通过MediaPlayer理解Binder的使用
理解Binder的使用是一件不容易的事,尤其由浅入深,本文参考Android深入浅出之Binder机制和Android Binder设计与实现这两文章为基础,从Java层的MediaPlayer开始分析Client, Server 和ServiceManager!至于Binder的实现可以搜索CSDN老罗的文章,也可以看http://blog.csdn.net/bathinbreeze/article/details/8989431,涉及到kernel这里不讨论,本文只作为分析android代码记忆用
首先,先从JAVA层的mediaplayer类看起
(framework/base/media/java/android/media/MediaPlayer)
在app调用MediaPlayer时,我们是先new 一个Mediaplayer,然后setDataSource,prepare,start
那这些函数在MediaPlayer是怎么实现的呢?我们看看MediaPlayer类
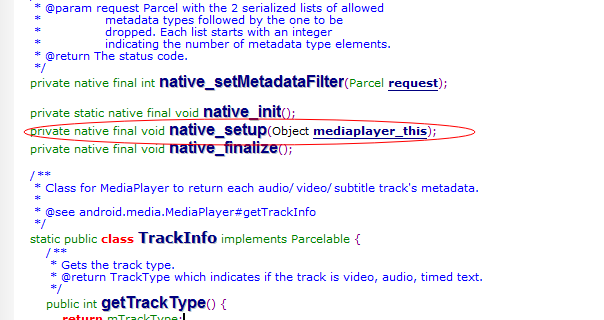
不看hanlder,直接看native_setup
Native_setup是一个jni函数,也就是说mediaplayer的建立不在java层,而setDataSource,start这些函数也一样不在java层
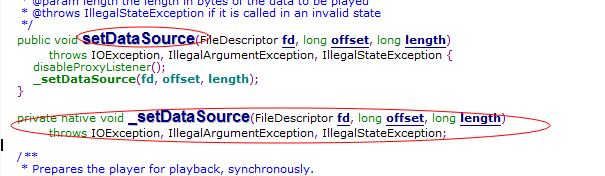
既然这样,我们就必须跑去jni层看看到底mediaplayer是怎么工作的
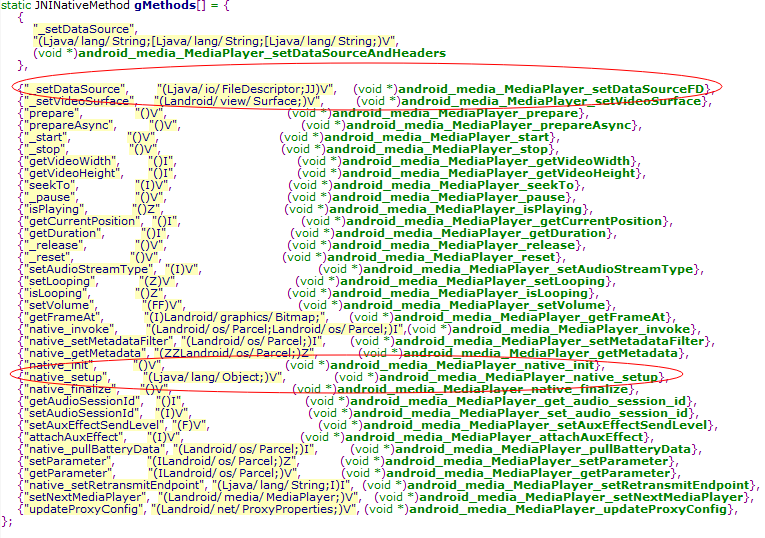
根据mediaplayer的包名,我可以锁定mediaplayer jni的c文件
(framework/base/media/jni/android_media_MediaPlayer.cpp)
在jni层里找到native_setup和setDataSource注册的原型
那看看这两个函数怎么实现
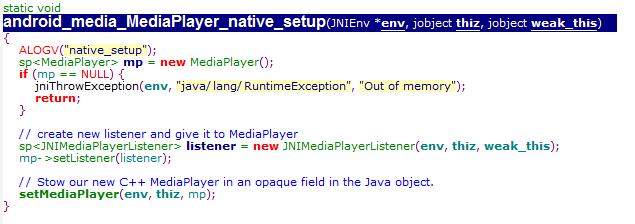
native_setup主要是创建了C++层的MediaPlayer对象
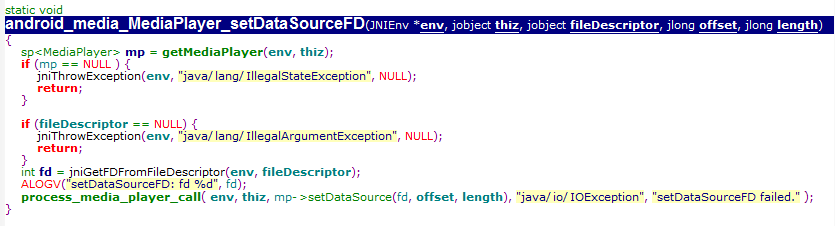
而setDatasource则是通过创建的mediaplayer对象,调用对象的setDataSource
从这里可以看出jni层实际上是通过调用C++的mediaplayer实现java层mediaplayer的功能。
为了进一步了解,我们跟踪到c++的mediaplayer类,同样以初始化和setdatasource为例
(framework/av/media/libmedia/mediaplayer.cpp)
从初始化看,Mediaplayer初始化只是初始化一些变量
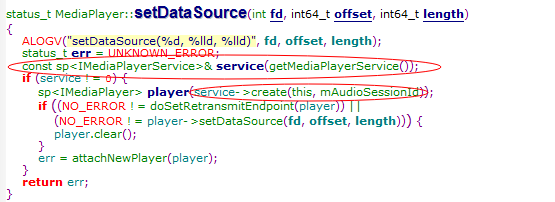
