nginx 源码学习笔记(十四)—— 全局变量ngx_cycle
再打算正式开始研究core模块式,发现有一个很重要的变量ngx_cycle_t,一直伴随,如果不懂ngx_cycle可能读起代码来回非常困难,这里就来详细学习一下吧。本文大部分灵感来自于。http://blog.csdn.net/livelylittlefish/article/details/7247080 和http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_677be95b0100iivi.html 谢谢作者提供很详细的资料。
依照惯例我们直接来看下
/src/core/ngx_cycle.h
struct ngx_cycle_s {
void ****conf_ctx; //配置上下文数组(含所有模块)
ngx_pool_t *pool; //内存池
ngx_log_t *log; //日志
ngx_log_t new_log;
ngx_connection_t **files; //连接文件
ngx_connection_t *free_connections; //空闲连接
ngx_uint_t free_connection_n; //空闲连接个数
ngx_queue_t reusable_connections_queue; //再利用连接队列
ngx_array_t listening; //监听数组
ngx_array_t pathes; //路径数组
ngx_list_t open_files; //打开文件链表
ngx_list_t shared_memory; //共享内存链表
ngx_uint_t connection_n; //连接个数
ngx_uint_t files_n; //打开文件个数
ngx_connection_t *connections; //连接
ngx_event_t *read_events; //读事件
ngx_event_t *write_events; //写事件
ngx_cycle_t *old_cycle; //old cycle指针
ngx_str_t conf_file; //配置文件
ngx_str_t conf_param; //配置参数
ngx_str_t conf_prefix; //配置前缀
ngx_str_t prefix; //前缀
ngx_str_t lock_file; //锁文件
ngx_str_t hostname; //主机名
};
其中,
- pathes数组元素结构为ngx_path_t;
- open_files链表元素结构为ngx_open_file_t;
- shared_memory链表元素结构为ngx_shm_zone_t;
- listening数组元素结构为ngx_listening_t,该数组用来存放监听套接字。
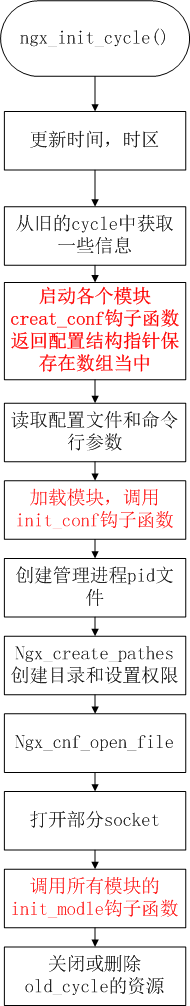
再来看下ngx_init_cycle函数的处理过程:
1.调用ngx_timezone_update()、ngx_timeofday()和ngx_time_update(0, 0)做时间校准;
2.创建一个新的ngx_cycle_t变量cycle,并且初始化其大部分的成员字段,有一些是从传入的old_cycle直接拷贝过来的,这些字段包括:log,conf_prefix,prefix,conf_file,conf_param;
src/core/ngx_cycle.c
cycle->pool = pool;
cycle->log = log;
cycle->new_log.log_level = NGX_LOG_ERR;
cycle->old_cycle = old_cycle;
cycle->conf_prefix.len = old_cycle->conf_prefix.len;
cycle->conf_prefix.data = ngx_pstrdup(pool, &old_cycle->conf_prefix);
cycle->prefix.len = old_cycle->prefix.len;
cycle->prefix.data = ngx_pstrdup(pool, &old_cycle->prefix);
cycle->conf_file.len = old_cycle->conf_file.len;
cycle->conf_file.data = ngx_pnalloc(pool, old_cycle->conf_file.len + 1);
ngx_cpystrn(cycle->conf_file.data, old_cycle->conf_file.data,
old_cycle->conf_file.len + 1);
cycle->conf_param.len = old_cycle->conf_param.len;
cycle->conf_param.data = ngx_pstrdup(pool, &old_cycle->conf_param);
还有一些字段会判断一下old_cycle中是否存在,如果存在,则取得这些字段的占用空间,在cycle中申请等大的空间,并初始化(不拷贝),否则就申请默认大小的空间,这些字段有:pathes,open_files,share_memory,listening;
src/core/ngx_cycle.c
n = old_cycle->pathes.nelts ? old_cycle->pathes.nelts : 10;
cycle->pathes.elts = ngx_pcalloc(pool, n * sizeof(ngx_path_t *));
cycle->pathes.nelts = 0;
cycle->pathes.size = sizeof(ngx_path_t *);
cycle->pathes.nalloc = n;
cycle->pathes.pool = pool;
if (old_cycle->open_files.part.nelts) {
