Android NFC 开发教程(3): Mifare Tag 读写示例
前面例子介绍了检测,读写NFC TAG开发的一般步骤,本例针对常用的Mifare Tag 具体说明。
Mifare Tag 可以有1K ,2K, 4K,其内存分区大同小异,下图给出了1K字节容量的Tag的内存分布:
数据分为16个区(Sector) ,每个区有4个块(Block) ,每个块可以存放16字节的数据,其大小为16 X 4 X 16 =1024 bytes
每个区最后一个块称为Trailer ,主要用来存放读写该区Block数据的Key ,可以有A,B两个Key,每个Key 长度为6个字节,缺省的Key值一般为全FF或是0. 由 MifareClassic.KEY_DEFAULT 定义。
因此读写Mifare Tag 首先需要有正确的Key值(起到保护的作用),如果鉴权成功
auth = mfc.authenticateSectorWithKeyA(j,
MifareClassic.KEY_DEFAULT);
然后才可以读写该区数据。
本例定义几个Mifare相关的类 MifareClassCard ,MifareSector, MifareBlock 和MifareKey 以方便读写Mifare Tag.
Android 系统来检测到NFC Tag, 将其封装成Tag类,存放到Intent的NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG Extra 数据包中,可以使用MifareClassic.get(Tag) 获取对象的 MifareClassic类。
Tag tagFromIntent = intent.getParcelableExtra(NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG); // 4) Get an instance of the Mifare classic card from this TAG // intent MifareClassic mfc = MifareClassic.get(tagFromIntent);
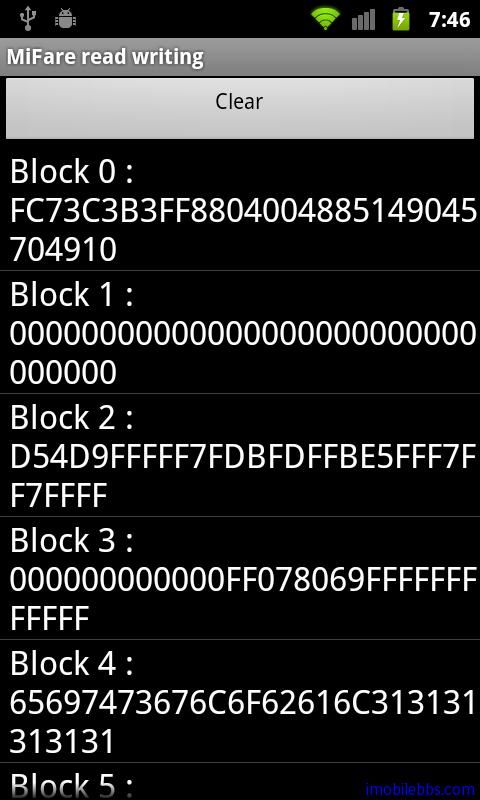
下面为读取Mifare card 的主要代码:
// 1) Parse the intent and get the action that triggered this intent
String action = intent.getAction();
// 2) Check if it was triggered by a tag discovered interruption.
if (NfcAdapter.ACTION_TECH_DISCOVERED.equals(action)) {
// 3) Get an instance of the TAG from the NfcAdapter
Tag tagFromIntent = intent.getParcelableExtra(NfcAdapter.EXTRA_TAG);
// 4) Get an instance of the Mifare classic card from this TAG
// intent
MifareClassic mfc = MifareClassic.get(tagFromIntent);
MifareClassCard mifareClassCard=null;
try { // 5.1) Connect to card
mfc.connect();
boolean auth = false;
// 5.2) and get the number of sectors this card has..and loop
// thru these sectors
int secCount = mfc.getSectorCount();
mifareClassCard= new MifareClassCard(secCount);
int bCount = 0;
int bIndex = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < secCount; j++) {
MifareSector mifareSector = new MifareSector();
mifareSector.sectorIndex = j;
// 6.1) authenticate the sector
auth = mfc.authenticateSectorWithKeyA(j,
MifareClassic.KEY_DEFAULT);
mifareSector.authorized = auth;
if (auth) {
// 6.2) In each sector - get the block count
bCount = mfc.getBlockCountInSector(j);
bCount =Math.min(bCount, MifareSector.BLOCKCOUNT);
bIndex = mfc.sectorToBlock(j);
for (int i = 0; i < bCount; i++) {
// 6.3) Read the block
byte []data = mfc.readBlock(bIndex);
MifareBlock mifareBlock = new MifareBlock(data);
mifareBlock.blockIndex = bIndex;
// 7) Convert the data into a string from Hex
// format.
bIndex++;
mifareSector.blocks[i] = mifareBlock;
}
mifareClassCard.setSector(mifareSector.sectorIndex,
mifareSector);
} else { // Authentication failed - Handle it
}
}
ArrayList<String> blockData=new ArrayList<String>();
int blockIndex=0;
for(int i=0;i<secCount;i++){
MifareSector mifareSector=mifareClassCard.getSector(i);
for(int j=0;j<MifareSector.BLOCKCOUNT;j++){
MifareBlock mifareBlock=mifareSector.blocks[j];
byte []data=mifareBlock.getData();
blockData.add("Block "+ blockIndex++ +" : "+
Converter.getHexString(data, data.length));
}
}
String []contents=new String[blockData.size()];
blockData.toArray(contents);
setListAdapter(new ArrayAdapter<String>(this,
android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, contents));
getListView().setTextFilterEnabled(true);
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, e.getLocalizedMessage());
showAlert(3);
}finally{
if(mifareClassCard!=null){
mifareClassCard.debugPrint();
}
}
}// End of method
本例下载