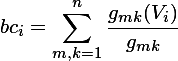文章关键词提取算法
本文只粘代码,理论方法请参见《基于语义的中文文本关键词提取算法》。
文本预处理部分
1.对于原始文档,我们要求是中文(包括标点符号),并且文档的一第句(即第一个全角句号之前的内容)应该是文章的标题。
2.采ISCTCLAS分词,并标注词性。
wordseg.cpp
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#define OS_LINUX
#include "ICTCLAS50.h"
using
namespace
std;
int
main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[])
{
if
(argc < 2) {
//命令行中需要给定要处理的文件名
cout <<
"Usage:command filename"
<< endl;
return
1;
}
string filename = argv[1];
string outfile = filename +
"_ws"
;
string initPath =
"/home/orisun/master/ICTCLAS50_Linux_RHAS_32_C/API"
;
if
(!ICTCLAS_Init(initPath.c_str())) {
cout <<
"Init fails"
<< endl;
return
-1;
}
ICTCLAS_FileProcess(filename.c_str(), outfile.c_str(), CODE_TYPE_UTF8,
1);
ICTCLAS_Exit();
return
0;
}
|
注意编译时要指明头文件和动态库的路径:
g++ wordseg.cpp -o wordseg -I /home/orisun/master/ICTCLAS50_Linux_RHAS_32_C/API -L /home/orisun/master/ICTCLAS50_Linux_RHAS_32_C/API -lICTCLAS50
3.保留特写词性的词语,其它的删掉。同时把文档合并成一行。
posfilter.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<cstring>
using
namespace
std;
int
main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[])
{
if
(argc < 2) {
//命令行中需要给定要处理的文件名
cout <<
"Usage:command filename"
<< endl;
return
1;
}
string arr_pos[] = {
"/n"
,
//名词
"/nr"
,
//人名
"/nr1"
,
//汉语姓氏
"/nr2"
,
//汉语名字
"/nrj"
,
//日语人名
"/ns"
,
//地名
"/nt"
,
//机构团体名
"/wj"
,
//句号
"/nl"
,
//名词性惯用语
"/ng"
,
//名词性语素
"/v"
,
//动词
"/vd"
,
//副动词
"/vn"
,
//名动词
"/vl"
,
//动词性惯用语
"/vg"
,
//动词性语素
"/a"
,
//形容词
"/an"
,
//名形词
"/ag"
,
//形容词性语素
"/al"
,
//形容词性惯用语
""
};
set < string > set_pos;
int
i;
for
(i = 0; arr_pos[i] !=
""
; ++i)
set_pos.insert(arr_pos[i]);
string filename(argv[1]);
string outfile = filename +
"_pos"
;
ifstream ifs(filename.c_str());
//打开输入文件
ofstream ofs(outfile.c_str());
//打开输出文件
if
(!(ifs && ofs)) {
cerr <<
"error:open file failed."
<< endl;
return
1;
}
string word;
while
(ifs >> word) {
bool
flag =
false
;
int
length = word.find(
"/"
);
//cout<<word<<"\t"<<length<<endl;
if
(length == 3 &&
strncmp
(word.c_str(),
"。"
, 3) != 0)
//过滤掉单个汉字,但是不过滤全角句号(因为一个汉字就3个字节)
continue
;
string pos = word.substr(length);
if
(set_pos.find(pos) != set_pos.end())
flag =
true
;
if
(flag)
ofs << word <<
"\t"
;
}
ifs.close();
ofs.close();
return
0;
}
|
4.把文章分为四大部分:标题,段首,段中,段尾。各部分之间用一个空行分开。标题是第一句,紧接着后两句是段首,文章末两句是段尾,其余属段中。
section.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<cassert>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
using
namespace
std;
int
main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[])
{
if
(argc < 2) {
//命令行中需要给定要处理的文件名
cout <<
"Usage:command filename"
<< endl;
return
1;
}
string filename(argv[1]);
//输入文件名
string outfile = filename +
"_part"
;
//输出文件名
ifstream ifs(filename.c_str());
//打开输入文件
ofstream ofs(outfile.c_str());
//打开输出文件
if
(!(ifs && ofs)) {
cerr <<
"error:open file failed."