那我们看看setdatasource函数
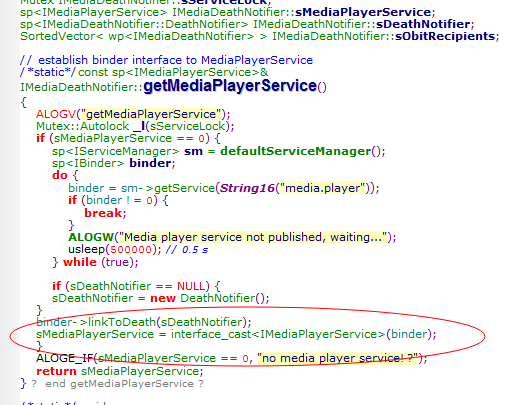
在这里面我们发送好像跟service有关的东西,对了,这就是Mediaplayer的客户端(Mediaplayer类是binder中的client)通过Binder的ServiceManger获取Mediaplayer服务端(MediaPlayerService是binder的 Server)实例,并调用服务端实例的函数!那Mediaplayer服务端在那里,servicemanager又是怎么一回事呢,我们继续往下分析,但这里不采取继续跟踪代码下去,我们先去了解Binder ServiceManager和MediaplayerSerice,从而了解binder的manager和server,然后再回到这边!但是我们要记住有个IServiceManager,IBinder和IMediaPlayerService这些类,等下我们就靠这些把ServiceManager, Mediaplayer Server,
Mediaplayer client贯通起来,从而建立起binder servicemanager,server,client的使用流程
Binder ServiceManager和Mediaplayer Server在系统开机时都被启动。
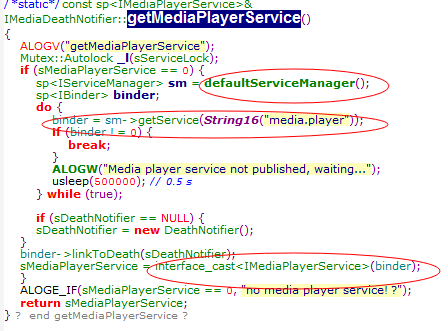
首先我们看看servicemanager
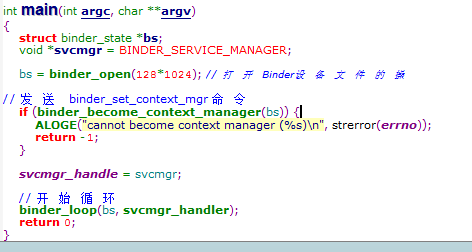
(framework/Native/cmds/ServiceManager/)
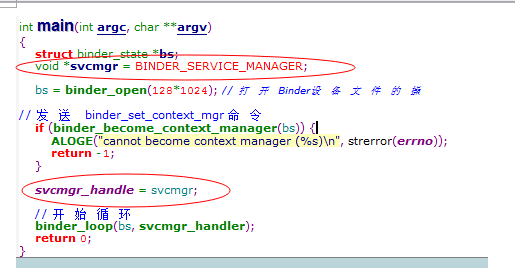
从这里可以看到SeviceManager打开了binder设备,并向binder发送命令,告诉binder成为binder manager,并进入循环。
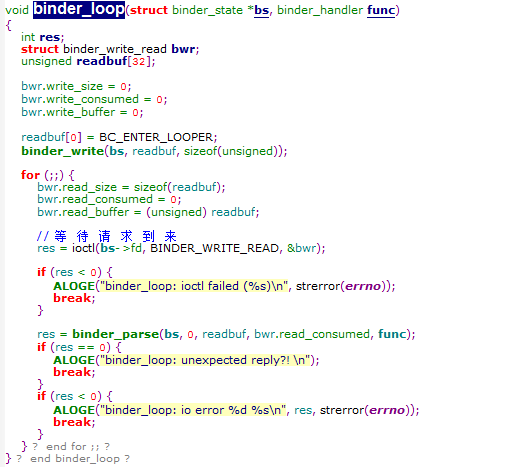
而循环主要是通过控制读取或写入binder设备,等待请求到来,如果有有请求则对所读到的
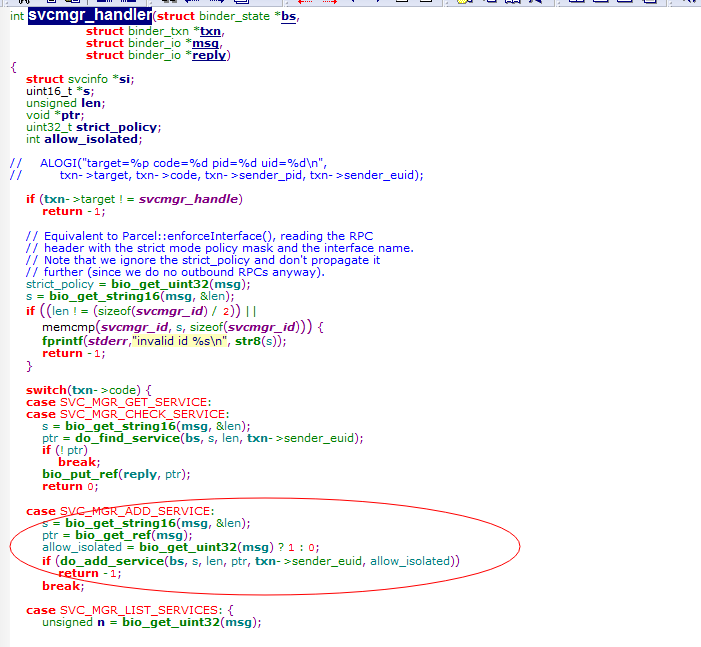
内容进行解析,解析之后回调给svcmgr_handler
从代码binder_transaction_data里面code知,servicemanager分了SVC_MGR_GET_SERVICE,
SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE,SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE,SVC_MGR_LIST_SERVICES,
几个消息
另外从代码中知道, addservice 和getservice都是从 svcinfolist增查,而svcinfo的结构如下
