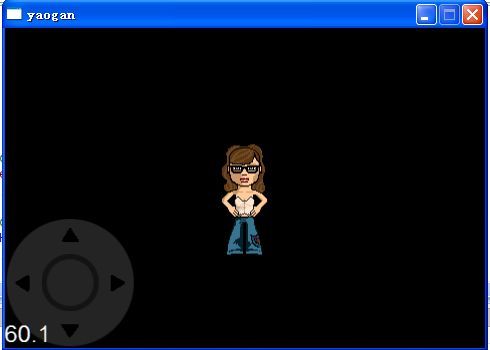
【Cocos2d-x】新手自学(三)虚拟屏幕摇杆,控制精灵移动
这个只是点我是读了 老G的博客,其中有一个游戏例子就是<是男人就坚持20秒>这标题引人遐想啊~
下面是老G的博客,里面有很多不错的例子...大家多关注啦
“老G的小屋” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://4137613.blog.51cto.com/4127613/757254
图中左下角为摇杆,本例子中用于控制小人这张图片的移动
我是直接修改HelloWorld例子,所以代码分几个步骤:
1.在HelloWorld类中添加需要的函数和成员变量,代码如下:
using namespace cocos2d;
class HelloWorld : public CCLayer
{
public:
virtual bool init();
static cocos2d::CCScene* scene();
//触摸相关的处理函数
virtual void ccTouchesBegan(CCSet *pTouches, CCEvent *pEvent);
virtual void ccTouchesMoved(CCSet *pTouches, CCEvent *pEvent);
virtual void ccTouchesEnded(CCSet *pTouches, CCEvent *pEvent);
void moveing(ccTime dt);//移动逻辑
private:
CCPoint centre;
CCSprite *yg2;//摇杆小圆圈,在类中创建是因为其他函数还会用到,不像背景只需要初始化加载就行
float radius;
//精灵相关
CCSprite * jl;
float speedX;
float speedY;
bool isMove;
LAYER_NODE_FUNC(HelloWorld);
};
代码中有许多陌生的类型(类即类型)这个就需要大家多看,不看几次是不会懂的,给出一个连接,官方的API结构说明,虽然是英文的,用翻译软件理解的大概也不错,以后用多了自然就懂了
http://www.cocos2d-x.org/embedded/cocos2d-x/classes.html
2.实现初始化函数...代码如下:
bool HelloWorld::init()
{
bool bRet = false;
do
{
CC_BREAK_IF(! CCLayer::init());
CCSize s = CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getWinSize();//获得屏幕大小,保持到s中
CCSprite *yg1 = CCSprite::spriteWithFile("yg1.png");//加载摇杆背景图
yg1->setOpacity(190); //设置透明度
yg1->setAnchorPoint(ccp(0,0)); //设置锚点位置
yg1->setPosition(ccp(0,0)); //设置显示位置
radius = yg1->getContentSize().width/2; //计算半径
centre = ccp(radius,radius); //计算中心
this->addChild(yg1,1); //添加到场景中
yg2 = CCSprite::spriteWithFile("yg2.png");//加载摇杆小圈
yg2->setPosition(ccp(centre.x, centre.y));
this->addChild(yg2,2);
jl = CCSprite::spriteWithFile("jl.png");//加载需要被控制的图片...叫精灵好听一些
CC_BREAK_IF(!jl);
jl->setPosition(ccp(s.width/2, s.height/2));
this->addChild(jl,1);
this->setIsTouchEnabled(true); //开启触摸,不开的话点击屏幕是没用的
this->schedule(schedule_selector(HelloWorld::moveing));//这句理解为开启逻辑吧,这里的逻辑是处理精灵的移动
bRet = true;
} while (0);
return bRet;
}
3.实现触摸逻辑:
//触摸开始..也就是点击屏幕
void HelloWorld::ccTouchesBegan(CCSet *pTouches, CCEvent *pEvent)
{
CCTouch *touch = (CCTouch*)pTouches->anyObject();
CCPoint location = touch->locationInView(touch->view());
CCPoint convertedLocation = CCDirector::sharedDirector()->convertToGL(location);
CCRect rect=yg2->boundingBox();
if (CCRect::CCRectContainsPoint(rect,convertedLocation))//判断触摸的范围。如果是在摇杆内的话,才响应
{
isMove=true;
}
}
//触摸移动的处理...也就是按下后再移动
void HelloWorld::ccTouchesMoved(CCSet *pTouches, CCEvent *pEvent)
{
CCTouch *touch = (CCTouch*)pTouches->anyObject();
CCPoint location = touch->locationInView(touch->view());
CCPoint convertedLocation = CCDirector::sharedDirector()->convertToGL(location);
bool inRange=pow(centre.x-convertedLocation.x,2)+pow(centre.y-convertedLocation.y,2)<pow(radius,2);
if(isMove&&inRange)
{
CCPoint position=jl->getPosition();
yg2->setPosition(convertedLocation);
float radius1=radius*2/6;//十字键中心区的内切圆半径
float side=radius*2/3;//九宫格中一个格子的边长
