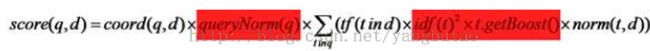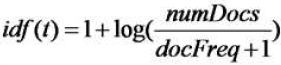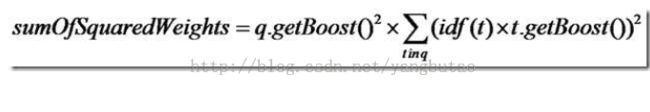结合源码分析Solr&Lucene查询打分的工作流程
基于solr4.4
solr中的搜索打分是在QueryComponent中进行的。
在prepare中根据查询的参数,QueryParser对查询语句进行分词,并生成Query对象树。
QParser parser = QParser.getParser(rb.getQueryString(), defType, req);
Query q = parser.getQuery();
if (q == null) {
// normalize a null query to a query that matches nothing
q = new BooleanQuery();
}
在process方法中,进行搜索打分的过程
调用SolrIndexSearcher进行查询,
SolrIndexSearcher searcher = req.getSearcher();
// normal search result
searcher.search(result,cmd);
search(Query query, Filter filter, Collector results)
SolrIndexSearcher集成lucene的IndexSearcher类,
最终调用IndexSearcher的search(Query query, Filter filter, Collector results)
public void search(Query query, Filter filter, Collector results)
throws IOException {
//在这个方法中,会先创建Weight树,计算TermWeight
search(leafContexts,
createNormalizedWeight(wrapFilter(query, filter)), results);
}
protected void search(List<AtomicReaderContext> leaves, Weight weight, Collector collector)
throws IOException {
.........
//根据weight树,构造Score对象树,以及SumScore对象树,为合并倒排表做准备
//
Scorer scorer = weight.scorer(ctx, !collector.acceptsDocsOutOfOrder(), true, ctx.reader().getLiveDocs());
if (scorer != null) {
try {
//根据SumScorer对象树,进行文档的合并,收集文档结果结合,并进行打分排名
scorer.score(collector);
} catch (CollectionTerminatedException e) {
// collection was terminated prematurely
// continue with the following leaf
}
}
}
}
1、先看一下Weight对象树的生成,
这一部分包括query的打分计算,参见红色部分
IndexSearcher.createNormalizedWeight(Query query)
//重写Query对象树
query = rewrite(query);
计算Weight分数,
float v = weight.getValueForNormalization();
//计算queryNorm
float norm = getSimilarity().queryNorm(v);
if (Float.isInfinite(norm) || Float.isNaN(norm)) {
norm = 1.0f;
}
//将queryNorm的计算打分,递归调用weight
weight.normalize(norm, 1.0f);
根据Query对象树,递归的调用query对象节点的createWeight方法
比如BooleanQuery对应的是BooleanWeight对象,每个BooleanWeight包含weight对象数组
最终叶子节点为TermWeight对象
public TermWeight(IndexSearcher searcher, TermContext termStates)
throws IOException {
assert termStates != null : "TermContext must not be null";
this.termStates = termStates;
this.similarity = searcher.getSimilarity();
//计算idf
this.stats = similarity.computeWeight(
getBoost(),
searcher.collectionStatistics(term.field()),
searcher.termStatistics(term, termStates));
}
public final SimWeight computeWeight(float queryBoost, CollectionStatistics collectionStats, TermStatistics... termStats) {
final Explanation idf = termStats.length == 1
? idfExplain(collectionStats, termStats[0])
: idfExplain(collectionStats, termStats);
return new IDFStats(collectionStats.field(), idf, queryBoost);
}
public Explanation idfExplain(CollectionStatistics collectionStats, TermStatistics termStats) {
final long df = termStats.docFreq();
final long max = collectionStats.maxDoc();
final float idf = idf(df, max);
return new Explanation(idf, "idf(docFreq=" + df + ", maxDocs=" + max + ")");
}
计算Weight分数
public float getValueForNormalization() throws IOException {
float sum = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0 ; i < weights.size(); i++) {