n = old_cycle->open_files.part.nelts;
for (part = old_cycle->open_files.part.next; part; part = part->next) {
n += part->nelts;
}
} else {
n = 20;
}
if (ngx_list_init(&cycle->open_files, pool, n, sizeof(ngx_open_file_t))
!= NGX_OK)
{
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
if (old_cycle->shared_memory.part.nelts) {
n = old_cycle->shared_memory.part.nelts;
for (part = old_cycle->shared_memory.part.next; part; part = part->next)
{
n += part->nelts;
}
} else {
n = 1;
}
if (ngx_list_init(&cycle->shared_memory, pool, n, sizeof(ngx_shm_zone_t))
!= NGX_OK)
{
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
n = old_cycle->listening.nelts ? old_cycle->listening.nelts : 10;
cycle->listening.elts = ngx_pcalloc(pool, n * sizeof(ngx_listening_t));
cycle->listening.nelts = 0;
cycle->listening.size = sizeof(ngx_listening_t);
cycle->listening.nalloc = n;
cycle->listening.pool = pool;
还有一些字段是重新创建或者第一次赋值的:pool,new_log.log_level(=NGX_LOG_ERR),old_cycle(=old_cycle),hostname(gethostname);
最重要的一个字段是conf_ctx,它被初始化为ngx_max_module个void *指针,这预示着conf_ctx是所有模块的配置结构的指针数组;
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (module->create_conf) {
rv = module->create_conf(cycle);//调用所有核心类模块的钩子create_conf
if (rv == NULL) {
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index] = rv;//返回的配置结构指针放到conf_ctx数组中,偏移位置为ngx_module_t.index
}
}
3.从命令行和配置文件中把所有配置更新到cycle的conf_ctx中:
首先调用ngx_conf_param把命令行中的指令(-g directives)转换为配置结构并把指针加入到cycle.conf_ctx中;
接着调用ngx_conf_parse(..,filename)把配置文件中的指令转换为配置结构并把指针加入到cycle.conf_ctx中。
conf.ctx = cycle->conf_ctx;
conf.cycle = cycle;
conf.pool = pool;
conf.log = log;
conf.module_type = NGX_CORE_MODULE;
conf.cmd_type = NGX_MAIN_CONF;
if (ngx_conf_param(&conf) != NGX_CONF_OK) {
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}
if (ngx_conf_parse(&conf, &cycle->conf_file) != NGX_CONF_OK) {
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}
ngx_conf_param最后也会调用ngx_conf_parse(..,NULL),所以配置的更新主要是在ngx_conf_parse中进行的,这个函数中有一个for循环,每次循环调用ngx_conf_read_token取得一个配置指令(以;结尾)(这里在上一节已经详细将结果),然后调用ngx_conf_handler处理这条指令,ngx_conf_handler每次都会遍历所有模块的指令集,查找这条配置指令并分析其合法性,如果指令正确,则会创建配置结构并把指针加入到cycle.conf_ctx中,配置结构的赋值是调用该指令的钩子set完成的。
遍历指令集的过程首先是遍历所有的核心类模块,若是event类的指令,则会遍历到ngx_events_module,这个模块是属于核心类的,其钩子set又会嵌套调用ngx_conf_parse去遍历所有的event类模块,同样的,若是http类指令,则会遍历到ngx_http_module,该模块的钩子set进一步遍历所有的http类模块,mail类指令会遍历到ngx_mail_module,该模块的钩子进一步遍历到所有的mail类模块。要特别注意的是:这三个遍历过程中会在适当的时机调用event类模块、http类模块和mail类模块的创建配置和初始化配置的钩子。从这里可以看出,event、http、mail三类模块的钩子是配置中的指令驱动的;4.调用所有核心类模块的钩子init_conf,把模块的配置结构作为一个参数传入:init_conf(cycle, cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index);
src/core/ngx_cycle.c
