FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)
=====================================================
HEVC源代码分析文章列表:
【解码 -libavcodec HEVC 解码器】
FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:概述
FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:CTU解码(CTU Decode)部分-PU
FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:CTU解码(CTU Decode)部分-TU
FFmpeg的HEVC解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(LoopFilter)
=====================================================
本文分析FFmpeg的libavcodec中的HEVC解码器的环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分的源代码。FFmpeg的HEVC解码器调用hls_decode_entry()函数完成了Slice解码工作。hls_decode_entry()则调用了ff_hevc_hls_filters()完成了滤波工作。本文记录该函数实现的功能。
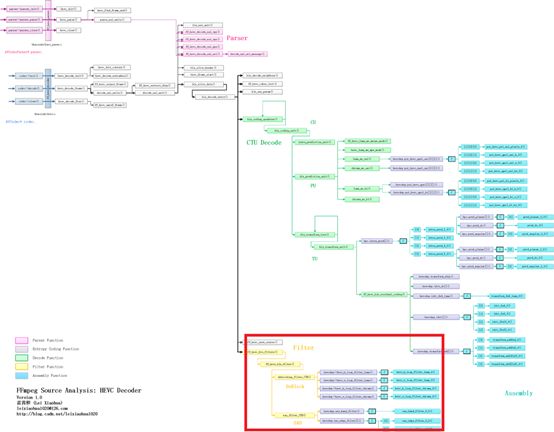
函数调用关系图
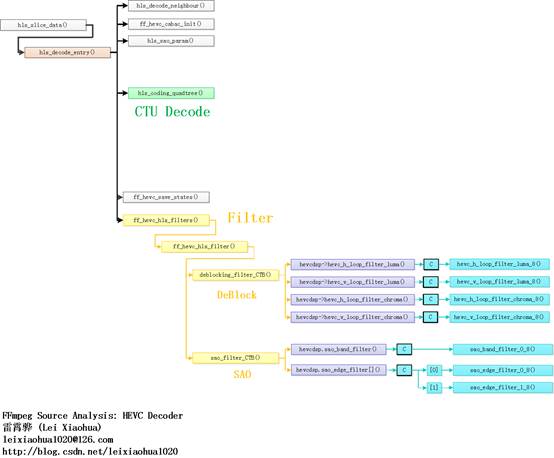
FFmpeg HEVC解码器的环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分在整个HEVC解码器中的位置如下图所示。从源代码可以看出,滤波模块对应的函数是ff_hevc_hls_filters(),该函数调用了函数ff_hevc_hls_filter()(注意函数名称少了一个“s”)。ff_hevc_hls_filter()调用了两个函数完成了两种滤波工作:deblocking_filter_CTB()用于完成去块效应滤波,而sao_filter_CTB()用于完成SAO滤波。
hls_decode_entry()
hls_decode_entry()是FFmpeg HEVC解码器中Slice解码的入口函数。该函数的定义如下所示。/* * 解码入口函数 * * 注释:雷霄骅 * [email protected] * http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020 * */ static int hls_decode_entry(AVCodecContext *avctxt, void *isFilterThread) { HEVCContext *s = avctxt->priv_data; //CTB尺寸 int ctb_size = 1 << s->sps->log2_ctb_size; int more_data = 1; int x_ctb = 0; int y_ctb = 0; int ctb_addr_ts = s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[s->sh.slice_ctb_addr_rs]; if (!ctb_addr_ts && s->sh.dependent_slice_segment_flag) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Impossible initial tile.\n"); return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; } if (s->sh.dependent_slice_segment_flag) { int prev_rs = s->pps->ctb_addr_ts_to_rs[ctb_addr_ts - 1]; if (s->tab_slice_address[prev_rs] != s->sh.slice_addr) { av_log(s->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Previous slice segment missing\n"); return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA; } } while (more_data && ctb_addr_ts < s->sps->ctb_size) { int ctb_addr_rs = s->pps->ctb_addr_ts_to_rs[ctb_addr_ts]; //CTB的位置x和y x_ctb = (ctb_addr_rs % ((s->sps->width + ctb_size - 1) >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size)) << s->sps->log2_ctb_size; y_ctb = (ctb_addr_rs / ((s->sps->width + ctb_size - 1) >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size)) << s->sps->log2_ctb_size; //初始化周围的参数 hls_decode_neighbour(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, ctb_addr_ts); //初始化CABAC ff_hevc_cabac_init(s, ctb_addr_ts); //样点自适应补偿参数 hls_sao_param(s, x_ctb >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size, y_ctb >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size); s->deblock[ctb_addr_rs].beta_offset = s->sh.beta_offset; s->deblock[ctb_addr_rs].tc_offset = s->sh.tc_offset; s->filter_slice_edges[ctb_addr_rs] = s->sh.slice_loop_filter_across_slices_enabled_flag; /* * CU示意图 * * 64x64块 * * 深度d=0 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个32x32 * * +--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+ * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --+ -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --+ * | | | * | | * | | | * + + * | | | * | | * | | | * + + * | | | * | | * | | | * + + * | | | * | | * | | | * +--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+--------+ * * * 32x32 块 * 深度d=1 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个16x16 * * +--------+--------+--------+--------+ * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * + -- -- -- -- + -- -- -- -- + * | | * | | | * | | * + | + * | | * | | | * | | * +--------+--------+--------+--------+ * * * 16x16 块 * 深度d=2 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个8x8 * * +--------+--------+ * | | * | | | * | | * + -- --+ -- -- + * | | * | | | * | | * +--------+--------+ * * * 8x8块 * 深度d=3 * split_flag=1时候划分为4个4x4 * * +----+----+ * | | | * + -- + -- + * | | | * +----+----+ * */ /* * 解析四叉树结构,并且解码 * * hls_coding_quadtree(HEVCContext *s, int x0, int y0, int log2_cb_size, int cb_depth)中: * s:HEVCContext上下文结构体 * x_ctb:CB位置的x坐标 * y_ctb:CB位置的y坐标 * log2_cb_size:CB大小取log2之后的值 * cb_depth:深度 * */ more_data = hls_coding_quadtree(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, s->sps->log2_ctb_size, 0); if (more_data < 0) { s->tab_slice_address[ctb_addr_rs] = -1; return more_data; } ctb_addr_ts++; //保存解码信息以供下次使用 ff_hevc_save_states(s, ctb_addr_ts); //去块效应滤波 ff_hevc_hls_filters(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, ctb_size); } if (x_ctb + ctb_size >= s->sps->width && y_ctb + ctb_size >= s->sps->height) ff_hevc_hls_filter(s, x_ctb, y_ctb, ctb_size); return ctb_addr_ts; }
从源代码可以看出,hls_decode_entry()主要调用了2个函数进行解码工作:
(1)调用hls_coding_quadtree()解码CTU。其中包含了PU和TU的解码。本文分析第二步的滤波过程。
(2)调用ff_hevc_hls_filters()进行滤波。其中包含了去块效应滤波和SAO滤波。
ff_hevc_hls_filters()