struct svcinfo
{
struct svcinfo *next;
void *ptr; // service pointer
struct binder_death death;
int allow_isolated;
unsigned len;
uint16_t name[0]; // service名字
};增加时,回复成功
而获取service时则需把引用填充如reply,最后发到binder里
而其中要注意的
要知道svcmgr_hanlde被赋值为0,在回调函数,遇到非0的都直接return -1,不做任何操作
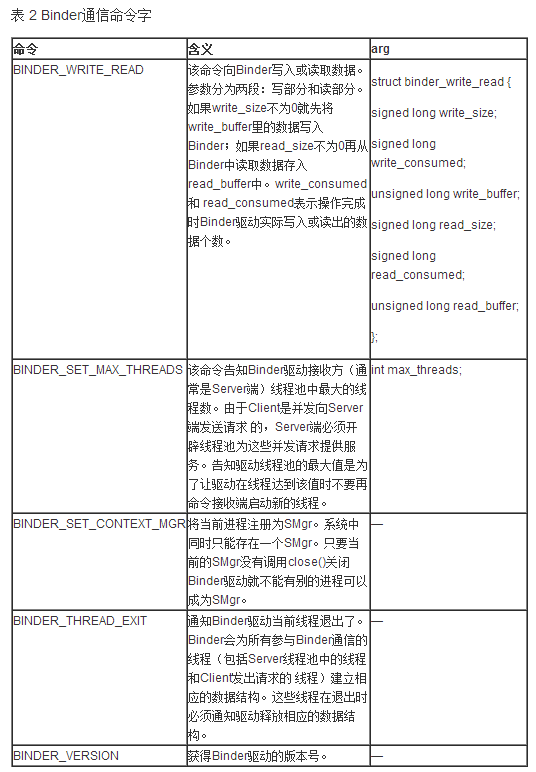
附:
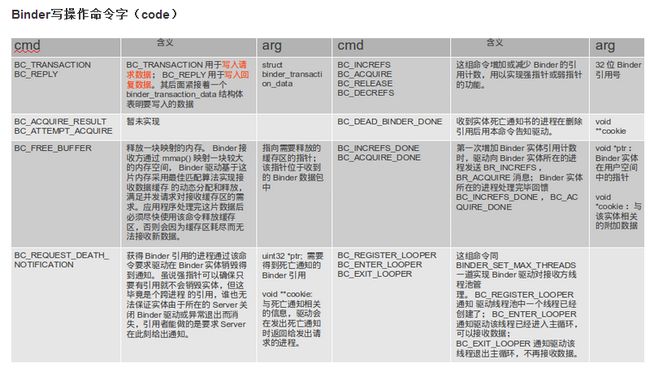
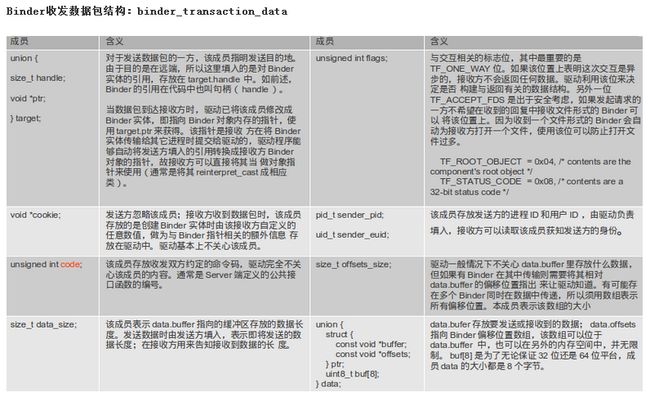
在这些命令中,最常用的是BC_TRANSACTION/BC_REPLY命令对,Binder数据通过这对命令发送给接收方。这对命令所承载的数 据包由结构体struct binder_transaction_data定义。Binder交互有同步和异步之分,利用binder_transaction_data中 flag域区分。如果flag域的TF_ONE_WAY位为1则为异步交互,即Client端发送完请求交互即结束, Server端不再返回BC_REPLY数据包;否则Server会返回BC_REPLY数据包,Client端必须等待接收完该数据包方才完成一次交 互。
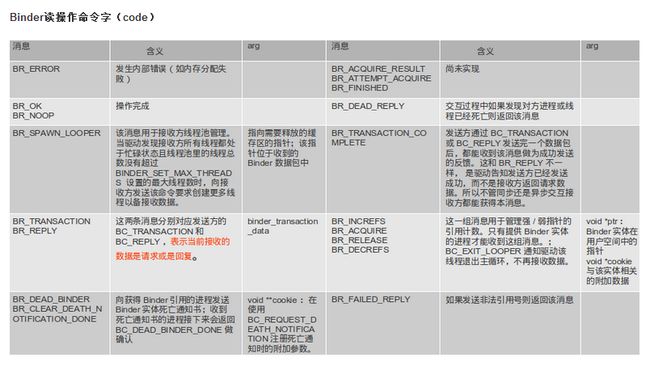
写数据一样,其中最重要的消息是BR_TRANSACTION 或BR_REPLY,表明收到了一个格式为binder_transaction_data的请求数据包(BR_TRANSACTION)或返回数据包 (BR_REPLY)
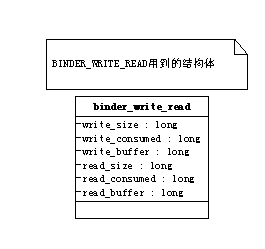
收发都是 消息ID+消息数据(binder_transaction_data)
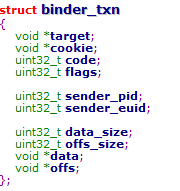
在android代码为数据接口binder_txn
其中其data在android表示为如下
Servicemanager就分析到这里,在这里没发现跟mediaplayer一点有关的东西,那我们去看看Mediaplayer Server
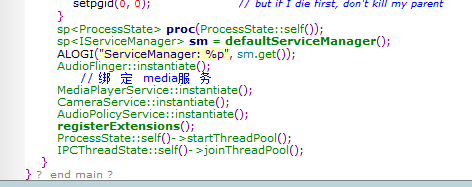
(framework/av/Media/MediaServer/Main_mediaserver.cpp)
在main函数中我们看到,创建了一个proc,获取了servicemanager,并初始化了MediaplayerService,并开启了线程池!在这里我们发现了跟media有关的MediaplayerService,暂时不理会,我们代码从第一个看起!
