模拟NTP协议实现时钟同步
Network Time Protocol(NTP)是用来使计算机时间同步化的一种协议,它可以使计算机对其服务器或时钟源(如石英钟,GPS等等)做同步化,它可以提供高精准度的时间校正(LAN上与标准间差小于1毫秒,WAN上几十毫秒),且可介由加密确认的方式来防止恶毒的协议攻击。
NTP提供准确时间,首先要有准确的时间来源,这一时间应该是国际标准时间UTC。 NTP获得UTC的时间来源可以是原子钟、天文台、卫星,也可以从Internet上获取。这样就有了准确而可靠的时间源。时间是按NTP服务器的等级传播。按照距离外部UTC 源的远近将所有服务器归入不同的Stratun(层)中。Stratum-1在顶层,有外部UTC接入,而Stratum-2则从Stratum-1获取时间,Stratum-3从Stratum-2获取时间,以此类推,但Stratum层的总数限制在15以内。所有这些服务器在逻辑上形成阶梯式的架构并相互连接,而Stratum-1的时间服务器是整个系统的基础。
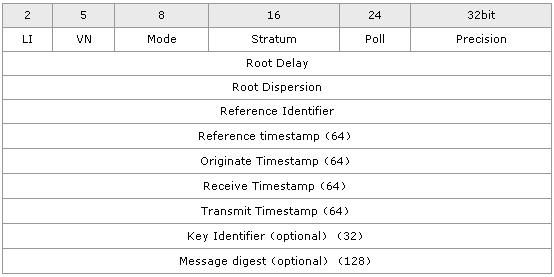
进行网络协议实现时最重要的是了解协议数据格式。NTP数据包有48个字节,其中NTP包头16字节,时间戳32个字节。其协议格式如下图所示。
其协议字段的含义如下所示。
LI:跳跃指示器,警告在当月最后一天的最终时刻插入的迫近闺秒(闺秒)。
VN:版本号。
Mode:工作模式。该字段包括以下值:0-预留;1-对称行为;3-客户机;4-服务器;5-广播;6-NTP控制信息。NTP协议具有3种工作模式,分别为主/被动对称模式、客户/服务器模式、广播模式。在主/被动对称模式中,有一对一的连接,双方均可同步对方或被对方同步,先发出申请建立连接的一方工作在主动模式下,另一方工作在被动模式下;客户/服务器模式与主/被动模式基本相同,惟一区别在于客户方可被服务器同步,但服务器不能被客户同步;在广播模式中,有一对多的连接,服务器不论客户工作在何种模式下,都会主动发出时间信息,客户根据此信息调整自己的时间。
Stratum:对本地时钟级别的整体识别。
Poll:有符号整数表示连续信息间的最大间隔。
Precision:有符号整数表示本地时钟精确度。
Root Delay:表示到达主参考源的一次往复的总延迟,它是有15~16位小数部分的符号定点小数。
Root Dispersion:表示一次到达主参考源的标准误差,它是有15~16位小数部分的无符号定点小数。
Reference Identifier:识别特殊参考源。
Originate Timestamp:这是向服务器请求分离客户机的时间,采用64位时标格式。
Receive Timestamp:这是向服务器请求到达客户机的时间,采用64位时标格式。
Transmit Timestamp:这是向客户机答复分离服务器的时间,采用64位时标格式。
Authenticator(Optional):当实现了NTP认证模式时,主要标识符和信息数字域就包括已定义的信息认证代码(MAC)信息。
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
以上对NTP协议原理的描述来自网络,感谢网络上的朋友!