ff_hevc_hls_filters()用于完成滤波工作。该函数的定义如下所示。/* * 去块效应滤波 * * 注释:雷霄骅 * [email protected] * http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020 * */ void ff_hevc_hls_filters(HEVCContext *s, int x_ctb, int y_ctb, int ctb_size) { //是否是水平边缘上的CTU int x_end = x_ctb >= s->sps->width - ctb_size; //是否是垂直边缘上的CTU int y_end = y_ctb >= s->sps->height - ctb_size; /* * (x)代表解码序号为x的CTU的滤波的图像块 * * 右边界 * | | | | || * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ * | | | | || * | (a) | (b) | (c)1 | (c)2 || * | | | | || * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ * | | | | || * | | a | b | c || * | | | | || * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ * * 。。。。。。 * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ * | | | | || * | (d)1 | (e)1 | (f)1 | (f)2 || * | | | | || * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ * | | | | || * | (d)2 | d (e)2 | e (f)3 | f || * | | | | || * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ 下边界 * ---+--------+--------+--------+--------++ */ //对左上方CTU滤波 if (y_ctb && x_ctb) ff_hevc_hls_filter(s, x_ctb - ctb_size, y_ctb - ctb_size, ctb_size); //如果是右边界上的CTU,再对上方的CTU滤波 if (y_ctb && x_end) ff_hevc_hls_filter(s, x_ctb, y_ctb - ctb_size, ctb_size); //如果是下边界上的CTU,再对左边的CTU滤波 if (x_ctb && y_end) ff_hevc_hls_filter(s, x_ctb - ctb_size, y_ctb, ctb_size); }
从源代码可以看出,ff_hevc_hls_filters()调用了ff_hevc_hls_filter()完成了滤波工作。ff_hevc_hls_filters()对于当前需要进行滤波的CTU的位置进行了判断:一般情况下对当前CTU左上方的CTU进行滤波处理;如果当前CTU位于右边边界处,则再对当前CTU上面的CTU进行滤波处理;若果当前CTU位于下边边界处,则再对当前CTU左边的CTU进行滤波处理。
ff_hevc_hls_filter()
ff_hevc_hls_filter()完成了一个CTU的滤波工作。该函数的定义如下所示。//滤波
void ff_hevc_hls_filter(HEVCContext *s, int x, int y, int ctb_size)
{
int x_end = x >= s->sps->width - ctb_size;
//去块效应滤波器
deblocking_filter_CTB(s, x, y);
if (s->sps->sao_enabled) {
//SAO(采样自适应偏移)滤波器
int y_end = y >= s->sps->height - ctb_size;
if (y && x)
sao_filter_CTB(s, x - ctb_size, y - ctb_size);
if (x && y_end)
sao_filter_CTB(s, x - ctb_size, y);
if (y && x_end) {
sao_filter_CTB(s, x, y - ctb_size);
if (s->threads_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME )
ff_thread_report_progress(&s->ref->tf, y, 0);
}
if (x_end && y_end) {
sao_filter_CTB(s, x , y);
if (s->threads_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME )
ff_thread_report_progress(&s->ref->tf, y + ctb_size, 0);
}
} else if (s->threads_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME && x_end)
ff_thread_report_progress(&s->ref->tf, y + ctb_size - 4, 0);
}
从源代码可以看出,ff_hevc_hls_filter()调用了两种滤波函数:
(1)调用deblocking_filter_CTB()进行去块效应滤波
(2)调用sao_filter_CTB()进行SAO(采样自适应偏移)滤波
下面分别看一下这两个函数。
deblocking_filter_CTB()
deblocking_filter_CTB()完成了去块效应滤波。该函数的定义如下所示。//去块效应滤波器
static void deblocking_filter_CTB(HEVCContext *s, int x0, int y0)
{
uint8_t *src;
int x, y;
int chroma, beta;
int32_t c_tc[2], tc[2];
uint8_t no_p[2] = { 0 };
uint8_t no_q[2] = { 0 };
int log2_ctb_size = s->sps->log2_ctb_size;
int x_end, x_end2, y_end;
int ctb_size = 1 << log2_ctb_size;
int ctb = (x0 >> log2_ctb_size) +
(y0 >> log2_ctb_size) * s->sps->ctb_width;
int cur_tc_offset = s->deblock[ctb].tc_offset;
int cur_beta_offset = s->deblock[ctb].beta_offset;
int left_tc_offset, left_beta_offset;
int tc_offset, beta_offset;
int pcmf = (s->sps->pcm_enabled_flag &&
s->sps->pcm.loop_filter_disable_flag) ||
s->pps->transquant_bypass_enable_flag;
if (x0) {
left_tc_offset = s->deblock[ctb - 1].tc_offset;
left_beta_offset = s->deblock[ctb - 1].beta_offset;
} else {
left_tc_offset = 0;
left_beta_offset = 0;
}
x_end = x0 + ctb_size;
if (x_end > s->sps->width)
x_end = s->sps->width;
y_end = y0 + ctb_size;
if (y_end > s->sps->height)
y_end = s->sps->height;
tc_offset = cur_tc_offset;
beta_offset = cur_beta_offset;
x_end2 = x_end;
if (x_end2 != s->sps->width)
x_end2 -= 8;
for (y = y0; y < y_end; y += 8) {
// vertical filtering luma
// 滤波垂直边界的滤波器
//
// |
// P2 P1 P0 | Q0 Q1 Q2
// |
//
for (x = x0 ? x0 : 8; x < x_end; x += 8) {
/*
* 以8x8块为单位
*
* | | | |
* | | | |
* | | | |
* | | | |
* | | | |
*
*/
const int bs0 = s->vertical_bs[(x + y * s->bs_width) >> 2];
const int bs1 = s->vertical_bs[(x + (y + 4) * s->bs_width) >> 2];
if (bs0 || bs1) {
const int qp = (get_qPy(s, x - 1, y) + get_qPy(s, x, y) + 1) >> 1;
beta = betatable[av_clip(qp + beta_offset, 0, MAX_QP)];
tc[0] = bs0 ? TC_CALC(qp, bs0) : 0;
tc[1] = bs1 ? TC_CALC(qp, bs1) : 0;
src = &s->frame->data[LUMA][y * s->frame->linesize[LUMA] + (x << s->sps->pixel_shift)];
if (pcmf) {
no_p[0] = get_pcm(s, x - 1, y);
no_p[1] = get_pcm(s, x - 1, y + 4);
no_q[0] = get_pcm(s, x, y);
no_q[1] = get_pcm(s, x, y + 4);
s->hevcdsp.hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_c(src,
s->frame->linesize[LUMA],
beta, tc, no_p, no_q);
} else
s->hevcdsp.hevc_v_loop_filter_luma(src,
s->frame->linesize[LUMA],
beta, tc, no_p, no_q);
}
}
if(!y)
continue;
// horizontal filtering luma
// 滤波水平边界的滤波器
// P2
// P1
// P0
// -----------
// Q0
// Q1
// Q2
for (x = x0 ? x0 - 8 : 0; x < x_end2; x += 8) {
/*
* 以8x8块为单位
*
* ---------------
*
* ---------------
*
* ---------------
*
* ---------------
*
*/
const int bs0 = s->horizontal_bs[( x + y * s->bs_width) >> 2];
const int bs1 = s->horizontal_bs[((x + 4) + y * s->bs_width) >> 2];
if (bs0 || bs1) {
const int qp = (get_qPy(s, x, y - 1) + get_qPy(s, x, y) + 1) >> 1;
tc_offset = x >= x0 ? cur_tc_offset : left_tc_offset;
beta_offset = x >= x0 ? cur_beta_offset : left_beta_offset;
beta = betatable[av_clip(qp + beta_offset, 0, MAX_QP)];
tc[0] = bs0 ? TC_CALC(qp, bs0) : 0;
tc[1] = bs1 ? TC_CALC(qp, bs1) : 0;
src = &s->frame->data[LUMA][y * s->frame->linesize[LUMA] + (x << s->sps->pixel_shift)];
if (pcmf) {