首先是ProcessState:self()

从代码中我们看出processstate构造函数初始化列表打开了binder设备,并向binder设备发送了两条命令,我们可以说processstate 记录着打开的binder设备,以便提供给后面提供操作。
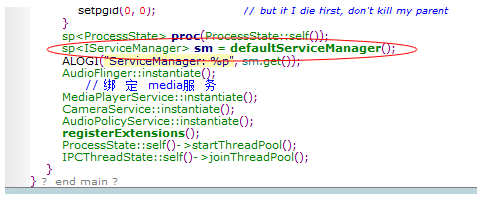
代码的第二步是获取一个servicemanager对象,我们跟踪进去看他是怎么获取的!
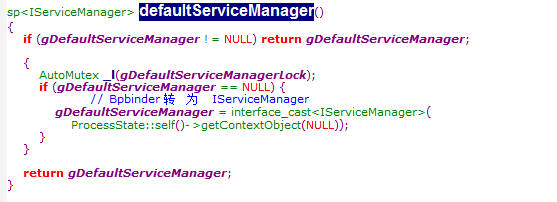
首先通过processstate获取了servicemanager的IBinder对象,并转化为IServiceManager(前面的MediaplayerClient也是这样获取哦),即获取了servicemanager对象
继续跟踪程序,看怎么获取IBinder对象和转化为IServiceManager
1.IBinder对象的获取
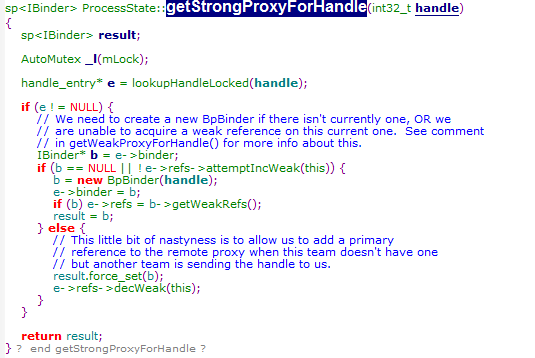
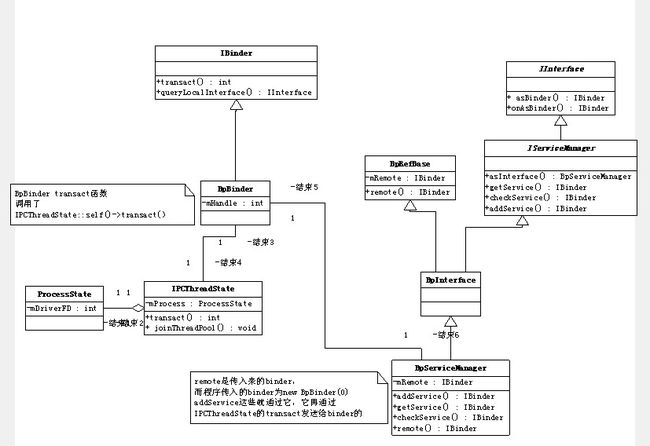
从代码可以看到,IBinder对象的获取实际上是new BpBinder(0);
那BpBinder是什么呢?

