xAA) Source Service Access Point (SSAP) : 1 byte (0xAA) Control Field : 1 byte (NetWare 0x03) Organizational Code : 3 bytes (0x00-00-00) Ethernet Type : 2 bytes (NetWare 0x81-37)
Hexadecimal AA (decimal 170) values are usually employed for the DSAP and SSAP values. Netware uses a hexadecimal 03 in the SNAP Control field and will use the 0x81-37 Ethernet Type value. Usually, the Organizational Code is coded as all 0s (0x00-00-00) and NetWare is no exception.
4.2 Ethernet SNAP协议报头详解
Ethernet SNAP协议报头结构.

4.3 Ethernet SNAP解码
下面我们通过解码视图来学习Ethernet SNAP协议
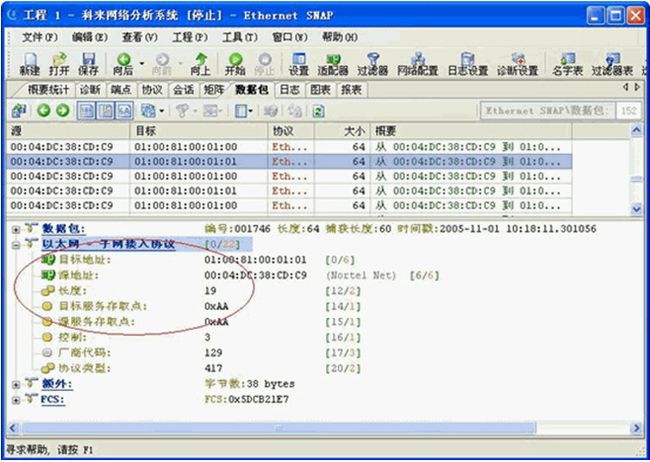
以下是对该数据包解码的详细介绍:
?目标地址:01:00:81:00:01:01
?源地址:00:04:0C:38:CD:C9;
?长度:协议长度为19;
?目标服务存取点:0xAA;
?源服务存取点:0xAA;
?厂商代码:129;
?协议类型:417;
前面我们分别介绍了以太网标准中定义的四种不同的帧类型,即Ethernet II、Ethernet802.3、Ethernet SNAP和Ethernet 802.2,这每一种帧类型都由不同的实体为不同的目的而设计。它们可以共存于一个网络中,但互不兼容,当用不同封装类型的工作站要交换信息时,必须通过支持的路由器来通信。
关于Ethernet 帧格式 (3)
2008年09月30日 星期二 10:48
历史上以太网帧格式有五种:
1.Ethernet V1:这是最原始的一种格式,是由Xerox PARC提出的3Mbps CSMA/CD以太网标准的封装格式,后来在1980年由DEC,Intel和Xerox标准化形成Ethernet V1标准.
2.Ethernet V2(ARPA):由DEC,Intel和Xerox在1982年公布其标准,主要更改了Ethernet V1的电气特性和物理接口,在帧格式上并无变化;Ethernet V2出现后迅速取代Ethernet V1成为以太网事实标准;Ethernet V2帧头结构为6bytes的源地址+6bytes的目标地址+2Bytes的协议类型字段+数据。
3.RAW 802.3:这是1983年Novell发布其划时代的Netware/86网络套件时采用的私有以太网帧格式,该格式以当时尚未正式发布的802.3标准为基础;但是当两年以后IEEE正式发布802.3标准时情况发生了变化—IEEE在802.3帧头中又加入了802.2 LLC(Logical Link Control)头,这使得Novell的RAW 802.3格式跟正式的IEEE 802.3标准互不兼容.
4.802.3/802.2 LLC:这是IEEE 正式的802.3标准,它由Ethernet V2发展而来。它将Ethernet V2帧头的协议类型字段替换为帧长度字段(取值为0000-05dc;十进制的1500);并加入802.2 LLC头用以标志上层协议,LLC头中包含DSAP,SSAP以及Crontrol字段.
5.802.3/802.2 SNAP:这是IEEE为保证在802.2 LLC上支持更多的上层协议同时更好的支持IP协议而发布的标准,与802.3/802.2 LLC一样802.3/802.2 SNAP也带有LLC头,但是扩展了LLC属性,新添加了一个2Bytes的协议类型域(同时将SAP的值置为AA),从而使其可以标识更多的上层协议类型;另外添加了一个3Bytes的OUI字段用于代表不同的组织,RFC 1042定义了IP报文在802.2网络中的封装方法和ARP协议在802.2 SANP中的实现.
802.3以太网帧格式备注:
前导码(7字节)、帧起始定界符(1字节)、目的MAC地址(6字节)、源MAC地址(6字节)、类型/长度(2字节)、数据(46~1500字节)、帧校验序列(4字节)[MAC地址可以用2-6字节来表示,原则上是这样,实际都是6字节]
|
|
Introduction
There are a variety of Ethernet Frame Types that may be observed in a Novell LAN environment. This depends upon the version of NetWare, and the applications employed.
NetWare 2.X : Ethernet 802.3 (Raw) Ethernet II NetWare 3.X : Ethernet 802.3 (Raw) Ethernet II Ethernet 802.2 Ethernet SNAP (Sub-Network Access Protocol)
Not all frame types can support all traffic variants. For example, NetWare IPX/SPX packets are usually transmitted by 802.3 (Raw) frames. In fact, the 802.3 frame type can only support IPX/SPX traffic. When TCP traffic is generated, the Ethernet II frame is often used. Some desktop LAN analyzers will employ SNAP frames.
