块设备驱动之NOR FLASH驱动
转载请注明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/ruoyunliufeng/article/details/25240947
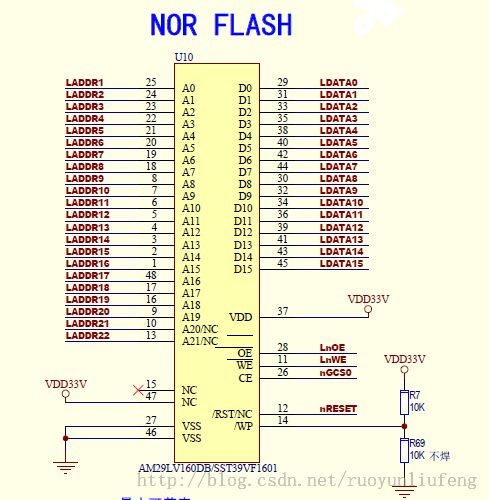
一.硬件原理
从原理图中我们能看到NOR FLASH有地址线,有数据线,能向内存一样读,不能向内存一样写(要发出某些命令)。这也使得NOR的数据非常可靠,所以一般用来存储bootloader。当然现在手机上都只有nand flash了,节约成本嘛。下节我会带大家去分析nand flash驱动,并进行总结。
二.驱动程序
/*
* 参考 drivers\mtd\maps\physmap.c
*/
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/mtd/mtd.h>
#include <linux/mtd/map.h>
#include <linux/mtd/partitions.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
static struct map_info *s3c_nor_map;
static struct mtd_info *s3c_nor_mtd;
/*分区数组*/
static struct mtd_partition s3c_nor_parts[] = {
[0] = {
.name = "bootloader_nor",
.size = 0x00040000,
.offset = 0,
},
[1] = {
.name = "root_nor",
.offset = MTDPART_OFS_APPEND, //紧接着上一个
.size = MTDPART_SIZ_FULL, //到最后
}
};
static int s3c_nor_init(void) //入口函数
{
/* 1. 分配map_info结构体 */
s3c_nor_map = kzalloc(sizeof(struct map_info), GFP_KERNEL);;
/* 2. 设置: 物理基地址(phys), 大小(size), 位宽(bankwidth), 虚拟基地址(virt) */
s3c_nor_map->name = "s3c_nor";
s3c_nor_map->phys = 0; //物理地址
s3c_nor_map->size = 0x1000000; /* >= NOR的真正大小 */
s3c_nor_map->bankwidth = 2; //位宽
s3c_nor_map->virt = ioremap(s3c_nor_map->phys, s3c_nor_map->size); //虚拟地址
simple_map_init(s3c_nor_map); //简单初始化
/* 3. 使用: 调用NOR FLASH协议层提供的函数来识别 */
printk("use cfi_probe\n");
s3c_nor_mtd = do_map_probe("cfi_probe", s3c_nor_map);
/*如果没识别就用jedec*/
if (!s3c_nor_mtd)
{
printk("use jedec_probe\n");
s3c_nor_mtd = do_map_probe("jedec_probe", s3c_nor_map);
}
/*如果仍然没事别就释放掉,返回错误*/
if (!s3c_nor_mtd)
{
iounmap(s3c_nor_map->virt);
kfree(s3c_nor_map);
return -EIO;
}
/* 4. add_mtd_partitions (添加分区)*/
add_mtd_partitions(s3c_nor_mtd, s3c_nor_parts, 2);
return 0;
}
static void s3c_nor_exit(void) //出口函数
{
del_mtd_partitions(s3c_nor_mtd);
iounmap(s3c_nor_map->virt);
kfree(s3c_nor_map);
}
module_init(s3c_nor_init);
module_exit(s3c_nor_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
三.驱动分析
1. 分配map_info结构体
2. 设置: 物理基地址(phys), 大小(size), 位宽(bankwidth), 虚拟基地址(virt)
3. 使用: 调用NOR FLASH协议层提供的函数来识别
4. add_mtd_partitions (添加分区)
其实我们的这个驱动,主要把硬件上的差异性写出来就可以了,大部分的工作内核已经帮我们做了。现在我主要来分析第三步。cfi和jedec,这里主要分析cfi
/*NOR FLASH识别过程*/
do_map_probe("cfi_probe", s3c_nor_map);
drv = get_mtd_chip_driver(name)
ret = drv->probe(map); // cfi_probe.c
cfi_probe
mtd_do_chip_probe(map, &cfi_chip_probe);
cfi = genprobe_ident_chips(map, cp);
genprobe_new_chip(map, cp, &cfi)
cp->probe_chip(map, 0, NULL, cfi)
cfi_probe_chip
// 进入CFI模式
cfi_send_gen_cmd(0x98, 0x55, base, map, cfi, cfi->device_type, NULL);
// 看是否能读出"QRY"
qry_present(map,base,cfi)
我们进行的操作其实在协议层已经帮我们写好了,我们需要提供的其实就是硬件上的差异。因为所有的nor都是支持这套协议的。
参考:韦东山视频第二期