BpBinder继承于IBinder,而IBinder实际是ServiceManager抽象出来的接口类,为Server提供接口操作binder,而BpBinder则是IBinder的实现,也可以说代理了Binder的操作( transact等)
2.IBinder转化为IServiceManager
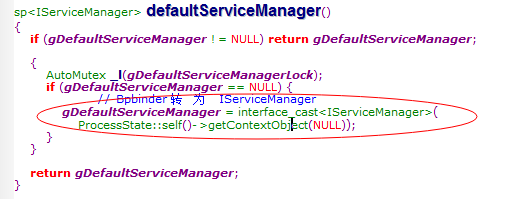
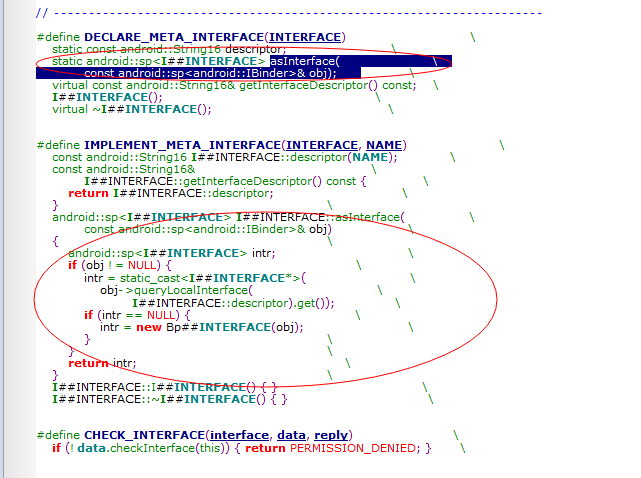
从代码可以看出interface_cast 模版函数把IBinder转化成ISeriviceManager实际上调用的是IServiceManager的asInteface函数,那我跟踪到IServiceManager类看看
在IServiceManager类中没看到asInterface函数哦,但是有个DECLARE_META_INTERFACE的宏,我们往这个走下去,看能找到asInterface不!
果然,asInterface用连接的方式写在了宏里面,那我们看看是怎么转,在前面

我们是传入了IServiceManager.asInterface(new BpBinder(0));
而asInterface把IBinder转化成IserviceManager,确是
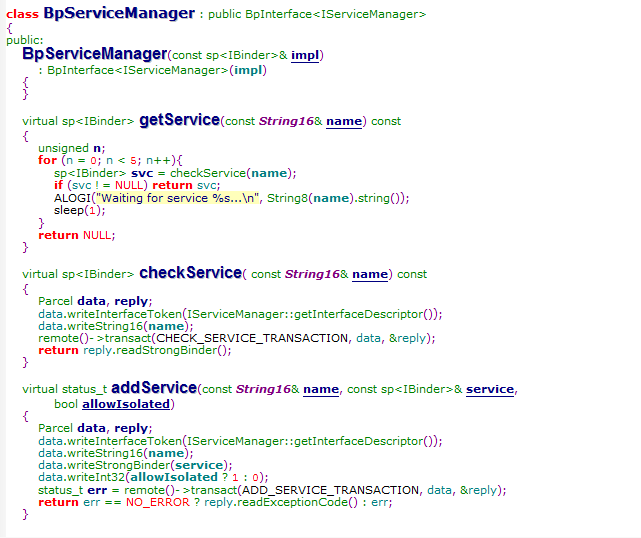
New BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0));也就是把IBinder对象赋予了IServiceManager子类BpServiceManager
而BpServiceManager则是代理了IBinder的操作,
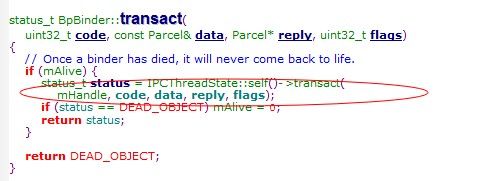
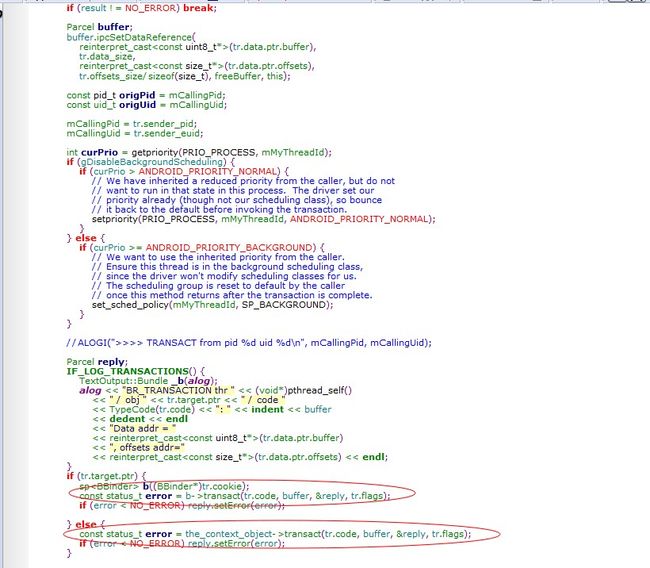
如果addService,调用了BpBinder(IBinder)的transact函数,发送ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION到Binder
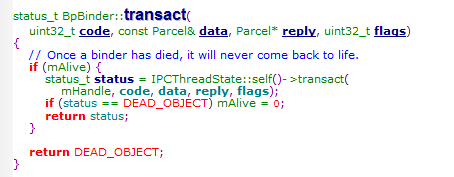
而BpBinder
则通过IPCThreadState:self()的transact发送数据给Binder
ServiceManager已经获得(通过new bpBinder(0),并转化成BpSeriviceManager),
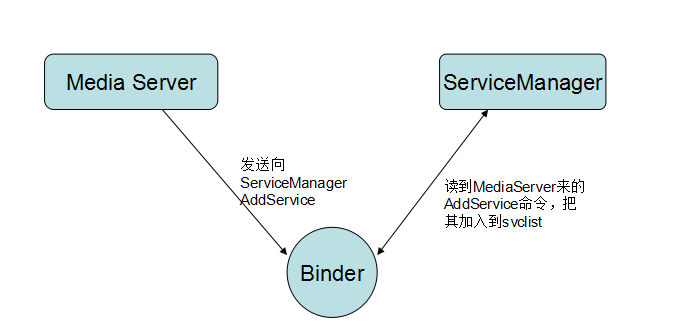
接着MediaplayerService把自己注册到ServiceManager里面
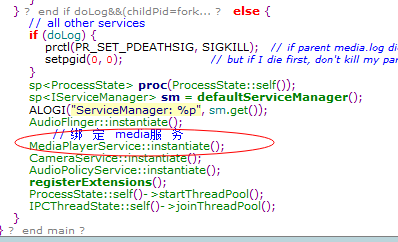
可以看到是调用BpServiceManager的addService(前面说到addService实际上就是通过new BpBinder(0)的transact函数,而BpBinder则是通过IPCThreadState的transact把数据发送给了binder),把自己注册给了ServiceManager,而ServiceManager也把他记录了起来
到这里我们就知道ServiceManager和MediaServer大概工作方式
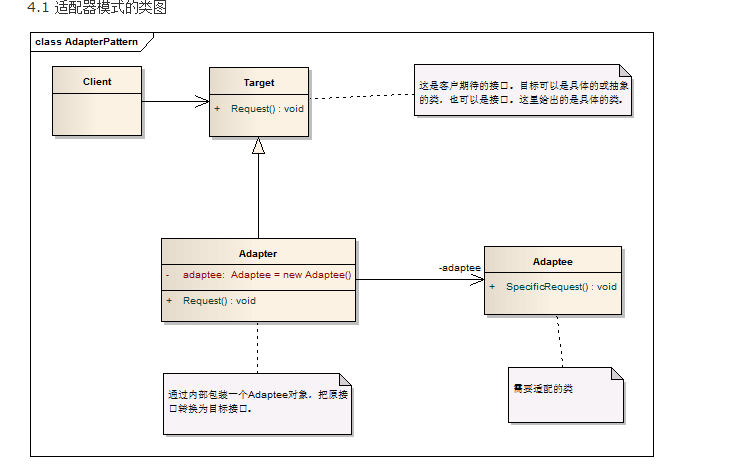