Ethernet Frame Types
Ethernet 802.3 (Raw)
This is the original (and default) frame type used by NetWare. IT CAN ONLY SUPPORT NOVELL IPX/SPX TRAFFIC! The frame is similar to that described in 802.3 except that it does not contain the Logical Link Control (LLC) information in the packet.
Preamble : 8 bytes Destination Address : 6 bytes Source Address : 6 bytes Length Field : 2 bytes Data Field : Between 46 and 1500 bytes Pad Characters : Variable, stuffs data field up to 46 bytes Frame Check Sequence: 4 bytes Min Frame Length : 64 bytes Max Frame Length : 1518 bytes (not including Preamble)
Ethernet 802.2
This frame includes fields from 802.3 and 802.2 (Logical Link Control) and can support the Novell IPX/SPX and FTAM (File Transfer, Access, and Management) protocols. The frame parameters are identical to those listed above, EXCEPT that the first three bytes of the data field are used to indicate 802.2 header (LLC) information.
Preamble : 8 bytes Destination Address : 6 bytes Source Address : 6 bytes Length Field : 2 bytes Data Field : Between 46 and 1500 bytes (including LLC) Pad Characters : Variable, stuffs data field up to 46 bytes Frame Check Sequence: 4 bytes Min Frame Length : 64 bytes Max Frame Length : 1518 bytes (not including Preamble)
The LLC field consists of:
Destination Service Access Point (DSAP): 1 byte (NetWare 0xE0) Source Service Access Point (SSAP) : 1 byte (NetWare 0xE0) Control Field : 1 byte (NetWare 0x03)
NetWare IPX/SPX packets will assign a hexadecimal value of E0 to the DSAP and SSAP fields and a hexadecimal value of 03 to the Control field. The "03" Control value indicates an unnumbered 802.2 layer.
Ethernet II
Again, a similar frame type, EXCEPT that the two-byte Length field has been replaced with a two-byte Type field (Ethertype). Ethernet II frames can support Novell IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, and AppleTalk Phase 1 protocols. Ethernet II frames do not use a LLC header in the data field.
Preamble : 8 bytes Destination Address : 6 bytes Source Address : 6 bytes Ethernet Type : 2 bytes (Novell 0x81-37) Data Field : Between 46 and 1500 bytes Pad Characters : Variable, stuffs data field up to 46 bytes Frame Check Sequence: 4 bytes Min Frame Length : 64 bytes Max Frame Length : 1518 bytes (not including Preamble)
The Ethernet Type field is coded with hexadecimal 8137 for transport of NetWare IPX/SPX packets.
Go here for more information on EtherType variable assignments
Ethernet SNAP
Sub-Network Access Protocol (SNAP) is similar to 802.2, with LLC parameters, but with expanded LLC capabilities. Ethernet SNAP can support IPX/SPX, TCP/IP, and AppleTalk Phase 2 protocols.
Preamble : 8 bytes Destination Address : 6 bytes Source Address : 6 bytes Length Field : 2 bytes Data Field : Between 46 and 1500 bytes (including LLC) Pad Characters : Variable, stuffs data field up to 46 bytes Frame Check Sequence: 4 bytes Min Frame Length : 64 bytes Max Frame Length : 1518 bytes (not including Preamble)
The LLC field (the first eight bytes in the data field) consists of:
Destination Service Access Point (DSAP): 1 byte (0xAA) Source Service Access Point (SSAP) : 1 byte (0xAA) Control Field : 1 byte (NetWare 0x03) Organizational Code : 3 bytes (0x00-00-00) Ethernet Type : 2 bytes (NetWare 0x81-37)
Go here for more information on EtherType variable assignments
Hexadecimal AA (decimal 170) values are usually employed for the DSAP and SSAP values. Netware uses a hexadecimal 03 in the SNAP Control field and will use the 0x81-37 Ethernet Type value. Usually, the Organizational Code is coded as all 0s (0x00-00-00) and NetWare is no exception.
Distinguishing Between Frame Types
1) Receive good frame.
2) Analyze frame. Perform the following steps, in order:
- If the EtherType/Length value is greater than 0x05-DC (decimal 1500), then process the frame as Ethernet II. Any EtherType value greater than 0x05-DC (such as 0x0800 for IP or 0x81-37 for NetWare IPX/SPX) will be interpreted as an Ethernet II frame.
- If the IPX header (0xFF-FF) follows the Length field, the frame is interpreted as a 802.3 (Raw) frame with Netware IPX/SPX traffic. Standard SSAP and DSAP values do not include hexadecimal FF, so the 802.3 (Raw) frame can be distinguished from LLC frames (Ethernet SNAP, 802.2).
- Next, the byte following the length field (DSAP) is examined. If the value is 0xAA, the frame is interpreted as a SNAP frame. Otherwise, it is interpreted as a 802.2 frame.
Hexadecimal Assignment Description ----------- --------------------------------- 0200 Xerox PUP 0201 Xerox PUP Address Translation 0600 Xerox NS IDP 0800 Internetworking Protocol (IP) 0801 X.75 0802 NBS 0803 ECMA 0804 Chaosnet 0805 X.25 Packet (Level 3) 0806 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) 0807 XNS Compatibility 1000 Berkeley Trailer 5208 BBN Simnet 6001 DEC MOP (Dump/Load) 6002 DEC MOP (Remote Console) 6003 DECNET Phase 4 6004 DEC LAT 6005 DEC 6006 DEC 8005 HP Probe 8010 Excelan 8035 Reverse ARP 8038 DEC LANBridge 809B AppleTalk 80F3 AppleTalk ARP 8137 NetWare IPX/SPX
Sources:
Layered Protocols for Data Communications, Uyless Black, Information Engineering Institute NetWare LAN Analysis, Laura Chappell, Novell Press