以下是我写的模拟NTP协议进行时钟同步的Demo程序。完整的代码可从这里下载: http://download.csdn.net/detail/chexlong/3787414
NTP.h
#ifndef NTP_H
#define NTP_H
#include <winsock2.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#pragma comment(lib, "WS2_32") // 链接到WS2_32.lib
#define LI 0
#define VN 3
#define MODE 3
#define STRATUM 0
#define POLL 4
#define PREC -6
#define JAN_1970 0x83aa7e80 /* 2208988800 1970 - 1900 in seconds */
#define NTPFRAC(x) (4294 * (x) + ((1981 * (x))>>11))
#define USEC(x) (((x) >> 12) - 759 * ((((x) >> 10) + 32768) >> 16))
typedef struct ntptime_t
{
unsigned int coarse;
unsigned int fine;
}ntptime;
typedef struct ntp_packet_t
{
//header
unsigned int leap_year_indicator:2;
unsigned int version_number:3;
unsigned int mode:3;
unsigned int stratum :8;
unsigned int poll :8;
unsigned int precision :8;
unsigned int root_delay;
unsigned int root_dispersion;
unsigned int reference_identifier;
//时间戳
ntptime reference_timestamp; //T4
ntptime originate_timestamp; //T1
ntptime receive_timestamp; //T2
ntptime transmit_timestamp; //T3
}ntp_packet;
typedef union
{
ntp_packet ntp;
char c[48];
}NTP_PACKET_T;
void GetNTPTime(ntptime *ntpTime)
{
SYSTEMTIME sysTime;
FILETIME fileTime;
GetSystemTime(&sysTime);
SystemTimeToFileTime(&sysTime,&fileTime);
ntpTime->coarse = fileTime.dwHighDateTime;
ntpTime->fine = fileTime.dwLowDateTime;
}
SOCKET CreateSock(char *psLocalIP, unsigned short usLocalPort, unsigned int iTimeOut)
{
//创建套节字
SOCKET sock = ::socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, IPPROTO_UDP);
if( INVALID_SOCKET == sock )
{
printf("Failed socket() %d \n", ::WSAGetLastError());
return 0;
}
if (0 != iTimeOut)
{
//设置套接字发送,接收超时时间
int iRet = setsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDTIMEO, (char*)&iTimeOut, sizeof(iTimeOut));
iRet = setsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVTIMEO, (char*)&iTimeOut, sizeof(iTimeOut));
}
//绑定本地地址
sockaddr_in addrLocal;
memset(&addrLocal, 0, sizeof(addrLocal));
addrLocal.sin_family = AF_INET;
addrLocal.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
addrLocal.sin_port = htons(usLocalPort);
if ( 0 != bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&addrLocal, sizeof(addrLocal)) )
{
printf("Failed bind() %d \n", ::WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(sock);
return 0;
}
return sock;
}
#endif
Base64.h
#ifndef BASE64_H
#define BASE64_H
const int pr2six[256]={
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,62,64,64,64,63,
52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,
10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,64,64,64,64,64,64,26,27,
28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,
64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64,64
};
char six2pr[64] = {
'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M',
'N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z',
'a','b','c','d','e','f','g','h','i','j','k','l','m',
'n','o','p','q','r','s','t','u','v','w','x','y','z',
'0','1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','+','/'
};
void Base64Decode(const char *bufcoded, char * dst,int *nbytes)
{
int nbytesdecoded;
const char *bufin = bufcoded;
unsigned char *bufout = (unsigned char*)dst;
int nprbytes;
/* Figure out how many characters are in the input buffer.
* If this would decode into more bytes than would fit into
* the output buffer, adjust the number of input bytes downwards.
*/
//bufin = bufcoded;
while(pr2six[(int)*(bufin++)] <= 63){}
nprbytes = (int)(bufin - bufcoded - 1);
nbytesdecoded = ((nprbytes+3)/4) * 3;
bufin = bufcoded;
while (nprbytes > 0)
{
*(bufout++) =
(unsigned char) (pr2six[(int)*bufin] << 2 | pr2six[(int)bufin[1]] >> 4);
*(bufout++) =
(unsigned char) (pr2six[(int)bufin[1]] << 4 | pr2six[(int)bufin[2]] >> 2);
*(bufout++) =
(unsigned char) (pr2six[(int)bufin[2]] << 6 | pr2six[(int)bufin[3]]);
bufin += 4;
nprbytes -= 4;
}
if(nprbytes & 03)
{
if(pr2six[(int)bufin[-2]] > 63)
nbytesdecoded -= 2;
else
nbytesdecoded -= 1;
}
dst[nbytesdecoded] = '\0';
if ( nbytes )
{
*nbytes = nbytesdecoded;
}
}
void Base64Encode(const unsigned char *bufin, unsigned int nbytes, char * dst)
{
unsigned char *outptr = (unsigned char *)dst;
unsigned int i;
for (i=0; i<nbytes; i += 3)
{
*(outptr++) = six2pr[*bufin >> 2]; /* c1 */
*(outptr++) = six2pr[((*bufin << 4) & 060) | ((bufin[1] >> 4) & 017)]; /*c2*/
*(outptr++) = six2pr[((bufin[1] << 2) & 074) | ((bufin[2] >> 6) & 03)];/*c3*/
*(outptr++) = six2pr[bufin[2] & 077]; /* c4 */
bufin += 3;
}
/* If nbytes was not a multiple of 3, then we have encoded too
* many characters. Adjust appropriately.