//我们使用海伦公式来计算面积,进而判断十字键中心区的精确方向
//向上
if(triangleContainPoint(centre.x,centre.y,centre.x-radius1,centre.y+radius1,centre.x+radius1,centre.y+radius1,convertedLocation.x,convertedLocation.y)
||CCRect::CCRectContainsPoint(CCRectMake(centre.x-radius1,centre.y+radius1,side,side),convertedLocation))
{
speedX=0;
speedY=1;
}
//向下
else if(triangleContainPoint(centre.x,centre.y,centre.x-radius1,centre.y-radius1,centre.x+radius1,centre.y-radius1,convertedLocation.x,convertedLocation.y)
||CCRect::CCRectContainsPoint(CCRectMake(centre.x-radius1,centre.y-radius1-side,side,side),convertedLocation))
{
speedX=0;
speedY=-1;
}
//向左
else if(triangleContainPoint(centre.x,centre.y,centre.x-radius1,centre.y+radius1,centre.x-radius1,centre.y-radius1,convertedLocation.x,convertedLocation.y)
||CCRect::CCRectContainsPoint(CCRectMake(centre.x-radius1-side,centre.y-radius1,side,side),convertedLocation))
{
speedX=-1;
speedY=0;
}
//向右
else if (triangleContainPoint(centre.x,centre.y,centre.x+radius1,centre.y+radius1,centre.x+radius1,centre.y-radius1,convertedLocation.x,convertedLocation.y)
||CCRect::CCRectContainsPoint(CCRectMake(centre.x+radius1+side,centre.y-radius1,side,side),convertedLocation))
{
speedX=1;
speedY=0;
}
//右上
else if(convertedLocation.x-centre.x>0&&convertedLocation.y-centre.y>0)
{
speedX=0.7f;
speedY=0.7f;
}
//左上
else if (convertedLocation.x-centre.x<0&&convertedLocation.y-centre.y>0)
{
speedX=-0.7f;
speedY=0.7f;
}
//左下
else if (convertedLocation.x-centre.x<0&&convertedLocation.y-centre.y<0)
{
speedX=-0.7f;
speedY=-0.7f;
}
//右下
else if (convertedLocation.x-centre.x>0&&convertedLocation.y-centre.y<0)
{
speedX=0.7f;
speedY=-0.7f;
}
}
}
//触摸结束..也就是松开后的处理
void HelloWorld::ccTouchesEnded(CCSet *pTouches, CCEvent *pEvent)
{
isMove=false; //关闭移动逻辑
yg2->setPosition(centre);//把摇杆小圈初始化为中心
speedX=speedY=0;
}
4.触摸中使用的海伦公式用到了两个函数,得自己写上,记得放在触摸处理之前,或是声明一下,不然找不到函数:
float heronsformula(float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2,float x3,float y3)
{
float a=sqrt(pow(x1-x2,2)+pow(y1-y2,2));
float b=sqrt(pow(x2-x3,2)+pow(y2-y3,2));
float c=sqrt(pow(x3-x1,2)+pow(y3-y1,2));
float s=(a+b+c)/2;
return sqrt(s*(s-a)*(s-b)*(s-c));
}
bool triangleContainPoint(float x1,float y1,float x2,float y2,float x3,float y3,float px,float py)
{
float s1=heronsformula(x1,y1,x2,y2,px,py);
float s2=heronsformula(x2,y2,x3,y3,px,py);
float s3=heronsformula(x3,y3,x1,y1,px,py);
float s=heronsformula(x1,y1,x2,y2,x3,y3);
return abs(s-(s1+s2+s3))<0.001f;
}
5.完成精灵的移动逻辑函数:
//移动逻辑的处理函数
void HelloWorld::moveing(ccTime dt)
{
if (isMove&&(speedX!=0||speedY!=0))
{
CCPoint position=ccp(jl->getPosition().x+speedX,jl->getPosition().y+speedY);
CCSize size=CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getWinSize();
CCRect rect=CCRectMake(0,0,size.width,size.height); //创建一个逻辑矩形,范围是屏幕的大小,用于判断边界
if(CCRect::CCRectContainsPoint(rect,position))
{
jl->setPosition(position);
}
}
}
这是用到的图片...如果格式有问题还需要自己转换一下..