Android 蓝牙低功耗Ble Gatt浅谈
随着物联网的越来越火,使用蓝牙方式进行设备间的通信也越来越多。而传统蓝牙协议(蓝牙2.0),由于其高功耗、连接速度慢及距离短等限制阻碍了蓝牙的推广应用。而12年推出来的蓝牙4.0 ble低功耗协议满足了物联网、医疗智能穿戴设备等方面的应用场景。
传统蓝牙与低功耗BLE的对比
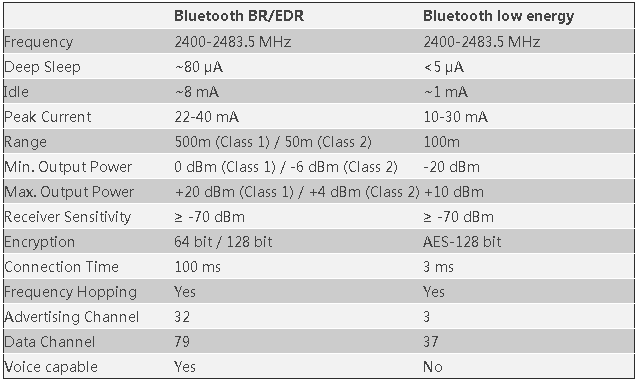
基本上所有的Android设备都支持经典蓝牙配置文件,它适合更耗电的操作比如视频流。而Android 4.3开始支持蓝牙低功耗及蓝牙智能(BluetoothSmart)技术,它能够支持GATT(GENERIC ATTRIBUTE PROFILE 通用属性剖面)配置的设备进行通信(比如有心脏检测器、计步器等)
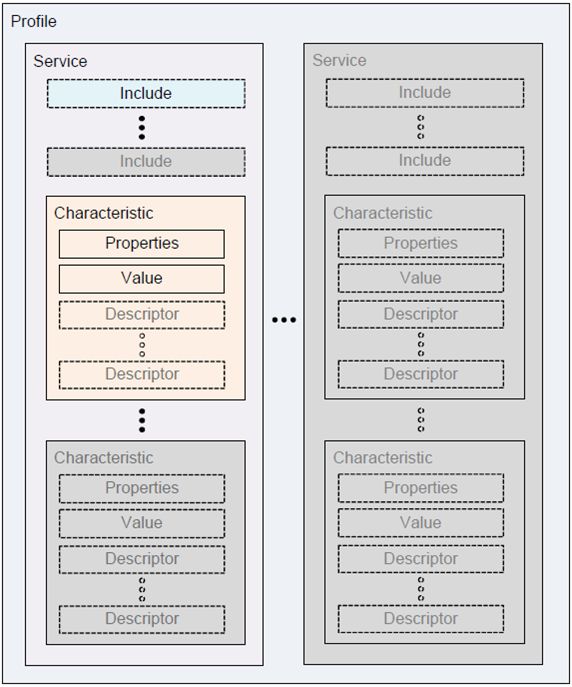
一个设备可以有多个服务,如电池、心率监视器和自行车骑行速度。每一个服务都有一些特性,如心率监听器的身体位置,或者自行车的RPM数量。有些特性,比如当前时间,支持从客户端写操作,而另一些只支持读取和/或通知。每个特性呢可以有多个描述符,描述符用来描述特性的额外信息。
一个设备—->服务(一设备n个服务)—->特性(一服务n特性)—->描述符(一特性n描述符)
1.0 权限及功能注册及声明
使用蓝牙低功耗ble时,需要注册相应的权限及申明相应的功能(过滤掉不支持的设备)
<users-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH" />
<users-permission android:name="android.permission.BLUETOOTH_ADMIN" />
<users-feature android:name="android.hardware.bluetooth_le" android:required="true" />按时required为true时,则应用只能在支持BLE的Android设备上安装运行;required为false时,Android设备均可正常安装运行,需要在代码运行时判断设备是否支持BLE feature:
// Use this check to determine whether BLE is supported on the device. Then
// you can selectively disable BLE-related features.
if (!getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) {
Toast.makeText(this, R.string.ble_not_supported, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
finish();
}1.1 判断蓝牙是否开启了
f(!mBluethoothAdapter.isEnable()){
Intent enableIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_EANBLE);
startActivityForResult(enableIntent,ENABLE_REQUEST);
}1.2 接下来可以扫描查找蓝牙低功耗设备
public void doStartBleScan(){
mLeScanCallback = new MyLeScanCallback();
BluetoothManager bluetoothManager = (BluetoothManage)getSystem(Context.BLUETOOTH_SERVICE);
mBluethoothAdapter = bluetoothManager.getAdapter();
mBluethoothAdapter.startLeScan(mLeScanCallback);
}1.3 查找的过程中,会回调LeScanCallback中的onLeScan方法,在此方法中判断是指定设备后进行连接。
private class MyLeScanCallback implements BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallbakc{
public void onLeScan(BluetoothDevice device,int rssi,byte[] scanRecode){
//...判断过程,
mBluethoothAdapter.stopLeScan(this);
mMyGattCallback = new MyGattCallback();
mGatt = device.connectGatt(BtleDemo.this,false,mMyGattCallback);
}
}1.4 连接完成后会回调onConnectionStateChange方法。此时可以查找发现远程设备上的可用服务
private class MyGattCallback extends BluetoothGattCallback{
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt,int status,int newState){
super.onConnectionStateChange(gatt,status,newState);
if(newState == BluetoothGatt.STATE_CONNECTED && status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS){
//远程设备名称
//String deviceName = gatt.getDevice().getName();
gatt.discoverServices();
}
}
}1.5 当发现可用服务后,会回调onServicesDiscovered方法,在此可以遍历服务和它的特性。对每个特性可以检查是否支持读写和/或通知,如果支持的话调用相应的方法。
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt,int status){
if(status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS){
List<BluetoothGattService> services = gatt.getServices();
for(BluetoothGattService service : services){
for(BluetoothGattCharacteristic chara : service.getCharacteristics()){
if(hasProperty(chara,BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_READ)){
gatt.readCharacteristic(chara);
}
if(hasProperty(chara,BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_NOTITY)){
gatt.setCharacteristicNotification(chara,true);
}
}
}
}
}
public static boolean hasProperty(BluetoothGattCharacteristic chara,int property){
int prop = chara.getProperties()&property;
return prop == property;
}1.6 对服务特性的读取与通知都是异步回调的。
public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic chara,int status){
super.onCharacteristicRead(gatt,chara,status);
if(status == BluetoothGatt.SUCCESS){
Integer value = chara.getIntValue(BluetoothGattCharacteristic.FROM_SINT32,0);
//todo 处理数据读取
}
}
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic chara){
super.onCharacteristicChanged(gatt,chara);
Integer value = chara.getIntValue(BluetoothGattCharacteristic.FROM_SINT32,0);
//todo 处理通知中的值
}官网Gatt资料https://developer.bluetooth.org/TechnologyOverview/Pages/GATT.aspx