【STL学习】堆相关算法详解与C++编程实现(Heap)
堆简介
堆并不是STL的组件,但是经常充当着底层实现结构。比如优先级队列(Priority Queue)等等。
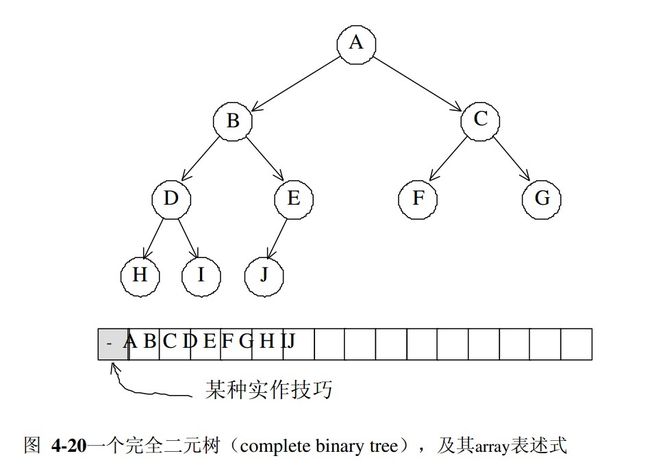
堆是一种完全二叉树,因此我们可以用数组来存储所有节点。在这里的实现中,采用了一个技巧:将数组中索引为0的元素保留,设置为极大值或者为极小值(依据大顶堆或者小顶堆而定)。那么当某个节点的索引是i时,其左子节点索引为2*i,右子节点索引为2*i+1.父节点是i/2(这里/表示高斯符号,取整)。这种以数组表示树的方式,我们成为隐式表述法(implicit reprentation)。我们这里用C++ STL中的容器vector实现替代数组的功能。
堆分为大顶堆和小顶堆。这里介绍并实现的是大顶堆。
堆的主要相关算法介绍
push_heap算法
此操作是向堆中添加一个节点。为了满足完全二叉树的条件,新加入的元素一定放在最下面的一层作为叶节点,并填补在由左至右的第一个空格,在这里放在底层容器vector的end()处。
很显然,新元素的加入很可能使得堆不在满足大顶堆的性质---每个节点的键值都大于或等于其子节点的键值。为了调整使得其重新满足大顶堆的特点,在这里执行一个上溯(percolate up)操作:将新节点与父节点比较,如果其键值比父节点大,就交换父子的位置,如此一直上溯,直到不需要交换或者到根节点为止。
pop_heap算法
此操作取走根节点。对于大顶堆,取得的是堆中值最大的节点,对于小顶堆,取得的是堆中值最小的节点。STL实现并不是将这个节点直接删除,而是将其放在底层容器vector的尾端。而原尾端的节点插入到前面的适当位置。
我们首先保存原vector尾端的节点值,然后将根节点值存储在此处。为了实将原尾端节点的值插入适当位置,重新构建大顶堆,我们实施如下调整堆的操作:
先执行下溯(percolate down)操作:从根节点开始将空洞节点(一开始是根节点)和较大子节点交换,并持续向下进行,直到到达叶节点为止。然后将已保存的原容器vector尾端节点赋给这个已到达叶层的空洞节点。
注意,到这里并没有结束。因为这时候可能还没有满足大顶堆的特性。还需要执行一次上溯操作。这样,便重新构建了大顶堆。
make_heap算法
此操作是依据已有的各元素构建堆。
其中,各元素已经存放在底层容器vector中。
构建堆实质是一个不断调整堆(即前面pop_heap算法中的调整堆的操作)的过程---通过不断调整子树,使得子树满足堆的特性来使得整个树满足堆的性质。
叶节点显然需要调整,第一个需要执行调整操作的子树的根节点是从后往前的第一个非叶结点。从此节点往前到根节点对每个子树执行调整操作,即可构建堆。
sort_heap算法
堆排序算法。执行此操作之后,容器vector中的元素按照从小到大的顺序排列。
构建大顶堆之后,不断执行pop_heap算法取出堆顶的元素,即可。因为每次取得的是最大的元素,将其放在容器vector的最尾端。所以到最后vector中的元素是从小到大排列的。
编程实现(C plus plus)
详细代码包括两个文件Heap.h以及HeapTest.cpp:
Heap.h:
//STL堆算法实现(大顶堆)
//包含容器vector的头文件:Heap用vector来存储元素
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#define MAX_VALUE 999999 //某个很大的值,存放在vector的第一个位置(最大堆)
const int StartIndex = 1;//容器中堆元素起始索引
using namespace std;
//堆类定义
//默认比较规则less
template <class ElemType,class Compare = less<ElemType> >
class MyHeap{
private:
vector<ElemType> heapDataVec;//存放元素的容器
int numCounts;//堆中元素个数
Compare comp;//比较规则
public:
MyHeap();
vector<ElemType> getVec();
void initHeap(ElemType *data,const int n);//初始化操作
void printfHeap();//输出堆元素
void makeHeap();//建堆
void sortHeap();//堆排序算法
void pushHeap(ElemType elem);//向堆中插入元素
void popHeap();//从堆中取出堆顶的元素
void adjustHeap(int childTree,ElemType adjustValue);//调整子树
void percolateUp(int holeIndex,ElemType adjustValue);//上溯操作
};
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::MyHeap()
:numCounts(0)
{
heapDataVec.push_back(MAX_VALUE);
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
vector<ElemType> MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::getVec()
{
return heapDataVec;
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::initHeap(ElemType *data,const int n)
{
//拷贝元素数据到vector中
for (int i = 0;i < n;++i)
{
heapDataVec.push_back(*(data + i));
++numCounts;
}
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::printfHeap()
{
cout << "Heap : ";
for (int i = 1;i <= numCounts;++i)
{
cout << heapDataVec[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::makeHeap()
{
