node.js 接收get请求
Get 请求的相关方法一定在http.ServerRequest下,ServerRequest有data、end、close3个事件,method、url、headers、trailers、httpVersion、connection6个属性,setEncoding、pause、resume3个方法。
url属性下有一段说明描述了怎么解析get请求:
request.url#
Request URL string. This contains only the URL that is present in the actual HTTP request. If the request is:
GET /status?name=ryan HTTP/1.1\r\n
Accept: text/plain\r\n
\r\n Then request.url will be:
'/status?name=ryan' If you would like to parse the URL into its parts, you can use require('url').parse(request.url). Example:
node> require('url').parse('/status?name=ryan')
{ href: '/status?name=ryan',
search: '?name=ryan',
query: 'name=ryan',
pathname: '/status' } If you would like to extract the params from the query string, you can use therequire('querystring').parse function, or pass true as the second argument to require('url').parse. Example:
node> require('url').parse('/status?name=ryan', true)
{ href: '/status?name=ryan',
search: '?name=ryan',
query: { name: 'ryan' },
pathname: '/status' }按照说明试一下吧(node> 表示 在命令行里敲代码)
那就结合 hello world 写一个动态的hello world
var http = require('http');
var server = http.createServer();
server.on('request',function (req, res){
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type': 'text/plain'});
var name = require('url').parse(req.url,true).query.name
res.end('Hello World ' + name);
});
server.listen(1337, "127.0.0.1");
console.log('Server running at http://127.0.0.1:1337/');将以上代码保存到 example3.js文件中,在cmd中敲入node example3.js

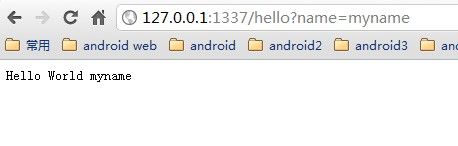
在浏览器地址栏中敲入 http://127.0.0.1:1337/hello?name=myname
挺简单的,下一节讲复杂的post