no_p[0] = get_pcm(s, x, y - 1);
no_p[1] = get_pcm(s, x + 4, y - 1);
no_q[0] = get_pcm(s, x, y);
no_q[1] = get_pcm(s, x + 4, y);
s->hevcdsp.hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_c(src,
s->frame->linesize[LUMA],
beta, tc, no_p, no_q);
} else
s->hevcdsp.hevc_h_loop_filter_luma(src,
s->frame->linesize[LUMA],
beta, tc, no_p, no_q);
}
}
}
//色度滤波
for (chroma = 1; chroma <= 2; chroma++) {
int h = 1 << s->sps->hshift[chroma];
int v = 1 << s->sps->vshift[chroma];
// vertical filtering chroma
for (y = y0; y < y_end; y += (8 * v)) {
for (x = x0 ? x0 : 8 * h; x < x_end; x += (8 * h)) {
const int bs0 = s->vertical_bs[(x + y * s->bs_width) >> 2];
const int bs1 = s->vertical_bs[(x + (y + (4 * v)) * s->bs_width) >> 2];
if ((bs0 == 2) || (bs1 == 2)) {
const int qp0 = (get_qPy(s, x - 1, y) + get_qPy(s, x, y) + 1) >> 1;
const int qp1 = (get_qPy(s, x - 1, y + (4 * v)) + get_qPy(s, x, y + (4 * v)) + 1) >> 1;
c_tc[0] = (bs0 == 2) ? chroma_tc(s, qp0, chroma, tc_offset) : 0;
c_tc[1] = (bs1 == 2) ? chroma_tc(s, qp1, chroma, tc_offset) : 0;
src = &s->frame->data[chroma][(y >> s->sps->vshift[chroma]) * s->frame->linesize[chroma] + ((x >> s->sps->hshift[chroma]) << s->sps->pixel_shift)];
if (pcmf) {
no_p[0] = get_pcm(s, x - 1, y);
no_p[1] = get_pcm(s, x - 1, y + (4 * v));
no_q[0] = get_pcm(s, x, y);
no_q[1] = get_pcm(s, x, y + (4 * v));
s->hevcdsp.hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma_c(src,
s->frame->linesize[chroma],
c_tc, no_p, no_q);
} else
s->hevcdsp.hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma(src,
s->frame->linesize[chroma],
c_tc, no_p, no_q);
}
}
if(!y)
continue;
// horizontal filtering chroma
tc_offset = x0 ? left_tc_offset : cur_tc_offset;
x_end2 = x_end;
if (x_end != s->sps->width)
x_end2 = x_end - 8 * h;
for (x = x0 ? x0 - 8 * h : 0; x < x_end2; x += (8 * h)) {
const int bs0 = s->horizontal_bs[( x + y * s->bs_width) >> 2];
const int bs1 = s->horizontal_bs[((x + 4 * h) + y * s->bs_width) >> 2];
if ((bs0 == 2) || (bs1 == 2)) {
const int qp0 = bs0 == 2 ? (get_qPy(s, x, y - 1) + get_qPy(s, x, y) + 1) >> 1 : 0;
const int qp1 = bs1 == 2 ? (get_qPy(s, x + (4 * h), y - 1) + get_qPy(s, x + (4 * h), y) + 1) >> 1 : 0;
c_tc[0] = bs0 == 2 ? chroma_tc(s, qp0, chroma, tc_offset) : 0;
c_tc[1] = bs1 == 2 ? chroma_tc(s, qp1, chroma, cur_tc_offset) : 0;
src = &s->frame->data[chroma][(y >> s->sps->vshift[1]) * s->frame->linesize[chroma] + ((x >> s->sps->hshift[1]) << s->sps->pixel_shift)];
if (pcmf) {
no_p[0] = get_pcm(s, x, y - 1);
no_p[1] = get_pcm(s, x + (4 * h), y - 1);
no_q[0] = get_pcm(s, x, y);
no_q[1] = get_pcm(s, x + (4 * h), y);
s->hevcdsp.hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma_c(src,
s->frame->linesize[chroma],
c_tc, no_p, no_q);
} else
s->hevcdsp.hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma(src,
s->frame->linesize[chroma],
c_tc, no_p, no_q);
}
}
}
}
}
从源代码可以看出,deblocking_filter_CTB()是以8x8块为单位进行滤波的。该函数首先调用HEVCDSPContext->hevc_v_loop_filter_luma()汇编函数对亮度垂直边界进行滤波,然后调用HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_h_loop_filter_luma()汇编函数对亮度水平边界进行滤波,最后还会调用HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma ()和HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma()对色度垂直边界和水平边界进行滤波。
sao_filter_CTB()
sao_filter_CTB()完成了SAO(采样自适应偏移)滤波。该函数的定义如下所示。#define CTB(tab, x, y) ((tab)[(y) * s->sps->ctb_width + (x)])
//SAO(采样自适应偏移)滤波器
static void sao_filter_CTB(HEVCContext *s, int x, int y)
{
int c_idx;
int edges[4]; // 0 left 1 top 2 right 3 bottom
int x_ctb = x >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size;
int y_ctb = y >> s->sps->log2_ctb_size;
int ctb_addr_rs = y_ctb * s->sps->ctb_width + x_ctb;
int ctb_addr_ts = s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[ctb_addr_rs];
SAOParams *sao = &CTB(s->sao, x_ctb, y_ctb);
// flags indicating unfilterable edges
uint8_t vert_edge[] = { 0, 0 };
uint8_t horiz_edge[] = { 0, 0 };
uint8_t diag_edge[] = { 0, 0, 0, 0 };
uint8_t lfase = CTB(s->filter_slice_edges, x_ctb, y_ctb);
uint8_t no_tile_filter = s->pps->tiles_enabled_flag &&
!s->pps->loop_filter_across_tiles_enabled_flag;
uint8_t restore = no_tile_filter || !lfase;
uint8_t left_tile_edge = 0;
uint8_t right_tile_edge = 0;
uint8_t up_tile_edge = 0;
uint8_t bottom_tile_edge = 0;
edges[0] = x_ctb == 0;
edges[1] = y_ctb == 0;
edges[2] = x_ctb == s->sps->ctb_width - 1;
edges[3] = y_ctb == s->sps->ctb_height - 1;
//位于图像边界处的特殊处理?
if (restore) {
if (!edges[0]) {
left_tile_edge = no_tile_filter && s->pps->tile_id[ctb_addr_ts] != s->pps->tile_id[s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[ctb_addr_rs-1]];
vert_edge[0] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb - 1, y_ctb)) || left_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[2]) {
right_tile_edge = no_tile_filter && s->pps->tile_id[ctb_addr_ts] != s->pps->tile_id[s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[ctb_addr_rs+1]];
vert_edge[1] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb + 1, y_ctb)) || right_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[1]) {
up_tile_edge = no_tile_filter && s->pps->tile_id[ctb_addr_ts] != s->pps->tile_id[s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[ctb_addr_rs - s->sps->ctb_width]];
horiz_edge[0] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb - 1)) || up_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[3]) {