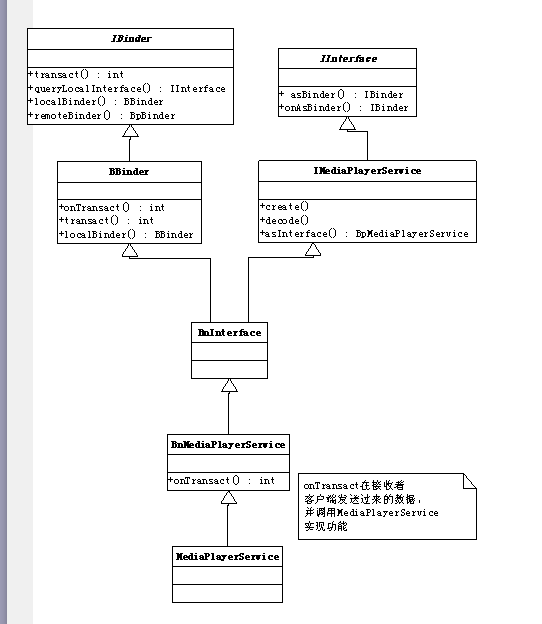
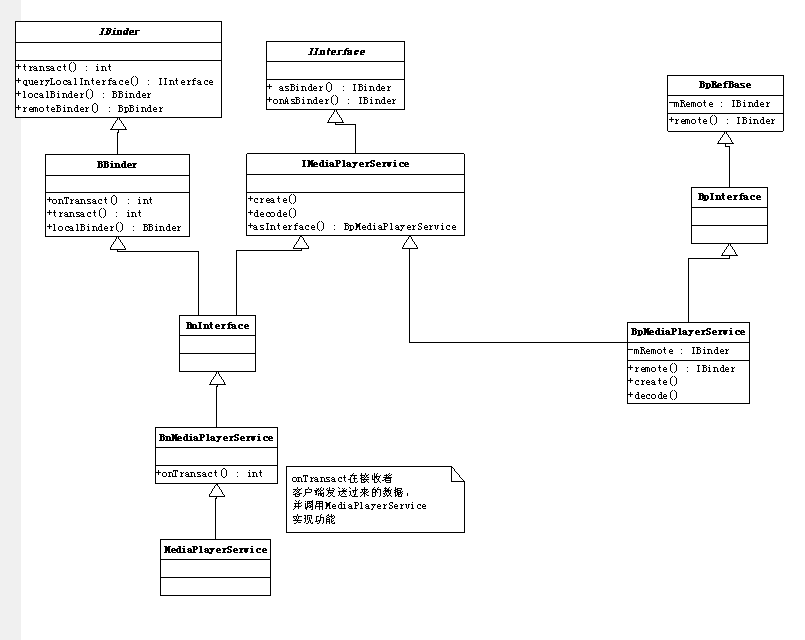
从继承结构可以看出这是一个对象适配器模式,而不是代理模式,因为他们没有共同的父类,更多的是对象的适配,而IBinder和BnBinder,和BpBinder才是代理模式,IServiceManager,BnServiceManager,BpServiceManger也是代理模式
void MediaPlayerService::instantiate() {
defaultServiceManager()->addService(
String16("media.player"), new MediaPlayerService());
}
virtual status_t addService(const String16& name, const sp<IBinder>& service,
bool allowIsolated = false)
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeString16(name);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
data.writeInt32(allowIsolated ? 1 : 0);
status_t err = remote()->transact(ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
return err == NO_ERROR ? reply.readExceptionCode() : err;
}
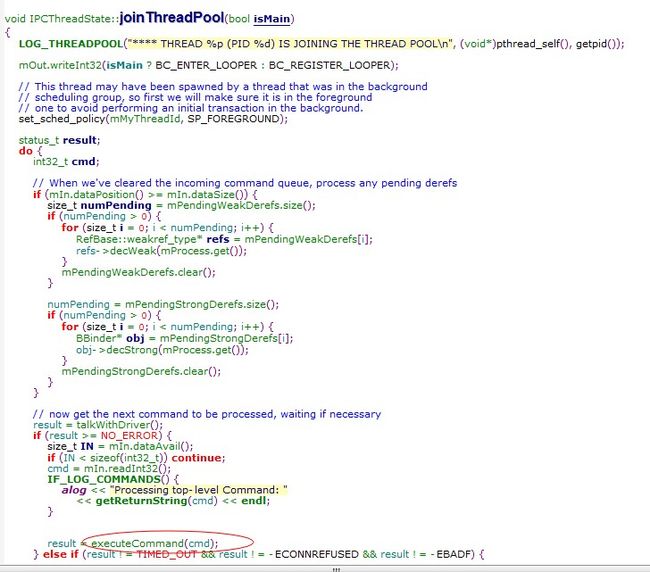
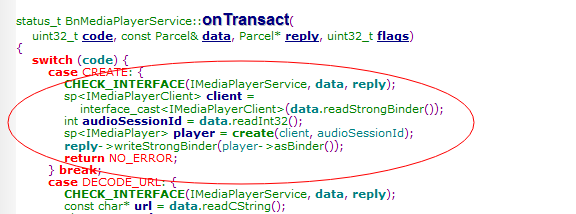
addService把MediaPlayerService传给了ServiceManager,BnMediaPlayerService的onTransact则负责接收实现功能(进程中开启的IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();里面调用BBinder接收信息,而MediaplayerService的父类BnMediaPlayerService则实现接收信息处理onTransact)
同时也开放了代理类,让客户端调用。
根据服务端,我们再回头看看 Media Client端,他是怎么通过ServiceManager跟MediaServer进行通讯的
代码中,先获取了Mediaplayer server,跟踪进去看看做了什么

首先获取了serviceManager,这个是media server是一样的!
然后通过获取到的serviceManager的getService函数获取到mediaplayer server,getService其实跟addService是一样的,但是我们为了清楚,跟踪进去看看
打开BpManagerService类,
getService函数,实际上就是根据名字向binder发送CHECK_SERVICE_TRANSACTION命令,从而让serviceManager回应获取到Mediaplayer server
我们到ServiceManger那边看看他怎么解析这些数据,并返回了什么
int svcmgr_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_txn *txn,
struct binder_io *msg, /** 是data */
struct binder_io *reply)
{
struct svcinfo *si;
uint16_t *s;
unsigned len;
void *ptr;
uint32_t strict_policy;
int allow_isolated;
// ALOGI("target=%p code=%d pid=%d uid=%d\n",
// txn->target, txn->code, txn->sender_pid, txn->sender_euid);
if (txn->target != svcmgr_handle)
return -1;
// Equivalent to Parcel::enforceInterface(), reading the RPC
// header with the strict mode policy mask and the interface name.
// Note that we ignore the strict_policy and don't propagate it
// further (since we do no outbound RPCs anyway).
strict_policy = bio_get_uint32(msg);
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
if ((len != (sizeof(svcmgr_id) / 2)) ||
memcmp(svcmgr_id, s, sizeof(svcmgr_id))) {
fprintf(stderr,"invalid id %s\n", str8(s));
return -1;
}
switch(txn->code) {
case SVC_MGR_GET_SERVICE:
case SVC_MGR_CHECK_SERVICE:
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
ptr = do_find_service(bs, s, len, txn->sender_euid);
if (!ptr)
break;
// 如果找到则填充ptr入reply
bio_put_ref(reply, ptr);
return 0;
.....
}
}
从代码看出是通过do_find_service找出Media.Player
void *do_find_service(struct binder_state *bs, uint16_t *s, unsigned len, unsigned uid)
{
struct svcinfo *si;
si = find_svc(s, len);
// ALOGI("check_service('%s') ptr = %p\n", str8(s), si ? si->ptr : 0);
if (si && si->ptr) {
if (!si->allow_isolated) {
// If this service doesn't allow access from isolated processes,
// then check the uid to see if it is isolated.