*/
if(i == nbytes+1)
{
/* There were only 2 bytes in that last group */
outptr[-1] = '=';
}
else if(i == nbytes+2)
{
/* There was only 1 byte in that last group */
outptr[-1] = '=';
outptr[-2] = '=';
}
*(outptr++) = '\0';
//size_t len = outptr - 1 - (unsigned char*)dst;
}
#endif
NTPClient.cpp
#include "../Include/NTP.h"
#include "../Include/Base64.h"
//NTP请求包打包
int CreateNtpPacket(NTP_PACKET_T &ntpPacket)
{
static unsigned long ulNTPId = 0;
ulNTPId++;
char szBuf[1024];
int iDataLen;
ntpPacket.ntp.leap_year_indicator = LI;
ntpPacket.ntp.version_number = VN;
ntpPacket.ntp.mode = MODE;
ntpPacket.ntp.stratum = STRATUM;
ntpPacket.ntp.poll = POLL;
ntpPacket.ntp.precision = (PREC&0xFF);
ntpPacket.ntp.root_delay = htonl(1<<16);
ntpPacket.ntp.root_dispersion = htonl(1<<16);
ntpPacket.ntp.reference_identifier = 0;
ntpPacket.ntp.reference_timestamp.coarse = 0;
ntpPacket.ntp.reference_timestamp.fine = 0;
GetNTPTime(&ntpPacket.ntp.originate_timestamp);
ntpPacket.ntp.receive_timestamp.coarse = 0;
ntpPacket.ntp.receive_timestamp.fine = 0;
ntpPacket.ntp.transmit_timestamp.coarse = 0;
ntpPacket.ntp.transmit_timestamp.fine = 0;
return 0;
}
int NtpRequest(SOCKET &sock)
{
int iRet;
sock = CreateSock("127.0.0.1", 4567, 5000);
if ( 0 == sock )
{
printf("Failed create sock1 \n");
return -1;
}
//填写远程地址信息
sockaddr_in addrRemote;
addrRemote.sin_family = AF_INET;
addrRemote.sin_port = htons(5678);
addrRemote.sin_addr.S_un.S_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
while (true)
{
char szTimeValue[128];
char szbuf[128];
memset(szTimeValue,0,128);
memset(szbuf,0,128);
NTP_PACKET_T ntpPacket;
memset(&ntpPacket,0,sizeof(ntpPacket));
CreateNtpPacket(ntpPacket);
//Base64进行编码
Base64Encode((unsigned char *)ntpPacket.c, sizeof(ntpPacket), szTimeValue);
//发送NTP请求数据包
iRet = ::sendto(sock, szTimeValue, strlen(szTimeValue), 0, (sockaddr*)&addrRemote, sizeof(addrRemote));
if ( SOCKET_ERROR == iRet )
{
printf("Failed sendto() sock %d \n", ::WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(sock);
}
else
{
printf("Successed sendto sock = %d, data lenth = %d \n", sock, iRet);
}
memset(szTimeValue,0,sizeof(szTimeValue));
int nLen = sizeof(addrRemote);
//接收NTP请求应答消息
iRet = ::recvfrom(sock, szbuf, 128, 0, (sockaddr*)&addrRemote, &nLen);
if(iRet > 0)
{
szbuf[iRet] = '\0';
printf(" 接收到数据(%s):%s \n", ::inet_ntoa(addrRemote.sin_addr), szbuf);
//Base54解码
Base64Decode(szbuf, szTimeValue, 0);
if ( '\0' == szTimeValue[0] )
{
printf("time value is empty. \n");
closesocket(sock);
::WSACleanup();
return -1;
}
memset(&ntpPacket,0,sizeof(ntpPacket));
memcpy(ntpPacket.c,szTimeValue,sizeof(ntpPacket));
//设置本地系统时钟
SYSTEMTIME sysTime;
struct tm *tm1 = _localtime32((__time32_t*)&ntpPacket.ntp.transmit_timestamp.coarse);