//建堆的过程就是一个不断调整堆的过程,循环调用函数adjustHeap依次调整子树
if (numCounts < 2)
return;
//第一个需要调整的子树的根节点多音
int parent = numCounts / 2;
while(1)
{
adjustHeap(parent,heapDataVec[parent]);
if (StartIndex == parent)//到达根节点
return;
--parent;
}
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::sortHeap()
{
//堆排序思路
//每执行一次popHeap操作,堆顶的元素被放置在尾端,然后针对前面的一次再执行popHeap操作
//依次下去,最后即得到排序结果
while(numCounts > 0)
popHeap();
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::pushHeap(ElemType elem)
{
//将新元素添加到vector中
heapDataVec.push_back(elem);
++numCounts;
//执行一次上溯操作,调整堆,以使其满足最大堆的性质
percolateUp(numCounts,heapDataVec[numCounts]);
}
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::popHeap()
{
//将堆顶的元素放在容器的最尾部,然后将尾部的原元素作为调整值,重新生成堆
ElemType adjustValue = heapDataVec[numCounts];
//堆顶元素为容器的首元素
heapDataVec[numCounts] = heapDataVec[StartIndex];
//堆中元素数目减一
--numCounts;
adjustHeap(StartIndex,adjustValue);
}
//调整以childTree为根的子树为堆
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::adjustHeap(int childTree,ElemType adjustValue)
{
//洞节点索引
int holeIndex = childTree;
int secondChid = 2 * holeIndex + 1;//洞节点的右子节点(注意:起始索引从1开始)
while(secondChid <= numCounts)
{
if (comp(heapDataVec[secondChid],heapDataVec[secondChid - 1]))
{
--secondChid;//表示两个子节点中值较大的那个
}
//上溯
heapDataVec[holeIndex] = heapDataVec[secondChid];//令较大值为洞值
holeIndex = secondChid;//洞节点索引下移
secondChid = 2 * secondChid + 1;//重新计算洞节点右子节点
}
//如果洞节点只有左子节点
if (secondChid == numCounts + 1)
{
//令左子节点值为洞值
heapDataVec[holeIndex] = heapDataVec[secondChid - 1];
holeIndex = secondChid - 1;
}
//将调整值赋予洞节点
heapDataVec[holeIndex] = adjustValue;
//此时可能尚未满足堆的特性,需要再执行一次上溯操作
percolateUp(holeIndex,adjustValue);
}
//上溯操作
template <class ElemType,class Compare>
void MyHeap<ElemType,Compare>::percolateUp(int holeIndex,ElemType adjustValue)
{
//将新节点与其父节点进行比较,如果键值比其父节点大,就父子交换位置。
//如此,知道不需要对换或直到根节点为止
int parentIndex = holeIndex / 2;
while(holeIndex > StartIndex && comp(heapDataVec[parentIndex],adjustValue))
{
heapDataVec[holeIndex] = heapDataVec[parentIndex];
holeIndex = parentIndex;
parentIndex /= 2;
}
heapDataVec[holeIndex] = adjustValue;//将新值放置在正确的位置
}
main.cpp:
#include "Heap.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const int n = 9;
int data[n] = {0,1,2,3,4,8,9,3,5};
MyHeap<int> *intHeapObj = new MyHeap<int>;
intHeapObj->initHeap(data,n);
intHeapObj->printfHeap();
intHeapObj->makeHeap();
intHeapObj->printfHeap();
intHeapObj->pushHeap(7);
intHeapObj->printfHeap();
intHeapObj->popHeap();
cout << "The top of heap :" << intHeapObj->getVec().back() << endl;
intHeapObj->getVec().pop_back();
intHeapObj->printfHeap();
intHeapObj->sortHeap();
cout << "Sorted data :";
for (int i = 1;i <= n;++i)
cout << intHeapObj->getVec()[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
delete intHeapObj;
return 0;
}
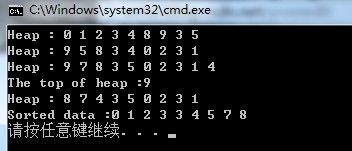
运行环境:Win7 + VS2008.
运行结果: