matplotlib绘制三维图形mplot3d(包含Mayavi.mlab模块)
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/40008005
Matplotlib mplot3d 工具包简介
The mplot3d toolkit adds simple 3D plotting capabilities to matplotlib by supplying an axes object that can create a 2D projection of a 3D scene. The resulting graph will have the same look and feel as regular 2D plots.
创建Axes3D对象
An Axes3D object is created just like any other axes using the projection=‘3d’ keyword. Create a new matplotlib.figure.Figure and add a new axes to it of type Axes3D:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=’3d’)
New in version 1.0.0: This approach is the preferred method of creating a 3D axes.
Note: Prior to version 1.0.0, the method of creating a 3D axes was di erent. For those using older versions of matplotlib, change ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=’3d’) to ax = Axes3D(fig).
要注意的地方
Axes3D展示三维图形时,其初始视图中x,y轴与我们一般看的视图(自己画的时候的视图)是反转的,matlab也是一样。
可以通过设置初始视图来改变角度:ax.view_init(30, 35)Note: 不过这样图形可能会因为旋转而有阴影,也可以通过代码中XY轴互换来实现视图中XY互换。不知道有没有其它方法,如matlab中就有surf(x,y,z);set(gca,'xdir','reverse','ydir','reverse')这样命令来实现这个功能[关于matlab三维图坐标轴原点位置的问题]。
lz总结绘制三维图形一般流程
创建Axes3D对象
fig = plt.figure() ax = Axes3D(fig)再进行坐标范围设定什么的(可选)
# 计算坐标极限值 xs = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable([xi[0] for xi in x])) x_max, x_min = max(xs), min(xs) ys = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable([xi[1] for xi in x])) y_max, y_min = max(ys), min(ys) zs = list(itertools.chain.from_iterable([xi[2] for xi in x])) z_max, z_min = max(zs), min(zs) margin = 0.1
再进行绘制,如
plt.scatter(x_new[0], x_new[1], c='r', marker='*', s=50, label='new x')再进行一些坐标什么的设置ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs, c=c, marker=marker, s=50, label=label)ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, label='Discrimination Interface')
# 设置图形展示效果 ax.set_xlim(x_min - margin, x_max + margin) ax.set_ylim(y_min - margin, y_max + margin) ax.set_zlim(z_min - margin, z_max + margin) ax.set_xlabel('x') ax.set_ylabel('y') ax.set_zlabel('z') ax.legend(loc='lower right') ax.set_title('Plot of class0 vs. class1') ax.view_init(30, 35)最后显示出来
plt.show()
皮皮blog
绘制不同三维图形
Line plots线图
Scatter plots散点图
Axes3D.scatter(xs, ys, zs=0, zdir=u'z', s=20, c=u'b', depthshade=True, *args, **kwargs)
Create a scatter plot
-
Keyword arguments are passed on to scatter().Argument Description xs, ys Positions of data points. zs Either an array of the same length as xs andys or a single value to place all points inthe same plane. Default is 0. zdir Which direction to use as z (‘x’, ‘y’ or ‘z’)when plotting a 2D set. s size in points^2. It is a scalar or an array of thesame length as x andy. c a color. c can be a single color format string, or asequence of color specifications of lengthN, or asequence ofN numbers to be mapped to colors using thecmap andnorm specified via kwargs (see below). Notethatc should not be a single numeric RGB or RGBAsequence because that is indistinguishable from an arrayof values to be colormapped.c can be a 2-D array inwhich the rows are RGB or RGBA, however. depthshade Whether or not to shade the scatter markers to givethe appearance of depth. Default isTrue. - Returns a Patch3DCollection
-
Note: scatter (
x,
y,
s=20,
c=u'b',
marker=u'o',
cmap=None,
norm=None,
vmin=None,
vmax=None,
alpha=None,
linewidths=None,
verts=None,
**kwargs )

Wireframe plots线框图
Surface plots曲面图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
X = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-4, 4, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=plt.cm.hot)
ax.contourf(X, Y, Z, zdir='z', offset=-2, cmap=plt.cm.hot)
ax.set_zlim(-2,2)
# savefig('../figures/plot3d_ex.png',dpi=48)
plt.show()结果图形输出:
[Matplotlib tutorial - 3D Plots]
皮皮blog
Tri-Surface plots三面图
Contour plots等高线图
Filled contour plots填充等高线图
Polygon plots多边形图
Axes3D.add_collection3d(col, zs=0, zdir=u'z')
Add a 3D collection object to the plot.
2D collection types are converted to a 3D version bymodifying the object and adding z coordinate information.