unsigned appid = uid % AID_USER;
if (appid >= AID_ISOLATED_START && appid <= AID_ISOLATED_END) {
return 0;
}
}
return si->ptr;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
看到返回的是SVCINFO的ptr,而这个就是MediaplayserService被写成flat_binder_object对象的引用
bio_put_ref(reply, ptr);
void bio_put_ref(struct binder_io *bio, void *ptr)
{
struct binder_object *obj;
if (ptr)
obj = bio_alloc_obj(bio);
else
obj = bio_alloc(bio, sizeof(*obj));
if (!obj)
return;
obj->flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
obj->type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
obj->pointer = ptr;
obj->cookie = 0;
}
把flat_binder_object赋值给了binder_object,通过Binder发回给MediaClient
MediaClient(BpMediaPlayerService)则
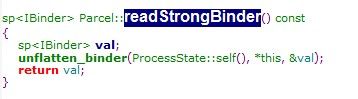
sp<IBinder> Parcel::readStrongBinder() const
{
sp<IBinder> val;
unflatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), *this, &val);
return val;
}
解出里面的Binder(MediaPlayerService)
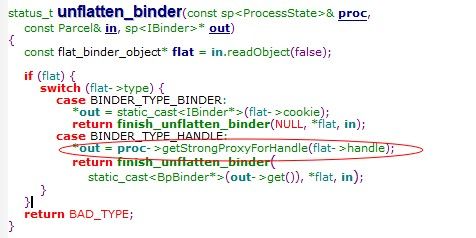
在ServiceManager那边返回的flat->type都为handle,所以获取Binder也是
通过*out = proc->getStrongProxyForHandle(flat->handle); 只不过这里的handler不是为0
相当于new BpBinder(flat->handle);
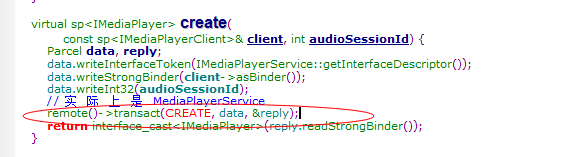
这样MediaClient获取获取到了mediaserver的对象,但获取到是binder对象,还需要转化成IMediaPlayerService这样,MediaClient才能跟MediaServer对话
从代码看出binder对象转化成了BpMediaPlayerService( new BpMediaPlayerService(binder))
我们看看BpMediaPlayerService

BpMediaPlayerService跟BpServiceManager类似,代理了binder和mediaplayerservice的之间交互。
此时这里的mHandle不为0哦
用MediaPlayer Server的binder(MediaplayerService)发送 create命令,而MediaPlayerService(MediaPlayerService继承BnMediaPlayerService继承BBinder继承IBinder)接收到create命令后
在BR_TRANSACTION回调给MediaplayerService(BPBinder)
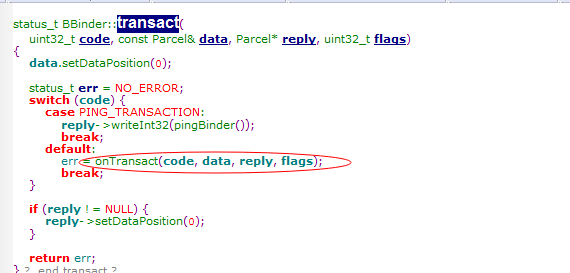
创建了Mediaplayer的client
其他Mediaplayer client start,sotp等函数都类似!
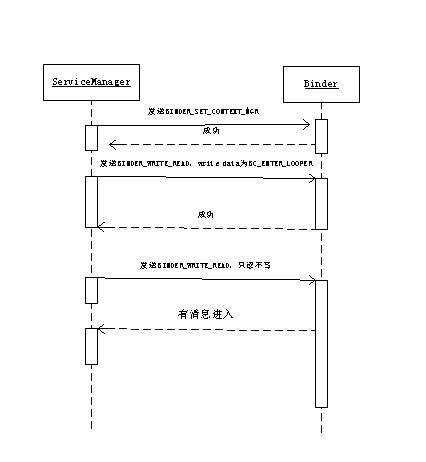
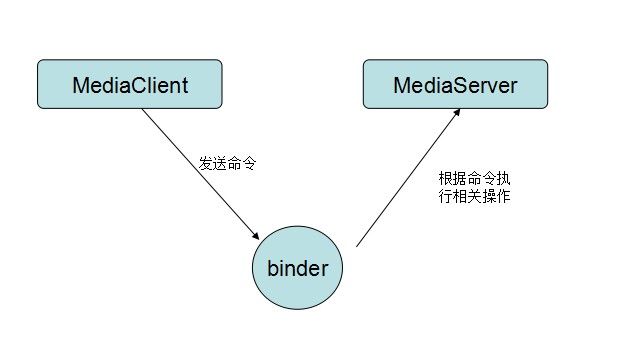
最后总结下binder 的server client servicemanager模式
第一步:通过binder向servicemanager注册自己的service
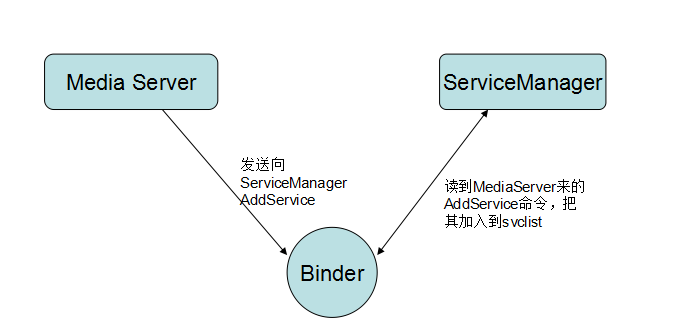
第二步:client通过servicemanager获取server
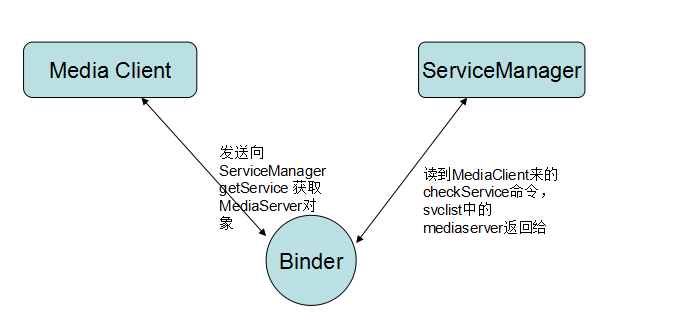
第三步:获取到server后,client通过binder跟sserver进行通讯