<< endl;
return
1;
}
string content, word;
while
(ifs >> word)
//把文件的内容全部读到content中,去除了换行符,相当于把整篇文档合并成了一行
content.append(word +
"\t"
);
string period =
"。/wj"
;
string::size_type front = content.find(period);
//寻找第一个句号所在的位置
assert
(front != string::npos);
content.replace(front, 6,
"\t\t\t\t\n\n"
);
front = content.find(period, front + 1);
//寻找第二个句号所在的位置
front = content.find(period, front + 1);
//寻找第三个句号所在的位置
content.replace(front, 6,
"\t\t\t\t\n\n"
);
string::size_type back = content.rfind(period);
//最后一个句号
assert
(back != string::npos);
content.replace(back, 3,
"."
);
back = content.rfind(period);
//倒数第二个句号
content.replace(back, 3,
"."
);
back = content.rfind(period);
//倒数第三个句号
content.replace(back, 6,
"\t\t\t\t\n\n"
);
ofs << content;
ifs.close();
ofs.close();
return
0;
}
|
5.构造元组(词语,词性,出现的次数,出现在标题,出现在段首,出现在段尾)
tuple.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using
namespace
std;
struct
Tuple {
string word;
//词语
string pos;
//词性
int
occurs;
//出现次数
short
local1;
//标题中出现
short
local2;
//段首出现
short
local3;
//段尾出现
//构造函数
Tuple() {
};
//由于Tuple要作为map的second,所以必须提供空参数构造函数
Tuple(string w, string p,
int
o = 1,
short
l1 = 0,
short
l2 =
0,
short
l3 = 0)
: word(w), pos(p), occurs(o), local1(l1), local2(l2), local3(l3) {
};
};
int
main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[])
{
if
(argc < 2) {
cout <<
"Usage:command filename."
<< endl;
return
0;
}
string infile(argv[1]);
string outfile = infile +
"_tuple"
;
ifstream ifs(infile.c_str());
ofstream ofs(outfile.c_str());
if
(!(ifs && ofs)) {
cerr <<
"Open file failed."
<< endl;
return
-1;
}
map < string, Tuple > tmap;
map < string, Tuple >::const_iterator itr;
string line;
for
(
int
i = 0; i < 7, getline(ifs, line); ++i) {
istringstream stream(line);
string word;
while
(stream >> word) {
int
index = word.find(
"/"
);
//斜杠之前是词语,斜杠之后是词性
string front = word.substr(0, index);
itr = tmap.find(front);
if
(itr == tmap.end()) {
//到目前为止没有出现过
string post = word.substr(index + 1);
if
(post ==
"wj"
)
continue
;
Tuple tuple(front, post);
switch
(i) {
case
0:
tuple.local1 = 1;
break
;
case
2:
tuple.local2 = 1;
break
;
case
6:
tuple.local3 = 1;
break
;
default
:
break
;
}
tmap[front] = tuple;
}
else
{
//词语曾出现过
Tuple tuple = tmap[front];
tuple.occurs++;
switch
(i) {
case
0:
tuple.local1 = 1;
break
;
case
2:
tuple.local2 = 1;
break
;
case
6:
tuple.local3 = 1;
break
;
default
:
break
;
}
tmap[front] = tuple;
}
}
}
for
(itr = tmap.begin(); itr != tmap.end(); ++itr) {
//将(词语,词性,次数,位置)写入文件
ofs << itr->second.word <<
"\t"
<< itr->
second.pos <<
"\t"
<< itr->second.
occurs <<
"\t"
<< itr->second.local1 <<
"\t"
<< itr->second.
local2 <<
"\t"
<< itr->second.local3 << endl;
}
ifs.close();
ofs.close();
return
0;
}
|
6.把同义词词林存入gdbm数据库
sy2db.cpp
#include<gdbm.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sstream>
using
namespace
std;
int
main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[])
{
string infile(
"同义词词林扩展版"
);
ifstream ifs(infile.c_str());
if
(!ifs) {
cerr <<
"open file failed!"