Supported are:
-
-
- PolyCollection
- LineColleciton
- PatchCollection
-
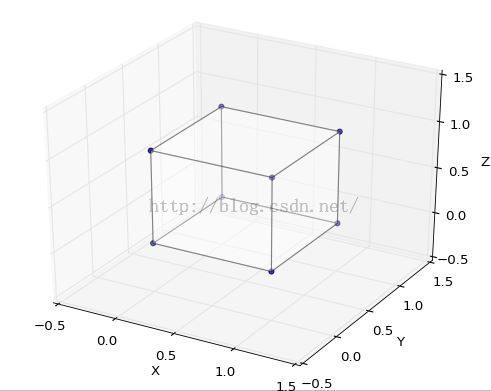
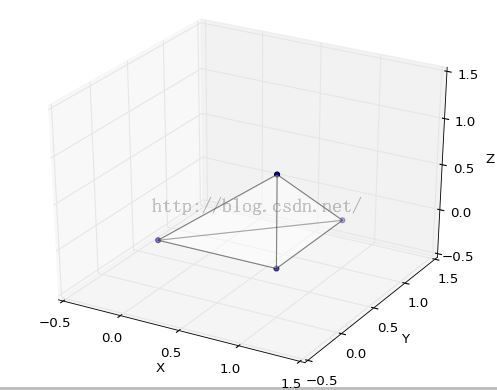
绘制正方体和四面体示例
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
__title__ = ''
__author__ = '皮'
__mtime__ = '9/27/2015-027'
__email__ = '[email protected]'
"""
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d import Poly3DCollection
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.gca(projection='3d')
# 正文体顶点和面
verts = [(0, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 1, 1), (1, 1, 1), (1, 0, 1)]
faces = [[0, 1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7], [0, 1, 5, 4], [1, 2, 6, 5], [2, 3, 7, 6], [0, 3, 7, 4]]
# 四面体顶点和面
# verts = [(0, 0, 0), (1, 0, 0), (1, 1, 0), (1, 0, 1)]
# faces = [[0, 1, 2], [0, 1, 3], [0, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]
# 获得每个面的顶点
poly3d = [[verts[vert_id] for vert_id in face] for face in faces]
# print(poly3d)
# 绘制顶点
x, y, z = zip(*verts)
ax.scatter(x, y, z)
# 绘制多边形面
ax.add_collection3d(Poly3DCollection(poly3d, facecolors='w', linewidths=1, alpha=0.3))
# ax.add_collection3d(Line3DCollection(poly3d, colors='k', linewidths=0.5, linestyles=':'))
# 设置图形坐标范围ax.set_xlabel('X')ax.set_xlim3d(-0.5, 1.5)ax.set_ylabel('Y')ax.set_ylim3d(-0.5, 1.5)ax.set_zlabel('Z')ax.set_zlim3d(-0.5, 1.5)plt.show()
皮皮blog
绘制结果截图
[Transparency for Poly3DCollection plot in matplotlib]
Bar plots条形图
2D plots in 3D三维图中的二维图
Text文本图
Subplotting子图
matplotlib绘制平行z轴的平面(垂直xy平面的平面)
方程:0*Z + A[0]X + A[1]Y + A[-1] = 0
X = np.arange(x_min - margin, x_max + margin, 0.05) Z = np.arange(z_min - margin, z_max + margin, 0.05) X, Z = np.meshgrid(X, Z) Y = -1 / A[1] * (A[0] * X + A[-1]) ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, label='Discrimination Interface')
皮皮blog
Mayavi的mlab模块绘制3D曲面
NumPy快速产生能进行广播运算的数组的ogrid对象
>>> x,y = np.ogrid[:5,:5]
>>> x
array([[0], [1], [2], [3], [4]])
>>> y
array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]])
ogrid是一个很有趣的对象,它和多维数组一样,用切片元组作为下标,返回的是一组可以用来广播计算的数组。其切片下标有两种形式:
-
开始值:结束值:步长,和“np.arange(开始值, 结束值, 步长)”类似
-
开始值:结束值:长度j,当第三个参数为虚数时,它表示所返回的数组的长度,和“np.linspace(开始值, 结束值, 长度)”类似:
>>> x, y = np.ogrid[:1:4j, :1:3j] >>> x array([[ 0. ], [ 0.33333333], [ 0.66666667], [ 1. ]]) >>> y array([[ 0. , 0.5, 1. ]])
利用ogrid的返回值,我们能很容易计算二元函数在等间距网格上的值。
绘制三维曲面![]()
02-numpy/numpy_ogrid_mlab.py
用ogird产生二维坐标网格,计算三维空间的曲面
import numpy as np
from enthought.mayavi import mlab
x, y = np.ogrid[-2:2:20j, -2:2:20j]
z = x * np.exp( - x**2 - y**2)
pl = mlab.surf(x, y, z, warp_scale="auto")
mlab.axes(xlabel='x', ylabel='y', zlabel='z')
mlab.outline(pl)
mlab.show()
此程序使用Mayavi的mlab模块快速绘制如【图:使用ogrid创建的三维曲面】所示的3D曲面,关于Mayavi的相关内容将在今后的章节进行介绍。
如果已经有了多个表示不同轴上的取值的一维数组。想计算出它们所构成的网格上的每点的函数值,可以使用ix_():
>>> x = np.array([0, 1, 4, 10])
>>> y = np.array([2, 3, 8])
>>> gy, gx = np.ix_(y, x)
>>> gx
array([[ 0, 1, 4, 10]])
>>> gy
array([[2], [3], [8]])
>>> gx+gy # 广播运算
array([[ 2, 3, 6, 12],
[ 3, 4, 7, 13],
[ 8, 9, 12, 18]])
在上面的例子中,通过ix_()将数组x和y转换成能进行广播运算的二维数组。注意数组y对应广播运算结果中的第0轴,而数组x与第1轴对应。
[ numpy教程- 通用函数ufunc]from:http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/40008005
ref:mplot3d tutorial(inside source code)
mplot3d API