bottom_tile_edge = no_tile_filter && s->pps->tile_id[ctb_addr_ts] != s->pps->tile_id[s->pps->ctb_addr_rs_to_ts[ctb_addr_rs + s->sps->ctb_width]];
horiz_edge[1] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb + 1)) || bottom_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[0] && !edges[1]) {
diag_edge[0] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb - 1, y_ctb - 1)) || left_tile_edge || up_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[1] && !edges[2]) {
diag_edge[1] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb + 1, y_ctb - 1)) || right_tile_edge || up_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[2] && !edges[3]) {
diag_edge[2] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb + 1, y_ctb + 1)) || right_tile_edge || bottom_tile_edge;
}
if (!edges[0] && !edges[3]) {
diag_edge[3] = (!lfase && CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb, y_ctb) != CTB(s->tab_slice_address, x_ctb - 1, y_ctb + 1)) || left_tile_edge || bottom_tile_edge;
}
}
for (c_idx = 0; c_idx < 3; c_idx++) {
int x0 = x >> s->sps->hshift[c_idx];
int y0 = y >> s->sps->vshift[c_idx];
int stride_src = s->frame->linesize[c_idx];
int stride_dst = s->sao_frame->linesize[c_idx];
int ctb_size_h = (1 << (s->sps->log2_ctb_size)) >> s->sps->hshift[c_idx];
int ctb_size_v = (1 << (s->sps->log2_ctb_size)) >> s->sps->vshift[c_idx];
int width = FFMIN(ctb_size_h, (s->sps->width >> s->sps->hshift[c_idx]) - x0);
int height = FFMIN(ctb_size_v, (s->sps->height >> s->sps->vshift[c_idx]) - y0);
uint8_t *src = &s->frame->data[c_idx][y0 * stride_src + (x0 << s->sps->pixel_shift)];
uint8_t *dst = &s->sao_frame->data[c_idx][y0 * stride_dst + (x0 << s->sps->pixel_shift)];
//SAO滤波类型
switch (sao->type_idx[c_idx]) {
case SAO_BAND: //边带补偿
copy_CTB(dst, src, width << s->sps->pixel_shift, height, stride_dst, stride_src);
s->hevcdsp.sao_band_filter(src, dst,
stride_src, stride_dst,
sao,
edges, width,
height, c_idx);
restore_tqb_pixels(s, x, y, width, height, c_idx);
sao->type_idx[c_idx] = SAO_APPLIED;
break;
case SAO_EDGE: //边界补偿
{
uint8_t left_pixels = !edges[0] && (CTB(s->sao, x_ctb-1, y_ctb).type_idx[c_idx] != SAO_APPLIED);
if (!edges[1]) {
uint8_t top_left = !edges[0] && (CTB(s->sao, x_ctb-1, y_ctb-1).type_idx[c_idx] != SAO_APPLIED);
uint8_t top_right = !edges[2] && (CTB(s->sao, x_ctb+1, y_ctb-1).type_idx[c_idx] != SAO_APPLIED);
if (CTB(s->sao, x_ctb , y_ctb-1).type_idx[c_idx] == 0)
memcpy( dst - stride_dst - (top_left << s->sps->pixel_shift),
src - stride_src - (top_left << s->sps->pixel_shift),
(top_left + width + top_right) << s->sps->pixel_shift);
else {
if (top_left)
memcpy( dst - stride_dst - (1 << s->sps->pixel_shift),
src - stride_src - (1 << s->sps->pixel_shift),
1 << s->sps->pixel_shift);
if(top_right)
memcpy( dst - stride_dst + (width << s->sps->pixel_shift),
src - stride_src + (width << s->sps->pixel_shift),
1 << s->sps->pixel_shift);
}
}
if (!edges[3]) { // bottom and bottom right
uint8_t bottom_left = !edges[0] && (CTB(s->sao, x_ctb-1, y_ctb+1).type_idx[c_idx] != SAO_APPLIED);
memcpy( dst + height * stride_dst - (bottom_left << s->sps->pixel_shift),
src + height * stride_src - (bottom_left << s->sps->pixel_shift),
(width + 1 + bottom_left) << s->sps->pixel_shift);
}
copy_CTB(dst - (left_pixels << s->sps->pixel_shift),
src - (left_pixels << s->sps->pixel_shift),
(width + 1 + left_pixels) << s->sps->pixel_shift, height, stride_dst, stride_src);
s->hevcdsp.sao_edge_filter[restore](src, dst,
stride_src, stride_dst,
sao,
edges, width,
height, c_idx,
vert_edge,
horiz_edge,
diag_edge);
restore_tqb_pixels(s, x, y, width, height, c_idx);
sao->type_idx[c_idx] = SAO_APPLIED;
break;
}
}
}
}
从源代码可以看出,sao_filter_CTB()根据SAO滤波的类型不同作不同的处理:
(1)滤波类型为边带补偿SAO_BAND的时候,调用HEVCDSPContext-> sao_band_filter()进行滤波。
(2)滤波类型为边界补偿SAO_EDGE的时候,调用HEVCDSPContext-> sao_edge_filter()进行滤波。
环路滤波知识
本章记录HEVC中两种环路滤波技术:DeBlock(去块效应)滤波和SAO(样点自适应补偿)滤波。
DeBlock(去块效应)滤波
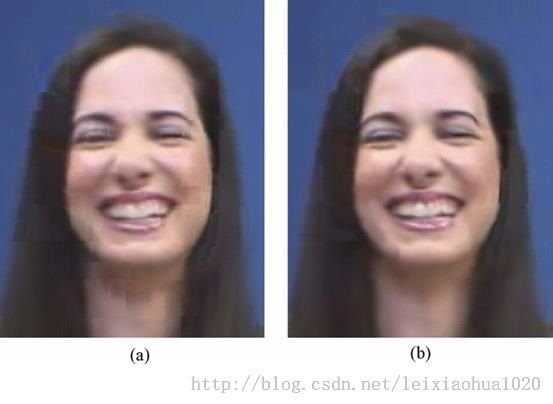
去块效应滤波器用于去除视频中的块效应。HEVC的去块效应滤波器和H.264中的去块效应滤波器是类似的。下面四幅图显示了HEVC中去块效应滤波器的效果。左边的两幅图是没有使用去块效应滤波器的解码图像,而右边的两幅图是使用了去块效应滤波器的图像。在HEVC中,去块效应滤波是以8x8的块为单位的,注意在实际处理的时候是将8x8的块边界上的像素分成2个4x4块独立进行处理的。其中边界强度Bs会影响滤波过程中的阈值。边界强度Bs可以取值为0、1、2,该值越大代表滤波的强度越大。边界强度的判断依据来自于边界两边P和Q两个4x4块的信息。其判定方式如下:
条件(针对两边的图像块) |
Bs |
P或Q采用帧内预测 |
2 |
P或Q满足一项条件:有非0变换系数; 使用不同的参考帧;MV个数不同;MV差值的绝对值大于4。 |
1 |
其它 |
0 |
滤波开关决策
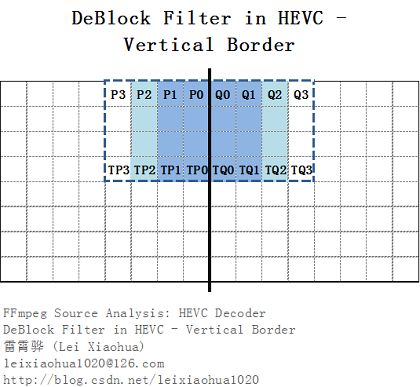
除了边界强度判断,滤波的过程中还包括了一个滤波开关决策。如果满足开关条件,才进行滤波。滤波开关决策判定的时候只取了P和Q最上面一行和最下面一行像素的值(P3、P2…等以及TP3、TP2…等)而没有使用中间两行像素的值,如下图所示。
定义了dp0、dq0、dp3、dq3四个值分别代表了P、Q最上面1行和最下面1行像素的值的变化率(即变化的剧烈程度),如下式所示。
滤波强弱的选择
“滤波强弱”和“边界强弱”要区分开。“边界强弱”影响滤波公式的阈值,而“滤波强弱”决定了滤波公式。滤波强弱可以分成强滤波和普通滤波两种。强滤波需要满足下面公式,否则就是普通滤波:
其中(1)(2)用于判断两边像素值变化率;(3)(4)用于判断两侧像素是否平坦;(5)(6)用于判断边界处像素跨度是否太大。beta的取值在前文已经叙述,tc的取值和beta类似,也是与两侧块的QP有关,可以通过查表得到,不再详细记录。
[强滤波]
强滤波会改变边界两边6个点的值,这些点的计算公式如下所示。可以看出P0、Q0的系数为(1,2,2,2,1)>>3;P1、Q1的系数为(1,1,1,1)>>2;P2、Q2的系数为(2,3,1,1,1)>>3。其中tc2=tc*2。
[普通滤波]
普通滤波会改变边界两边至多4个点的值。再滤波之前首先计算边界处像素的变化程度delta0来确定P0、Q0是否需要滤波:
SAO(样点自适应补偿)滤波
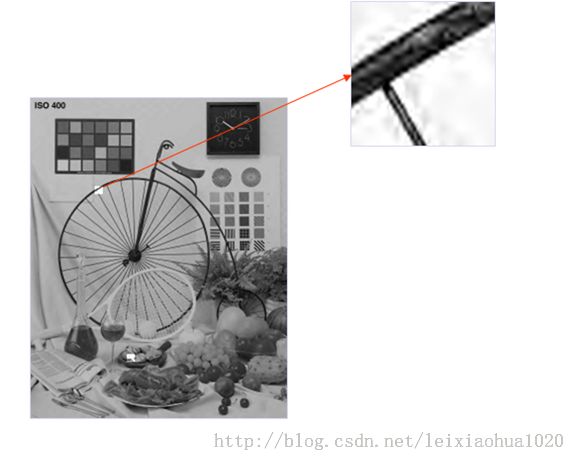
HEVC中允许使用较大的块进行DCT变换,这一方面能够提供更好的能量集中效果,但是另一方面在量化后却会带来更多的振铃效应。典型的振铃效应如下图所示。SAO(样点自适应补偿)滤波就是为消除这种振铃效应而设计的。它通过对重建图像的分类,对每一类图像像素值加减一个偏移,达到减少失真的目的。在HEVC中包含了两种像素值补偿方法:边界补偿(Edge Offset,EO)以及边带补偿(Band Offset,BO)。在HEVC中SAO是以CTU为基本单位的。边界补偿(EO)
