Solr In Action
2. solrconfig.xml – Defines the main settings for a specific Solr core
3. schema.xml – Defines the structure of your index including fields and field types
<solr persistent="true"> #A
<logging enabled="true">
<watcher size="100" threshold="INFO" />
</logging>
<cores adminPath="/admin/cores" #B
defaultCoreName="collection1"
host="${host:}" hostPort="${jetty.port:}"
hostContext="${hostContext:}"
zkClientTimeout="${zkClientTimeout:15000}">
<core name="collection1" instanceDir="collection1" /> #C
</cores>
</solr>#A persistent attribute controls whether changes made from the core admin API are persisted to this file
#B define one or more cores under the <cores> element
#C the collection1 core configuration and index files are in the collection1 directory under solr home
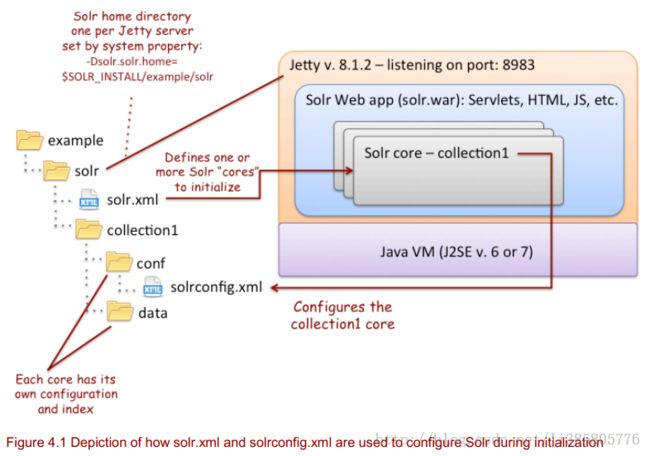
The initial configuration only has a single core named "collection1", but in general there can be many cores defined in solr.xml. For each core, Solr locates the solrconfig.xml file, under $SOLR_HOME/$instanceDir /conf/solrconfig.xml, where $ instanceDir is the directory for a specific core as specified in solr.xml. Solr uses the solrconfig.xml file to initialize the core
solrconfig.xml
<config>
<luceneMatchVersion>LUCENE_40</luceneMatchVersion> #A
<lib dir="../../../contrib/extraction/lib" regex=".*\.jar" /> #B
<dataDir>${solr.data.dir:}</dataDir > #C
<directoryFactory name="DirectoryFactory" class="..."/> #C
<indexConfig> ... </indexConfig> #C
<jmx /> #D
<updateHandler class="solr.DirectUpdateHandler2"> #E
<updateLog> ... </updateLog> #E
<autoCommit> ... </autoCommit> #E
</updateHandler> #E
<query>
<filterCache ... /> #F
<queryResultCache ... /> #F
<documen tCache ... /> #F
<listener event="newSearcher" class="solr.QuerySenderListener"> #G
<arr name="queries"> ... </arr> #G
</listener> #G
<list ener event="firstSearcher" class="solr.QuerySenderListener"> #G
<arr name="queries"> ... </arr> #G
</listener> #G
</query>
<requestDispatcher handleSelect="false" > #H
<requestParsers ... />
<httpCaching never304="true" />
</requestDispatcher>
<requestHandler name="/select" class="solr.SearchHandler"> #I
<lst name="defaults"> ... </lst> #I
<lst name="appends"> ... </lst> #I
<lst name="invariants"> ... </lst> #I
<arr name="components"> ... </arr> #I
<arr name="last -com ponents"> ... </arr> #I
</requestHandler> #I
<searchComponent name="spellcheck" #J
class="solr.SpellCheckComponent"> ... </searchComponent >
<updateRequestProcessorChain name="langid"> ... #K
</updateRequestProcessorChain>
<queryResponseWriter name="json" #L
class="solr.JSONResponseWriter"> ... </queryResponseWriter>
<valueSourceParser name="myfunc" ... /> #M
<transformer name="db" #N
class="com.mycompany.LoadFromDatabaseTransformer">
... </transformer>
</config>
#A Activates version -dependent features in Lucene, see 4.2.1
#B Lib directives indicate where Solr can find JAR files for extensions , see 4.2.1
#C Index management settings covered in chapter 5
#D Enable JMX instrumentation of Solr MBeans, see 4.2.1
#E Update handler for indexing documents, see chapter 5
#F Cache management settings , see section 4.4
#G Register event handlers for searcher events, e.g. queries to execute to warm new searchers ,
section 4.3
#H Unified request dispatcher, section 4.2
#I Request handler to process queries using a chain of search components, 4.2.4
#J Example search component for doing spell correction on queries
#K Extend indexing behavior using update request processors, such as language detection
#L Format the response as JSON
#M Declare a custom function for boosting, ranking or sorting documents
#N Transforms result documents
Listing 4.4 HTTP GET request to query the example Solr server
http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/select ? #A
q=iPod& #B
fq=manu%3ABelkin& #C
sort=price+asc& #D
fl=name%2Cprice%2Cfeatures%2Cscore& #E
df=text& #F
wt=xml& #G
start=0&rows=10 #H
#A Invokes the "select" request handler for the "collection1" core
#B Main query component looking for documents containing "iPod"
#C Filter documents that have manu field equal to "Belkin"
#D Sort results by price in ascending order (smallest to largest)
#E Return the name, price, features, and score fields in results
#F Default search field is "text"
#G Return results in XML format
#H Start at page 0 and return up to 10 results
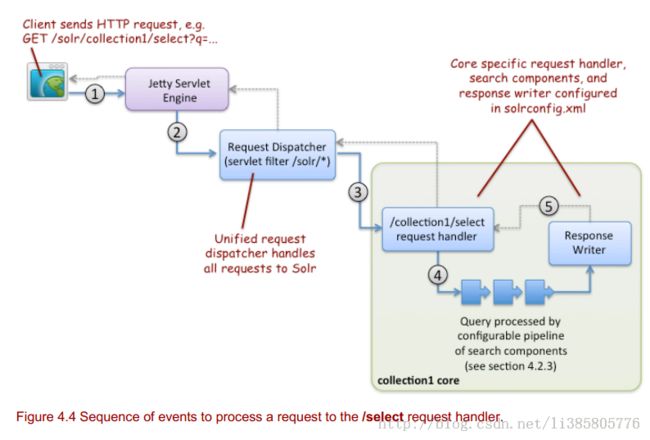
Starting at the top-left of figure 4.4:
1. A client application sends an HTTP GET request to http://localhost:8983/solr/collection1/select?q=... Query parameters are passed along in the query string of the GET request.