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (module->init_conf) {
if (module->init_conf(cycle, cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index])
== NGX_CONF_ERROR)
{
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}
}
}
5.获得核心模块ngx_core_dodule的配置结构,然后调用ngx_create_pidfile创建pid文件。获取配置结构的代码:ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module),这里的ngx_get_conf是一个宏定义:#define ngx_get_conf(conf_ctx, module) conf_ctx[module.index];
ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(cycle->conf_ctx, ngx_core_module);
if (ngx_test_config) {
if (ngx_create_pidfile(&ccf->pid, log) != NGX_OK) {
goto failed;
}
} else if (!ngx_is_init_cycle(old_cycle)) {
/*
* we do not create the pid file in the first ngx_init_cycle() call
* because we need to write the demonized process pid
*/
old_ccf = (ngx_core_conf_t *) ngx_get_conf(old_cycle->conf_ctx,
ngx_core_module);
if (ccf->pid.len != old_ccf->pid.len
|| ngx_strcmp(ccf->pid.data, old_ccf->pid.data) != 0)
{
/* new pid file name */
if (ngx_create_pidfile(&ccf->pid, log) != NGX_OK) {
goto failed;
}
ngx_delete_pidfile(old_cycle);
}
}
6.调用ngx_test_lockfile(filename,log),ngx_create_pathes(cycle,user),接着打开errorlog文件并赋值给cycle->new_log.file:cycle->new_log.file = ngx_conf_open_file(cycle, &error_log);
7.打开新文件,在第2步的时候提到cycle->open_files这个链表是空的,只是给它预先分配了空间,并没有数据,这里之所以可能会有文件被打开,估计是前面读配置文件的时候,调用各个钩子的过程中,填充了这个链表,把ngx_open_file_t结构变量填充进来(结构体中包含要打开文件的路径信息),这是我猜测的,之后再验证:)接着修改一下cycle的成员:cycle->log = &cycle->new_log;pool->log = &cycle->new_log;
8.创建共享内存,和open_files类似,在第2步的时候cycle->share_memory也初始化为一个空的链表,也是预分配了空间,如果此时链表中已经被填充了ngx_shm_zone_t结构变量(其中包含需要共享内存的尺寸和标识等信息),那么这里就会分配共享内存,并且调用合适的初始化钩子初始化分配的共享内存,每块共享内存都会有name标识,这里也会做一些排重,已经分配的就不会再去分配,从对open_files和share_memory的处理过程可以看出,nginx在资源管理上是集中分配的,请求资源的时候分配说明性的结构变量,然后在恰当的时机才去真正分配资源;
9.处理listening sockets,cycle->listening是ngx_listening_t结构的数组,把cycle->listening于old_cycle->listening进行比较,设置cycle->listening的一些状态信息,接着调用ngx_open_listening_sockets(cycle)启动cycle->listening中的所有监听socket,循环调用socket,bind,listen完成服务端监听socket的启动。接着调用ngx_configure_listening_sockets(cycle)配置监听socket,会根据ngx_listening_t中的状态信息设置socket的读写缓存和TCP_DEFER_ACCEPT;
10.调用所有模块的钩子init_module;
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->init_module) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->init_module(cycle) != NGX_OK) {
/* fatal */
exit(1);
}
}
}
11.关闭或者删除一些残留在old_cycle中的资源,首先释放不用的共享内存,接着关闭不使用的监听socket,再关闭不使用的打开文件,最后把old_cycle放入ngx_old_cycles中,这是一个ngx_cycle_t *的数组,最后设定一个定时器,定期回调ngx_cleaner_event清理ngx_old_cycles,这里设置了30000ms清理一次。
if (!ngx_cleaner_event.timer_set) {
ngx_add_timer(&ngx_cleaner_event, 30000);
ngx_cleaner_event.timer_set = 1;
}
放上一张图