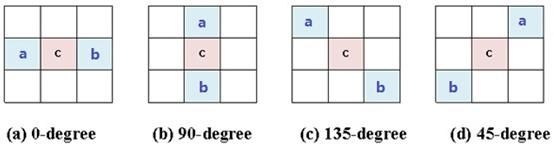
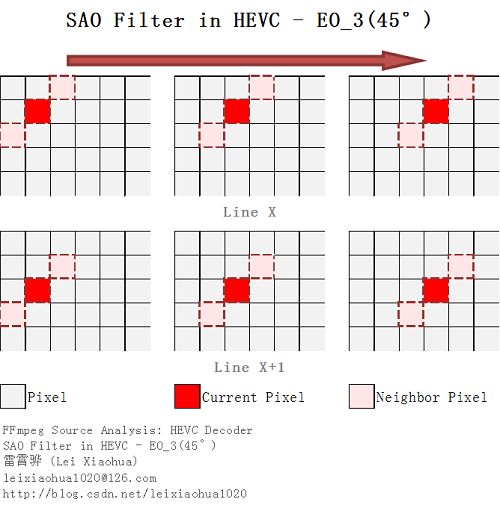
边界补偿通过比较和当前像素相邻的2个像素点的值,对像素点进行归类。然后将同类像素补偿同样的值。根据相邻像素的位置不同,边界补偿分成了4种模板:水平方向(EO_0)、垂直方向(EO_1)、135度方向(EO_2)、45度方向(EO_3)。这4种模板相邻像素的位置如下图所示。
在任意一种模板下,可以根据以下条件将所有像素划分为5类:
(1)种类1:c<a且c<b
(2)种类2:c<a且c==b,或者c==a且c<b
(3)种类3:c>a且c==b,或者c==a且c>b
(4)种类4:c>a且c<b
(5)种类5:其它
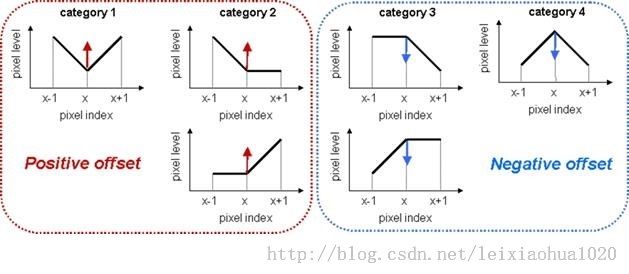
上述五种类型中的前4种的像素取值关系如下图所示。从图中可以看出:种类1的像素值为“凸”型,种类2的像素值为“半凸”型,种类3的像素值为“半凹”型,种类4的像素值为“凹”型。
边界补偿的过程中,对于种类1和种类2的补偿值大于等于0,对于种类3和种类4的补偿值小于等于0,对于种类5则不进行补偿。下图显示了解码时候的SAO滤波过程。图中选用了边界补偿(EO)方法的45度方向(EO_3)模板逐个比较每个像素,得到它们的分类,并将不同的分类叠加上不同的值。
边带补偿(BO)
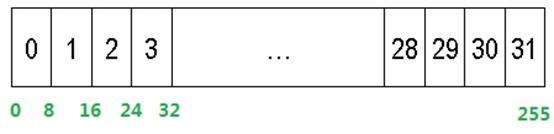
边带补偿根据像素值对像素进行归类。它将像素范围等分为32个边带。例如对于8bit图像来说,像素取值0-255,这样每个边带包含8个像素值,如下图所示。
对于每个边带中的像素,使用相同的补偿值。HEVC中规定,CTB只能选择4条连续的边带并对其像素进行补偿。这样在编码的时候只需要传递最小边带号和4个补偿值就可以了。
环路滤波实例
本节以一段《Sintel》动画的码流为例,看一下HEVC码流中的环路滤波相关的信息。
【去块效应滤波】下图为一个解码后的图像。
图中的网格标记了去块效应滤波的位置。其中红色的边界代表了无需去块效应滤波的边界。
下图选择了一个具体的8x8的CU,看一下其中的具体信息。
下图显示了选择的8x8 CU的具体信息。图中黄色的像素值代表了经过去块效应滤波修正之后的像素值。
下图中灰色方框中的数值是相应位置上没有经过去块效应滤波修正的像素值。可以看出垂直边界最下面位置两边原来的数值是“222”和“220”,而经过去块效应滤波之后,这两个数值变成了“221”和“221”。
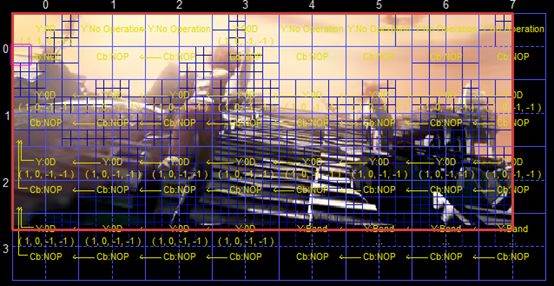
【SAO滤波】
下图为一个解码后的图像。
图中记录了每个CTU的SAO滤波相关的参数。
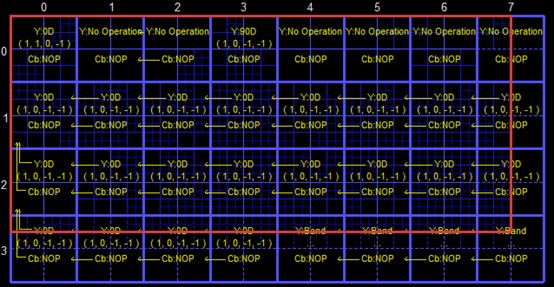
上图看的不太清晰,去掉图像内容后的信息如下图所示。图中记录了每个CTU使用的边界补偿的模板,以及4类像素的补偿值。在这里需要注意SAO滤波和去块效应滤波的基本单位是不一样的。SAO滤波是以CTU为基本单位的。
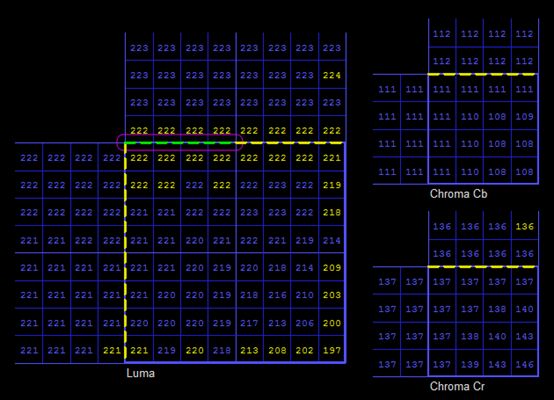
下面选择图像中一个具体的CU,看一下详细的信息。
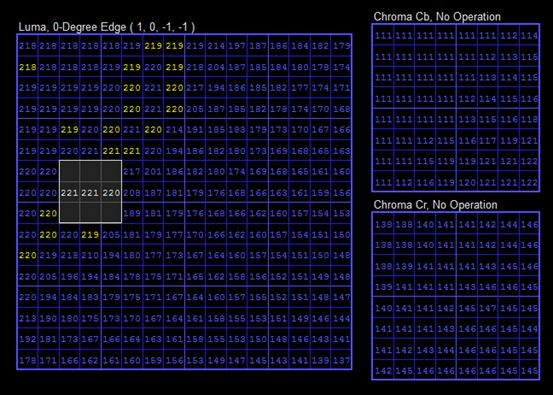
CU的像素信息如下所示。该CU采用了水平方向(EO_0)模板,4类像素的补偿值依次为(1,0,-1,-1)。图中黄色的像素值代表了经过SAO补偿之后的像素值。
下图灰色框中的内容为SAO补偿之前的像素值。可以看出3个像素值的取值依次为“221”、“221”、“220”,这三个值属于“半凸”型的种类(种类3),应该补偿“-1”。对比上图可知补偿后中间像素的值为“220”。
环路滤波相关的汇编函数
环路滤波相关的汇编函数位于HEVCDSPContext中。HEVCDSPContext的初始化函数是ff_hevc_dsp_init()。该函数对HEVCDSPContext结构体中的函数指针进行了赋值。FFmpeg HEVC解码器运行的过程中只要调用HEVCDSPContext的函数指针就可以完成相应的功能。ff_hevc_dsp_init()
ff_hevc_dsp_init()用于初始化HEVCDSPContext结构体中的汇编函数指针。该函数的定义如下所示。void ff_hevc_dsp_init(HEVCDSPContext *hevcdsp, int bit_depth)
{
#undef FUNC
#define FUNC(a, depth) a ## _ ## depth
#undef PEL_FUNC
#define PEL_FUNC(dst1, idx1, idx2, a, depth) \
for(i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) \
{ \
hevcdsp->dst1[i][idx1][idx2] = a ## _ ## depth; \
}
#undef EPEL_FUNCS
#define EPEL_FUNCS(depth) \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel, 0, 1, put_hevc_epel_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel, 1, 0, put_hevc_epel_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel, 1, 1, put_hevc_epel_hv, depth)
#undef EPEL_UNI_FUNCS
#define EPEL_UNI_FUNCS(depth) \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_uni_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni, 0, 1, put_hevc_epel_uni_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni, 1, 0, put_hevc_epel_uni_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni, 1, 1, put_hevc_epel_uni_hv, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni_w, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_uni_w_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni_w, 0, 1, put_hevc_epel_uni_w_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni_w, 1, 0, put_hevc_epel_uni_w_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_uni_w, 1, 1, put_hevc_epel_uni_w_hv, depth)
#undef EPEL_BI_FUNCS
#define EPEL_BI_FUNCS(depth) \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_bi_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi, 0, 1, put_hevc_epel_bi_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi, 1, 0, put_hevc_epel_bi_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi, 1, 1, put_hevc_epel_bi_hv, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi_w, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_bi_w_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi_w, 0, 1, put_hevc_epel_bi_w_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi_w, 1, 0, put_hevc_epel_bi_w_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_epel_bi_w, 1, 1, put_hevc_epel_bi_w_hv, depth)
#undef QPEL_FUNCS
#define QPEL_FUNCS(depth) \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel, 0, 1, put_hevc_qpel_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel, 1, 0, put_hevc_qpel_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel, 1, 1, put_hevc_qpel_hv, depth)
#undef QPEL_UNI_FUNCS
#define QPEL_UNI_FUNCS(depth) \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_uni_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni, 0, 1, put_hevc_qpel_uni_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni, 1, 0, put_hevc_qpel_uni_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni, 1, 1, put_hevc_qpel_uni_hv, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni_w, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_uni_w_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni_w, 0, 1, put_hevc_qpel_uni_w_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni_w, 1, 0, put_hevc_qpel_uni_w_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_uni_w, 1, 1, put_hevc_qpel_uni_w_hv, depth)
#undef QPEL_BI_FUNCS