<< endl;
return
-1;
}
GDBM_FILE dbm_ptr;
dbm_ptr = gdbm_open(
"sydb"
, 0, GDBM_WRCREAT, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR, NULL);
datum key, data;
string line, word;
while
(getline(ifs, line)) {
istringstream stream(line);
stream >> word;
//取出每行的第一列作为key
key.dptr = (
char
*)word.c_str();
key.dsize = word.size() + 1;
data.dptr = (
char
*)line.c_str();
data.dsize = line.size() + 1;
gdbm_store(dbm_ptr, key, data, GDBM_REPLACE);
}
ifs.close();
gdbm_close(dbm_ptr);
return
0;
}
|
算法部分
7.计算词语之间的相似度
simMatrix.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<gdbm.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<climits>
#include<cassert>
#include<vector>
using
namespace
std;
/**相似度计算相关参数设置**/
const
double
init_dist = 10;
const
double
alpha = 5.0;
const
double
beta = 0.66;
const
double
weight[6] = { 1.0, 0.5, 0.25, 0.125, 0.06, 0.03 };
GDBM_FILE dbm_ptr;
//数据库句柄
vector <string> words;
//存储文章中出现的词
/**读出所有的词,存入vector**/
void
initWords(string filename)
{
ifstream ifs(filename.c_str());
assert
(ifs);
string line;
while
(getline(ifs, line)) {
istringstream stream(line);
string word;
stream >> word;
//读出一行中的首列词语即可
words.push_back(word);
}
ifs.close();
}
/**计算两个编码(编码分为code位和标志位)的距离**/
double
calDist(string code1, string code2)
{
if
(code1[7] ==
'@'
|| code2[7] ==
'@'
)
/*词语自我封闭、独立,在同义词词林中既没有同义词,也没有相关词 */
return
init_dist;
double
dist = -10;
//初始距离给一个负数
int
eqi = 0;
//两个code相同的倍数
int
i;
for
(i = 0; i < 7; ++i) {
if
(code1[i] != code2[i])
break
;
eqi++;
}
if
(i < 7) {
//code位不同
switch
(eqi) {
case
0:
case
1:
case
2:
dist = weight[eqi] * init_dist;
break
;
case
3:
case
4:
case
5:
dist = weight[eqi - 1] * init_dist;
break
;
case
6:
dist = weight[eqi - 2] * init_dist;
break
;
default
:
break
;
}
}
else
{
//code位相同
if
(code1[i] == code2[i]) {
//标志位相同
if
(code1[i] ==
'='
)
//同义
dist = 0;
else
if
(code1[i] ==
'#'
)
//同类
dist = weight[5] * init_dist;
}
else
{
//只有code位相同,标志位就一定相同,所以else的情况不会了生
cout << code1 <<
"和"
<< code2 <<
"code位相同,标志位居然不相同!"
<<
endl;
return
-1;
}
}
return
dist;
}
/**计算两个词的相似度**/
double
calSim(string word1, string word2)
{
if
(word1 == word2)
//如果是同一个词,则相似度为1
return
1;
datum key1, data1, key2, data2;
key1.dptr = (
char
*)word1.c_str();
key1.dsize = word1.size() + 1;
data1 = gdbm_fetch(dbm_ptr, key1);
int
size1 = data1.dsize;
key2.dptr = (
char
*)word2.c_str();
key2.dsize = word2.size() + 1;
data2 = gdbm_fetch(dbm_ptr, key2);
int
size2 = data2.dsize;
if
(size1 != 0 && size2 != 0) {
//两个词都在词林中找得到
int
i, j;
string word1;
vector <string> vec1, vec2;
string buffer1(data1.dptr);
istringstream stream1(buffer1);
stream1 >> word1;
stream1 >> word1;
//路过前两列
while
(stream1 >> word1) {
vec1.push_back(word1);
//把词对应的编码都存入vector中
}
string word2;
string buffer2(data2.dptr);
istringstream stream2(buffer2);
stream2 >> word2;
stream2 >> word2;
//路过前两列
while
(stream2 >> word2) {
vec2.push_back(word2);
}
double
minDist = INT_MAX;
//初始距离为无穷大
for
(
int
i = 0; i != vec1.size(); ++i) {
for
(
int
j = 0; j != vec2.size(); ++j) {
//cout<<vec1[i]<<"和"<<vec2[j]<<"的距离"<<endl;
double
dist = calDist(vec1[i], vec2[j]);
if
(dist < minDist)
minDist = dist;
//两个词的距离是所有编码组合中距离的最小值
}
}
return
alpha / (alpha + minDist);
//从距离到相似度的转换
}
else
//只要有一个词不在词林中,则返回相似度为0
return
0;
}
int
main(
int
argc,
char
*argv[])
{
if
(argc < 2) {
cout <<
"Usage:command filename."