sysTime.wYear = tm1->tm_year+1900;
sysTime.wMonth = tm1->tm_mon+1;
sysTime.wDay = tm1->tm_mday;
sysTime.wHour = tm1->tm_hour;
sysTime.wMinute = tm1->tm_min;
sysTime.wSecond = tm1->tm_sec;
sysTime.wMilliseconds = 0;
//SetLocalTime(&sysTime);
printf("NTP ok, %4d-%02d-%02d %02d:%02d:%02d %d \n", sysTime.wYear,sysTime.wMonth,sysTime.wDay,sysTime.wHour,sysTime.wMinute,sysTime.wSecond,sysTime.wMilliseconds);
}
else
{
printf("Failed recvfrom() sock %d \n", ::WSAGetLastError());
}
Sleep(5000);
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int iRet;
WSADATA wsaData;
WORD sockVersion = MAKEWORD(2, 2);
if(::WSAStartup(sockVersion, &wsaData) != 0)
{
exit(0);
}
SOCKET sock;
iRet = NtpRequest(sock);
if (0 != iRet)
{
printf("ntp request failed. \n");
}
system("pause");
closesocket(sock);
::WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
NTPServer.cpp
#include "../Include/Base64.h"
#include "../Include/NTP.h"
int StartNtpServer(SOCKET &sock)
{
int iRet;
sock = CreateSock("127.0.0.1", 5678, 0);
if ( 0 == sock )
{
printf("Failed create sock1 \n");
return -1;
}
sockaddr_in addrRemote;
char szTimeValue[128];
char szbuf[128];
memset(szTimeValue,0,128);
memset(szbuf,0,128);
NTP_PACKET_T ntpPacket;
while (true)
{
memset(&addrRemote,0,sizeof(addrRemote));
int nLen = sizeof(addrRemote);
//接收来自客户端的NTP请求消息
iRet = ::recvfrom(sock, szbuf, 128, 0, (sockaddr*)&addrRemote, &nLen);
if(iRet > 0)
{
szbuf[iRet] = '\0';
printf(" 接收到数据(%s):%s \n", ::inet_ntoa(addrRemote.sin_addr), szbuf);
}
//base64解码消息
Base64Decode(szbuf, szTimeValue, 0);
//构造NTP请求应答数据包
memset(&ntpPacket,0,sizeof(ntpPacket));
memcpy(ntpPacket.c,szTimeValue,sizeof(ntpPacket));
ntpPacket.ntp.mode = 4;
ntpPacket.ntp.transmit_timestamp.coarse = _time32(NULL);
memset(szTimeValue,0,sizeof(szTimeValue));
//Base64编码NTP请求应答消息
Base64Encode((unsigned char *)ntpPacket.c,sizeof(NTP_PACKET_T),szTimeValue);
//填写远程地址信息
addrRemote.sin_family = AF_INET;
addrRemote.sin_port = htons(4567);
addrRemote.sin_addr.S_un.S_addr = inet_addr("127.0.0.1");
//发送NTP请求应答消息
iRet = ::sendto(sock, szTimeValue, strlen(szTimeValue), 0, (sockaddr*)&addrRemote, sizeof(addrRemote));
if ( SOCKET_ERROR == iRet )
{
printf("Failed sendto() sock %d \n", ::WSAGetLastError());
closesocket(sock);
return -1;
}
else
{
printf("Successed sendto sock = %d, data lenth = %d \n", sock, iRet);
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
WSADATA wsaData;
WORD sockVersion = MAKEWORD(2, 2);
if(::WSAStartup(sockVersion, &wsaData) != 0)
{
exit(0);
}
SOCKET sock;
int iRet = StartNtpServer(sock);
if (0 != iRet)
{
printf("start ntp server failed. \n");
}
system("pause");
closesocket(sock);
::WSACleanup();
return 0;
}
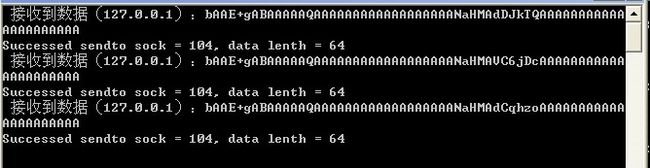
上述代码代码在VC2005环境中已测试通过,以下是客户端和服务端程序截图:
客户端
服务端