#define QPEL_BI_FUNCS(depth) \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_bi_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi, 0, 1, put_hevc_qpel_bi_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi, 1, 0, put_hevc_qpel_bi_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi, 1, 1, put_hevc_qpel_bi_hv, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi_w, 0, 0, put_hevc_pel_bi_w_pixels, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi_w, 0, 1, put_hevc_qpel_bi_w_h, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi_w, 1, 0, put_hevc_qpel_bi_w_v, depth); \
PEL_FUNC(put_hevc_qpel_bi_w, 1, 1, put_hevc_qpel_bi_w_hv, depth)
#define HEVC_DSP(depth) \
hevcdsp->put_pcm = FUNC(put_pcm, depth); \
hevcdsp->transform_add[0] = FUNC(transform_add4x4, depth); \
hevcdsp->transform_add[1] = FUNC(transform_add8x8, depth); \
hevcdsp->transform_add[2] = FUNC(transform_add16x16, depth); \
hevcdsp->transform_add[3] = FUNC(transform_add32x32, depth); \
hevcdsp->transform_skip = FUNC(transform_skip, depth); \
hevcdsp->transform_rdpcm = FUNC(transform_rdpcm, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct_4x4_luma = FUNC(transform_4x4_luma, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct[0] = FUNC(idct_4x4, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct[1] = FUNC(idct_8x8, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct[2] = FUNC(idct_16x16, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct[3] = FUNC(idct_32x32, depth); \
\
hevcdsp->idct_dc[0] = FUNC(idct_4x4_dc, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct_dc[1] = FUNC(idct_8x8_dc, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct_dc[2] = FUNC(idct_16x16_dc, depth); \
hevcdsp->idct_dc[3] = FUNC(idct_32x32_dc, depth); \
\
hevcdsp->sao_band_filter = FUNC(sao_band_filter_0, depth); \
hevcdsp->sao_edge_filter[0] = FUNC(sao_edge_filter_0, depth); \
hevcdsp->sao_edge_filter[1] = FUNC(sao_edge_filter_1, depth); \
\
QPEL_FUNCS(depth); \
QPEL_UNI_FUNCS(depth); \
QPEL_BI_FUNCS(depth); \
EPEL_FUNCS(depth); \
EPEL_UNI_FUNCS(depth); \
EPEL_BI_FUNCS(depth); \
\
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_luma = FUNC(hevc_h_loop_filter_luma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_luma = FUNC(hevc_v_loop_filter_luma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma = FUNC(hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma = FUNC(hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_c = FUNC(hevc_h_loop_filter_luma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_c = FUNC(hevc_v_loop_filter_luma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma_c = FUNC(hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma, depth); \
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma_c = FUNC(hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma, depth)
int i = 0;
switch (bit_depth) {
case 9:
HEVC_DSP(9);
break;
case 10:
HEVC_DSP(10);
break;
case 12:
HEVC_DSP(12);
break;
default:
HEVC_DSP(8);
break;
}
if (ARCH_X86)
ff_hevc_dsp_init_x86(hevcdsp, bit_depth);
}
从源代码可以看出,ff_hevc_dsp_init()函数中包含一个名为“HEVC_DSP(depth)”的很长的宏定义。该宏定义中包含了C语言版本的各种函数的初始化代码。ff_hevc_dsp_init()会根据系统的颜色位深bit_depth初始化相应的C语言版本的函数。在函数的末尾则包含了汇编函数的初始化函数:如果系统是X86架构的,则会调用ff_hevc_dsp_init_x86()初始化X86平台下经过汇编优化的函数。下面以8bit颜色位深为例,看一下“HEVC_DSP(8)”的展开结果中和环路滤波相关的函数。
hevcdsp->sao_band_filter = sao_band_filter_0_8;
hevcdsp->sao_edge_filter[0] = sao_edge_filter_0_8;
hevcdsp->sao_edge_filter[1] = sao_edge_filter_1_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_luma = hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_luma = hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma = hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma = hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_c = hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_c = hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma_c = hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma_8;
hevcdsp->hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma_c = hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma_8通过上述代码可以总结出下面几个用于环路滤波的函数:
HEVCDSPContext->sao_band_filter():SAO滤波边带补偿函数。C语言版本函数为sao_band_filter_0_8()下文例举其中的几个函数进行分析。
HEVCDSPContext->sao_edge_filter[]():SAO滤波边界补偿函数。C语言版本函数为sao_edge_filter_0_8()等
HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_h_loop_filter_luma():去块效应滤波水平边界亮度处理函数。C语言版本函数为hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8()
HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_v_loop_filter_luma():去块效应滤波垂直边界亮度处理函数。C语言版本函数为hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8()
HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma():去块效应滤波水平边界色度处理函数。C语言版本函数为hevc_h_loop_filter_chroma_8()
HEVCDSPContext-> hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma():去块效应滤波水平边界色度处理函数。C语言版本函数为hevc_v_loop_filter_chroma_8()
去块效应滤波器汇编函数
下面记录一下C语言版本去块效应滤波器亮度处理函数hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8()和hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8()。
hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8()
hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8()是处理垂直边界亮度数据的去块效应滤波器。该函数的定义如下所示。//滤波垂直边界的滤波器
//
// |
// P2 P1 P0 | Q0 Q1 Q2
// |
//
static void FUNC(hevc_v_loop_filter_luma)(uint8_t *pix, ptrdiff_t stride,
int beta, int32_t *tc, uint8_t *no_p,
uint8_t *no_q)
{
//xstrice=1
//ystride=stride
FUNC(hevc_loop_filter_luma)(pix, sizeof(pixel), stride,
beta, tc, no_p, no_q);
}