<< endl;
return
0;
}
string infile(argv[1]);
initWords(infile);
dbm_ptr = gdbm_open(
"sydb"
, 0, GDBM_READER, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR, NULL);
ofstream ofs(
"simadj"
);
ofs << words.size() << endl;
//把邻接矩阵的规模写入文件首行
for
(
int
i = 0; i != words.size(); ++i) {
ofs << i <<
"\t"
;
for
(
int
j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
//把顶点之间的相似度存入下三角矩阵
double
sim = calSim(words[i], words[j]);
if
(sim > beta)
//相似度大于阈值时才认为两个顶点之间有边
ofs << j <<
"("
<< sim <<
")"
<<
"\t"
;
}
ofs << endl;
}
ofs.close();
gdbm_close(dbm_ptr);
return
0;
}
|
8.根据词语的语义相似度矩阵,计算词语居间度
顶点Vi的居间度bci定义为:
n是顶点的个数,gmk是顶点m和k之间的最短路径的个数,gmk(Vi)是顶点m和k之间的最短路径中经过顶点Vi的条数。
对于无向图可以表示为
Dijkstra算法可以找到单源节点的最短径,但是只能找出一条,要想找到两顶点之间的所有最短路径只需对经典Dijkstra稍作修改(见下面的代码)。在Dijkstra中运用PairingHeap可以提高算法效率,见我的另外一篇博客《用PairingHeap改进Dijkstra算法》。分别指定不同的顶点作起点就可以找出图中所有的最短路径。
代码中使用一个全局数组PairDependencyArray [ num_of_vertex ] 来保存各个节点的居间度,数组初始化为0,随着新的最短路径的发现,数组元素不断增加。比如运行一次Dijkstra后我们发现了顶点V1到其他顶点之间的最短路径:
| V | known | d | p |
| V1 | T | 0 | 0 |
| V2 | T | 1 | V1 |
| V3 | T | 4 | V4 |
| V4 | T | 2 | V1,V2 |
| V5 | T | 3 | V4 |
| V6 | T | 7 | V7 |
| V7 | T | 6 | V4,V5 |
我们直观地画出V1到V6的最短路径(有多条):
现在我们要更新每条路径上除两端点之外的中间节点的居间度,它们的居间度要增加一个值,这个值怎么计算呢?终点赋予1.0,它的前继节点平分这个值。
PairDependencyArray [7]增加1;
PairDependencyArray [4]增加0.5+0.5;
PairDependencyArray [5]增加0.5;
PairDependencyArray [2]增加0.25+0.25;
pariheap.h
#ifndef _PAIRHEAP_H
#define _PAIRHEAP_H
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<vector>
#include<utility>
using
namespace
std;
struct
PairNode {
int
nodeindex;
double
element;
PairNode *prev, *leftChild, *nextSibling;
PairNode() {
} PairNode(
int
i,
double
d, PairNode * p = NULL, PairNode * l =
NULL, PairNode * n = NULL)
: nodeindex(i), element(d), prev(p), leftChild(l), nextSibling(n) {
}
};
/**
* 打印配对堆
*/
void
printNode(PairNode * root)
{
if
(root == NULL)
return
;
else
{
cout << root->nodeindex <<
"("
<< root->element <<
")"
<<
"\t"
;
cout << root->nodeindex <<
"'s next:"
;
printNode(root->nextSibling);
if
(root->element < INT_MAX) {
cout << root->nodeindex <<
"'s leftChild:"
;
printNode(root->leftChild);
}
}
}
/**
* 合并以first和second为根的两棵树
* 函数开始时first->nextSibling必须为NULL
* second可以为NULL
* 树合并后,first成为新树的根节点
*/
void
compareAndLink(PairNode * &first, PairNode * second)
{
if
(second == NULL)
return
;
if
(second->element < first->element) {
//谁小谁作父节点
second->prev = first->prev;
first->prev = second;
first->nextSibling = second->leftChild;
if
(first->nextSibling != NULL)
first->nextSibling->prev = first;
second->leftChild = first;
first = second;
}
else
{
second->prev = first;
first->nextSibling = second->nextSibling;
if
(first->nextSibling != NULL)
first->nextSibling->prev = first;
second->nextSibling = first->leftChild;
if
(second->nextSibling != NULL)
|