2. Jetty accepts the request and routes it to Solr's unified request dispatcher using the /solr context in the request path. In technical terms, the unified request dispatcher
is a Java servlet f ilter mapped to /* for the solr Web application, see org.apache.solr.servlet.SolrDispatchFilter.
3. Solr's request dispatcher uses the "collection1" part of the request path to determine the core name. Next, the dispatcher locates the /select request handler registered in solrconfig.xml for the collection1 core.
4. The /select request handler processes the request using a pipeline of search comp onents (covered in section 4.2.4 below).
5. After the request is processed, results are formatted by a response writer component and returned to the client application , by default the /select handler returns results as XML. Response writers are covered in section 4.5.
The main purpose of the request dispatcher is to locate the correct core to handle the request, such as collection1, and then route the request to the appropriate request handler registered in the core, in this case /select . In practice , the default configuration for the request dispatcher is sufficient for most applications . On the other hand, it is common to define a custom search req uest handler or to customize one of the existing handler s, such as /select . Let's dig into how the /select handler works to gain a better understanding of how to customize a request handler .
Listing 4.5 Definition of /select request handler from solrconfig.xml
<requestHandler name="/select" #A
class="solr.SearchHandler"> #B
<lst name="defaults"> #C
<str name="echoParams">explicit</str>
<int name="rows">10</int> #D
<str name="df">text</str>
</lst>
</requestHandler>
#A A specific type of request handler designed to process queries
#B Java class that implements the request handler
#C List of defau lt parameters (name/value pairs)
#D Sets the default page size to 10
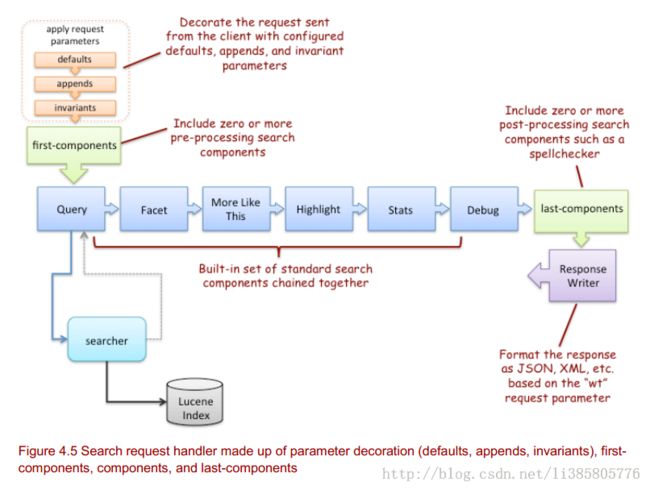
1. request parameter decoration using:
a. defaults: set default parameters on the request if they are not explic itly provided by the client
b. invariants : set parameters to static values, which override values provided by the client
c. appends : additional parameters to be combined with the parameters provided by the client
2. first-components : optional chain of search components that are applied first to perform pre -processing tasks
3. components : primary chain of search components; must at least include the query component
4. last-components: optional chain of search components that are applied last to perform post-processing tasks
<requestHandler name="/browse" class="solr.SearchHandler"> #A
<lst name="defaults"> #B
<str name="echoParams">explicit</str>
<str name="wt">velocity</str> #C
<str name="v.template">browse</str> #C
<str name="v.layout">layout</str> #C
<str name="title">Solritas</str> #C
<str name="defType">edismax</str> # D
<str name="qf">text^0.5 features^1.0 ...</str> #E
<str name="mlt.qf">text^0.5 features^1.0 ...</str> #F
<str name="facet">on</str> #G
...
<str name="hl">on</str> #H
...
<str name="spellcheck">on</str> #I
...
</lst>
<arr name="last -components">
<str>spellcheck</str> #J
</arr>
</requestHandler>
#A A SearchHandler invokes query processing pipeline
#B default list of query parameters
#C VelocityResponseWriter settings
#D Use the extended dismax query parser
#E Query settings
#F Enable the MoreLikeThis component
#G Enable the Facet component
#H Enable the Highlight component
#I Enable spell checking
#J Invoke the spell checking component as the last step in the pipelin e