【Android基础】listview控件的使用(3)------Map与SimpleAdapter组成的多显示条目的Listview
前面介绍的两种listview的使用都是最基础的,所以有很大的局限性,比如只能在一个item(即每一行的条目)中显示一个文本信息,这一篇我将介绍Map与SimpleAdapter组成的多显示条目的Listview的使用方法,这样就可以在每个item中显示多个文本的信息
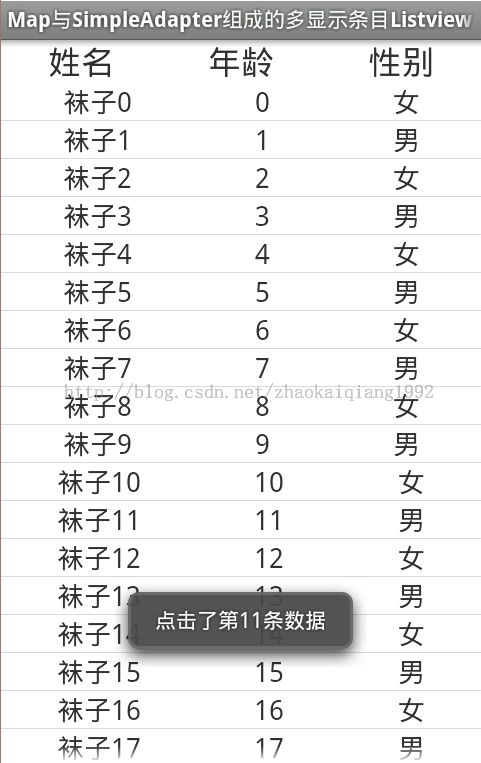
先上效果图
由于需要自定义item的布局,所以这次有两个布局文件
主listview的布局文件
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<!-- LinearLayout中包裹的内容是为了给listview加一个表头的效果,看起来更加的清晰 -->
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="姓名"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="年龄"
android:textSize="22sp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="性别"
android:textSize="22sp" />
</LinearLayout>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listview3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
自定义的每个item的布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/age"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sex"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:textSize="18sp" />
</LinearLayout>
在activity中的代码实现
package com.example.listviewdemo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
//Activity实现OnItemClickListener接口,这样就不用另外定义一个类实现了
public class ThreeActivity extends Activity implements OnItemClickListener {
private ListView listview;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_three);
listview = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview3);
// 获取数据
List<Map<String, String>> data = getSource();
// 这里使用了系统自带的SimpleAdapter,这是一个简单的适配器,适配器的主要作用就是将资源文件(布局以及显示的文本信息)与listview控件进行绑定
// SimpleAdapter(上下文对象, 填充的数据,自定义的item的布局文件,
// map对象中的键的数组,item的布局文件中控件id数组)
// 注意:【map对象中的键的数组】中的元素将与【item的布局文件中控件id数组】的元素一一对应
SimpleAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(ThreeActivity.this, data,
R.layout.item_three, new String[] { "name", "age", "sex" },
new int[] { R.id.name, R.id.age, R.id.sex });
// 设置适配器
listview.setAdapter(adapter);
// 绑定item的点击事件
listview.setOnItemClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> arg0, View arg1, int position,
long arg3) {
Toast.makeText(this, "点击了第" + position + "条数据", 0).show();
}
/**
* 该方法是为了获取模拟的数据
*
* @return 填充好数据的List对象
*/
public static List<Map<String, String>> getSource() {
List<Map<String, String>> list = new ArrayList<Map<String, String>>();
Map<String, String> map = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("name", "袜子" + i);
map.put("age", i + "");
map.put("sex", i % 2 == 0 ? "女" : "男");
list.add(map);
}
return list;
}
}
文中注释比较详细,如还有疑问,请留言