从源代码可以看出,hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8()调用了另一个函数hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()。需要注意传递给hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()的第2个参数stride取值为1,而第3个参数ystride取值为stride。
hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()
hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()完成了具体的去块效应滤波工作。该函数的定义如下所示。/*
* 滤波开关决策点
*
* P(4x4) Q(4x4)
* +----------------++-----------------+
* (0) | P3 P2 P1 P0 || Q0 Q1 Q2 Q3 |
* (1) | || |
* (2) | || |
* (3) |TP3 TP2 TP1 TP0 || TQ0 TQ1 TQ2 TQ3 |
* +----------------++-----------------+
*
*/
// line zero
//第0行(边界两边4x4块的第1行)
#define P3 pix[-4 * xstride]
#define P2 pix[-3 * xstride]
#define P1 pix[-2 * xstride]
#define P0 pix[-1 * xstride]
#define Q0 pix[0 * xstride]
#define Q1 pix[1 * xstride]
#define Q2 pix[2 * xstride]
#define Q3 pix[3 * xstride]
// line three. used only for deblocking decision
//第3行(边界两边4x4块的最后1行)
#define TP3 pix[-4 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TP2 pix[-3 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TP1 pix[-2 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TP0 pix[-1 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TQ0 pix[0 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TQ1 pix[1 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TQ2 pix[2 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
#define TQ3 pix[3 * xstride + 3 * ystride]
//环路滤波器-亮度
static void FUNC(hevc_loop_filter_luma)(uint8_t *_pix,
ptrdiff_t _xstride, ptrdiff_t _ystride,
int beta, int *_tc,
uint8_t *_no_p, uint8_t *_no_q)
{
/*
* 去块效应滤波是对8x8的块边界进行处理
* 边界强度是通过位于边界两边4x4的块P、Q来判断
*
* 【水平边界】
* ystride=1
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+ +
* | P | |
* +----+----+
* | Q | |
* +----+ +
* | |
* +----+----+
*
* 【垂直边界】
* xstride=1
* +----+----+----+----+
* | | P | Q | |
* | +----+----+ |
* | | |
* +----+----+----+----+
*
*/
int d, j;
pixel *pix = (pixel *)_pix;
ptrdiff_t xstride = _xstride / sizeof(pixel);
ptrdiff_t ystride = _ystride / sizeof(pixel);
beta <<= BIT_DEPTH - 8;
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
//都是用于滤波开关决策
//dp0,dq0,dp3,dq3都代表了像素值的变化率
//例如dp0=abs((P2-P1)-(P1-P0))=abs(P2 - 2 * P1 + P0)
//P块0行变化率
const int dp0 = abs(P2 - 2 * P1 + P0);
//Q块0行变化率
const int dq0 = abs(Q2 - 2 * Q1 + Q0);
//P块3行变化率
const int dp3 = abs(TP2 - 2 * TP1 + TP0);
//Q块3行变化率
const int dq3 = abs(TQ2 - 2 * TQ1 + TQ0);
const int d0 = dp0 + dq0;
const int d3 = dp3 + dq3;
const int tc = _tc[j] << (BIT_DEPTH - 8);
const int no_p = _no_p[j];
const int no_q = _no_q[j];
//纹理度Cb=d0+d3=dp0+dq0+dp3+dq3
//Cb代表了区域的平坦程度,当区域很不平坦的时候,就不用滤波了
if (d0 + d3 >= beta) {
pix += 4 * ystride;
continue;
} else {
const int beta_3 = beta >> 3;
const int beta_2 = beta >> 2;
const int tc25 = ((tc * 5 + 1) >> 1);
//判断是否满足强滤波条件
if (abs(P3 - P0) + abs(Q3 - Q0) < beta_3 && abs(P0 - Q0) < tc25 &&
abs(TP3 - TP0) + abs(TQ3 - TQ0) < beta_3 && abs(TP0 - TQ0) < tc25 &&
(d0 << 1) < beta_2 && (d3 << 1) < beta_2) {
// strong filtering
// 强滤波
// 修改边界两边一共6个点的像素-一共涉及到8个点的计算
// av_clip() 用于限幅
const int tc2 = tc << 1;
// 循环滤波4个点
for (d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
const int p3 = P3;
const int p2 = P2;
const int p1 = P1;
const int p0 = P0;
const int q0 = Q0;
const int q1 = Q1;
const int q2 = Q2;
const int q3 = Q3;
//p和q的滤波公式
if (!no_p) {
P0 = p0 + av_clip(((p2 + 2 * p1 + 2 * p0 + 2 * q0 + q1 + 4) >> 3) - p0, -tc2, tc2);
P1 = p1 + av_clip(((p2 + p1 + p0 + q0 + 2) >> 2) - p1, -tc2, tc2);
P2 = p2 + av_clip(((2 * p3 + 3 * p2 + p1 + p0 + q0 + 4) >> 3) - p2, -tc2, tc2);
}
if (!no_q) {
Q0 = q0 + av_clip(((p1 + 2 * p0 + 2 * q0 + 2 * q1 + q2 + 4) >> 3) - q0, -tc2, tc2);
Q1 = q1 + av_clip(((p0 + q0 + q1 + q2 + 2) >> 2) - q1, -tc2, tc2);
Q2 = q2 + av_clip(((2 * q3 + 3 * q2 + q1 + q0 + p0 + 4) >> 3) - q2, -tc2, tc2);
}
pix += ystride;
}
} else {
// normal filtering
// 普通滤波
// 修改边界两边一共4个点的像素-一共涉及到6个点的计算
int nd_p = 1;
int nd_q = 1;
const int tc_2 = tc >> 1;
if (dp0 + dp3 < ((beta + (beta >> 1)) >> 3))
nd_p = 2;
if (dq0 + dq3 < ((beta + (beta >> 1)) >> 3))
nd_q = 2;
for (d = 0; d < 4; d++) {
const int p2 = P2;
const int p1 = P1;
const int p0 = P0;
const int q0 = Q0;
const int q1 = Q1;
const int q2 = Q2;
int delta0 = (9 * (q0 - p0) - 3 * (q1 - p1) + 8) >> 4;
//判断该行像素是否需要修正
//delta0较大,说明边界处变化程度较大,则不需要修正
if (abs(delta0) < 10 * tc) {
delta0 = av_clip(delta0, -tc, tc);
//修正P0和Q0
if (!no_p)
P0 = av_clip_pixel(p0 + delta0);
if (!no_q)
Q0 = av_clip_pixel(q0 - delta0);
//修正P1和Q1
if (!no_p && nd_p > 1) {
const int deltap1 = av_clip((((p2 + p0 + 1) >> 1) - p1 + delta0) >> 1, -tc_2, tc_2);
P1 = av_clip_pixel(p1 + deltap1);
}
if (!no_q && nd_q > 1) {
const int deltaq1 = av_clip((((q2 + q0 + 1) >> 1) - q1 - delta0) >> 1, -tc_2, tc_2);
Q1 = av_clip_pixel(q1 + deltaq1);
}
}
pix += ystride;
}
}
}
}
}
从源代码中可以看出,hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()完成了前文记录的去块效应滤波的公式。由于源代码中已经做了比较详细的注释,在这里就不在详细叙述了。
hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8()
hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8()是处理水平边界亮度数据的去块效应滤波器。该函数的定义如下所示。//滤波水平边界的滤波器
// P2
// P1
// P0
// -----------
// Q0
// Q1
// Q2
static void FUNC(hevc_h_loop_filter_luma)(uint8_t *pix, ptrdiff_t stride,
int beta, int32_t *tc, uint8_t *no_p,
uint8_t *no_q)
{
//xstrice=stride
//ystride=1
FUNC(hevc_loop_filter_luma)(pix, stride, sizeof(pixel),
beta, tc, no_p, no_q);
}