// call sumOfSquaredWeights for all clauses in case of side effects
float s = weights.get(i).getValueForNormalization(); // sum sub weights
if (!clauses.get(i).isProhibited())
// only add to sum for non-prohibited clauses
sum += s;
}
sum *= getBoost() * getBoost(); // boost each sub-weight
return sum ;
}
2、根据weight树,构造Score对象树,以及SumScore对象树,为合并倒排表做准备
Scorer scorer = weight.scorer(ctx, !collector.acceptsDocsOutOfOrder(), true, ctx.reader().getLiveDocs());
BooleanWeight递归调用节点weight.score创建score对象
public Scorer scorer(AtomicReaderContext context, boolean scoreDocsInOrder,
boolean topScorer, Bits acceptDocs)
throws IOException {
List<Scorer> required = new ArrayList<Scorer>();
List<Scorer> prohibited = new ArrayList<Scorer>();
List<Scorer> optional = new ArrayList<Scorer>();
Iterator<BooleanClause> cIter = clauses.iterator();
for (Weight w : weights) {
BooleanClause c = cIter.next();
Scorer subScorer = w.scorer(context, true, false, acceptDocs);
required.add(subScorer);
return new BooleanScorer2(this, disableCoord, minNrShouldMatch, required, prohibited, optional, maxCoord);
}
//在创建BooleanScore2的过程中,计算coord
BooleanQuery$BooleanWeight,coord,
public float coord(int overlap, int maxOverlap) {
return maxOverlap == 1 ? 1F : similarity.coord(overlap, maxOverlap);
}
//最终调用TermWeight.scorer方法,创建score对象
public Scorer scorer(AtomicReaderContext context, boolean scoreDocsInOrder,
boolean topScorer, Bits acceptDocs) throws IOException {
assert termStates.topReaderContext == ReaderUtil.getTopLevelContext(context) : "The top-reader used to create Weight (" + termStates.topReaderContext + ") is not the same as the current reader's top-reader (" + ReaderUtil.getTopLevelContext(context);
final TermsEnum termsEnum = getTermsEnum(context);
if (termsEnum == null) {
return null;
}
//Term对应的docs
DocsEnum docs = termsEnum.docs(acceptDocs, null);
assert docs != null;
//TermScorer负责doc的打分
return new TermScorer(this, docs, similarity.simScorer(stats, context));
}
TermScorer(Weight weight, DocsEnum td, Similarity.SimScorer docScorer) {
super(weight);
this.docScorer = docScorer;
this.docsEnum = td;
}
3、根据SumScorer对象树,进行文档的合并,收集文档结果结合,并进行打分排名
scorer.score(collector);
public void score(Collector collector) throws IOException {
assert docID() == -1; // not started
collector.setScorer(this);
int doc;
//在nextDoc的过程中合并document,合并倒排表是按照树的结构进行,先合并子树,子树与子树合并,一直到根
while ((doc = nextDoc()) != NO_MORE_DOCS) {
//收集doc,并打分,根据文档的打分,放入优先级队列(最小堆)中
collector.collect(doc);
}
}
//
整个Score以及SumScorer对象数的打分计算,最终会落到叶子节点TermScorer上
TermScorer:
@Override
public float score() throws IOException {
assert docID() != NO_MORE_DOCS;
return docScorer.score(docsEnum.docID(), docsEnum.freq());
}
//打分计算公式:tf * norm * weightValue = tf * norm *queryNorm * idf^2 * t.getBoost()
TFIDFSimilarity$TFIDFSimScorer
@Override
public float score(int doc, float freq) {
//weight是在创建weight阶段的query分词的打分,
final float raw = tf(freq) * weightValue; // compute tf(f)*weight,weight=
queryNorm * idf^2 * t.getBoost()
return norms == null ? raw : raw * decodeNormValue(norms.get(doc)); // normalize for field,
norm部分
}