从源代码可以看出,hevc_h_loop_filter_luma_8()和hevc_v_loop_filter_luma_8()的逻辑是类似的,都调用了hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()。唯一的不同在于它传递给hevc_loop_filter_luma_8()的第2个参数stride取值为stride,而第3个参数ystride取值为1。
SAO(采样自适应偏移)滤波器汇编函数
下面记录一下C语言版SAO滤波器边界补偿函数sao_edge_filter_0_8()和边带补偿函数sao_band_filter_0_8()。sao_edge_filter_0_8()
sao_edge_filter_0_8()用于进行SAO滤波中的边界补偿。该函数的定义如下所示。//SAO滤波-边界补偿-0
static void FUNC(sao_edge_filter_0)(uint8_t *_dst, uint8_t *_src,
ptrdiff_t stride_dst, ptrdiff_t stride_src, SAOParams *sao,
int *borders, int _width, int _height,
int c_idx, uint8_t *vert_edge,
uint8_t *horiz_edge, uint8_t *diag_edge)
{
int x, y;
pixel *dst = (pixel *)_dst;
pixel *src = (pixel *)_src;
int16_t *sao_offset_val = sao->offset_val[c_idx];
int sao_eo_class = sao->eo_class[c_idx];
int init_x = 0, init_y = 0, width = _width, height = _height;
stride_dst /= sizeof(pixel);
stride_src /= sizeof(pixel);
if (sao_eo_class != SAO_EO_VERT) {
if (borders[0]) {
int offset_val = sao_offset_val[0];
for (y = 0; y < height; y++) {
dst[y * stride_dst] = av_clip_pixel(src[y * stride_src] + offset_val);
}
init_x = 1;
}
if (borders[2]) {
int offset_val = sao_offset_val[0];
int offset = width - 1;
for (x = 0; x < height; x++) {
dst[x * stride_dst + offset] = av_clip_pixel(src[x * stride_src + offset] + offset_val);
}
width--;
}
}
if (sao_eo_class != SAO_EO_HORIZ) {
if (borders[1]) {
int offset_val = sao_offset_val[0];
for (x = init_x; x < width; x++)
dst[x] = av_clip_pixel(src[x] + offset_val);
init_y = 1;
}
if (borders[3]) {
int offset_val = sao_offset_val[0];
int y_stride_dst = stride_dst * (height - 1);
int y_stride_src = stride_src * (height - 1);
for (x = init_x; x < width; x++)
dst[x + y_stride_dst] = av_clip_pixel(src[x + y_stride_src] + offset_val);
height--;
}
}
//边界补偿-内部函数
FUNC(sao_edge_filter)((uint8_t *)dst, (uint8_t *)src, stride_dst, stride_src, sao, width, height, c_idx, init_x, init_y);
}
从源代码可以看出,sao_edge_filter_0_8()调用了另外一个函数sao_edge_filter_8()完成具体的滤波工作。
sao_edge_filter_8()
sao_edge_filter_8()完成了具体的边带补偿工作。该函数的定义如下所示。#define CMP(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? 1 : ((a) == (b) ? 0 : -1))
//SAO滤波-边界补偿-内部函数
static void FUNC(sao_edge_filter)(uint8_t *_dst, uint8_t *_src,
ptrdiff_t stride_dst, ptrdiff_t stride_src, SAOParams *sao,
int width, int height,
int c_idx, int init_x, int init_y) {
static const uint8_t edge_idx[] = { 1, 2, 0, 3, 4 };
//4种边界补偿的方向信息
static const int8_t pos[4][2][2] = {
{ { -1, 0 }, { 1, 0 } }, // horizontal
{ { 0, -1 }, { 0, 1 } }, // vertical
{ { -1, -1 }, { 1, 1 } }, // 45 degree
{ { 1, -1 }, { -1, 1 } }, // 135 degree
};
//存储了补偿的数值
int16_t *sao_offset_val = sao->offset_val[c_idx];
//边界补偿模式,水平EO_0,垂直EO_1,135度EO_2,45度EO_3,
int sao_eo_class = sao->eo_class[c_idx];
pixel *dst = (pixel *)_dst;
pixel *src = (pixel *)_src;
int y_stride_src = init_y * stride_src;
int y_stride_dst = init_y * stride_dst;
//取出pos[]数组中的值
//例如边界补偿为EO_2的时候
// pos_0_0=-1
// pos_0_1=-1
// pos_1_0=1
// pos_1_1=1
//
int pos_0_0 = pos[sao_eo_class][0][0];
int pos_0_1 = pos[sao_eo_class][0][1];
int pos_1_0 = pos[sao_eo_class][1][0];
int pos_1_1 = pos[sao_eo_class][1][1];
int x, y;
//例如边界补偿为EO_2的时候
// y_stride_0_1=(init_y - 1) * stride_src
// y_stride_1_1=(init_y + 1) * stride_src
//
int y_stride_0_1 = (init_y + pos_0_1) * stride_src;
int y_stride_1_1 = (init_y + pos_1_1) * stride_src;
//依次处理每个点
for (y = init_y; y < height; y++) {
for (x = init_x; x < width; x++) {
/*
* EO_2的时候
*
* 1
* X
* 2
*
* x lines
* | |
* 1: src[x + pos_0_0 + y_stride_0_1]
* 2: src[x + pos_1_0 + y_stride_1_1]
*
*/
//CMP(a,b)的结果。若a>b则取1,a==b择取0,a<b择取-1
int diff0 = CMP(src[x + y_stride_src], src[x + pos_0_0 + y_stride_0_1]);
int diff1 = CMP(src[x + y_stride_src], src[x + pos_1_0 + y_stride_1_1]);
//根据取值判断像素类型:(1)"\/" (2)"\_"或"_/" (3)"/ˉ"或"ˉ\" (4)"/\" (5)其它
int offset_val = edge_idx[2 + diff0 + diff1];
//补偿,从sao_offset_val[]中取值
dst[x + y_stride_dst] = av_clip_pixel(src[x + y_stride_src] + sao_offset_val[offset_val]);
}
y_stride_src += stride_src;
y_stride_dst += stride_dst;
y_stride_0_1 += stride_src;
y_stride_1_1 += stride_src;
}
}
从源代码中可以看出,sao_edge_filter_8()完成了前文记录的SAO滤波中的边带补偿功能。由于源代码中已经做了比较详细的注释,在这里就不在详细叙述了。
sao_band_filter_0_8()
sao_band_filter_0_8()用于进行SAO滤波中的边带补偿。该函数的定义如下所示。//SAO滤波-边带补偿
static void FUNC(sao_band_filter_0)(uint8_t *_dst, uint8_t *_src,
ptrdiff_t stride_dst, ptrdiff_t stride_src, SAOParams *sao,
int *borders, int width, int height,
int c_idx)
{
pixel *dst = (pixel *)_dst;
pixel *src = (pixel *)_src;
int offset_table[32] = { 0 };
int k, y, x;
int shift = BIT_DEPTH - 5;
//4条连续边带的补偿值
int16_t *sao_offset_val = sao->offset_val[c_idx];
//需要补偿的边带序号
int sao_left_class = sao->band_position[c_idx];
stride_dst /= sizeof(pixel);
stride_src /= sizeof(pixel);
//offset_table[]存储了32个边带中每个边带需要补偿的值
//只有4个边带是需要补偿的,其它边带补偿值为0
for (k = 0; k < 4; k++)
offset_table[(k + sao_left_class) & 31] = sao_offset_val[k + 1];
//逐个像素点处理,进行补偿
for (y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (x = 0; x < width; x++)
dst[x] = av_clip_pixel(src[x] + offset_table[src[x] >> shift]);//根据边带的取值,加上不同的补偿值
dst += stride_dst;
src += stride_src;
}
}
从源代码中可以看出,sao_band_filter_0_8()完成了前文记录的SAO滤波中的边带补偿功能。由于源代码中已经做了比较详细的注释,在这里就不在详细叙述了。
至此有关FFmpeg HEVC解码器中的环路滤波部分的源代码就分析完毕了。
雷霄骅
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020