设计模式之 Delegation 授权
Delegation is a way of making composition as powerful for reuse as inheritance[Lie86, JZ91]. In delegation, two objects are involved in handling a request: a receiving object delegates operations toits delegate. This is analogous tosubclasses deferring requests to parentclasses. But with inheritance, an inherited operation can always refer to thereceiving object through the this
member variable in C++ and self in Smalltalk. To achieve the same effect with delegation, the receiver passes itself to the delegate to let the delegated operation refer to the receiver.
为了在继承中实现重用,授权是个组成构件的强有力的方法。在授权的过程中,涉及到两个对象对命令的掌控。接受对象给它的代表授权运算。这和子类遵从来自父类的命令是相似的。但是,和继承相伴的是,在c++的成员变量和smalltalk本身中,继承的运算自始至终都涉及到接收的对象。为了在授权中达到相同的效果,接受者批准指向自己的授权让它所代表的运算和接收者有关。
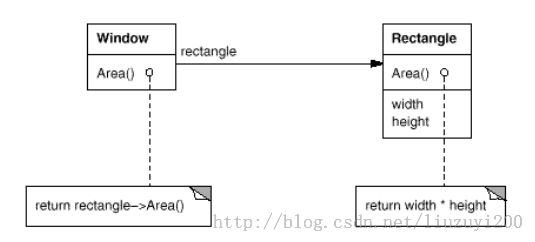
For example, instead of making class Window a subclass of Rectangle (because windows happen to be rectangular), the Window class might reuse the behavior of Rectangle by keeping a Rectangle instance variable and delegating Rectangle-specific behavior to it. In otherwords, instead of a Window being a Rectangle, it would have a Rectangle.Window must now forward requests to its Rectangle instance explicitly, where as before it would have inherited those operations.
例如,子类窗口可以用矩形类来代替(因为窗口碰巧是矩形),通过保留巨响实例化的变量和代表矩形特殊的行为,窗口可能重用矩形的行为。换句话说,窗口被矩形来代替,它将成为矩形。窗口可以精确的发送命令给实例化的矩形,在做这些之前,窗口必须继承这些运算。
The following diagram depicts the Window class delegating its Area operation to a Rectangle instance. A plain arrowhead line indicates that aclass keeps a reference to an instance of another class. The reference has anoptional name, "rectangle" in this case.
接下来的图表窗口类授权area运算类矩形类的实例化。普通的箭头表明类保持了另一个类实例化的引用。在这个案例中,”矩形”这个引用的名字、
The main advantage of delegation is that it makes it easy to compose behaviors at run-time and to change the way they'recomposed. Our window can become circular at run-time simply by replacing its Rectangle instance with a Circle instance,
assuming Rectangle and Circle have the same type.
在运行时他可以很容易的组合行为和改变它们组合的行为,这是授权的优势。如果矩形和圆有相同的类型,窗口可以很容易的被用矩形实例化的圆来代替,。
Delegation has a disadvantage it shares with other techniques that make software more flexible through object composition:Dynamic, highly parameterized software is harder to understand than more static software. There are also run-time inefficiencies, but the human inefficiencies are more important in the long run. Delegation is a good design choice only when it simplifies more than it complicates.
It isn't easy to give rules that tell youexactly when to use delegation, because how effective it will be depends on thecontext and on how much experience you have with it. Delegation works best whenit's used in highly stylized ways—that
is, in standard patterns.
它自始至终用对象组合通过共享和其他的技术来使软件更加灵活,这是授权的不利之处:多态,很高参数化的软件是很难理解那些更多静态的软件。在运行时这也是低效率的,但是这种低效率从长远看是很重要的。
Several design patterns use delegation. TheState (338), Strategy (349), and Visitor (366) patterns depend on it. In theState pattern, an object delegates requests to a State object that representsits current state. In the Strategy pattern, an object delegates a specificrequest to an object that represents a strategy for carrying out the request. Anobject will only have one state, but it can have many strategies for differentrequests. The purpose of both patterns is to change the behavior of an object bychanging the objects to which it delegates requests. In Visitor, the operation thatgets performed on each element of an
object structure is always delegated to theVisitor object.
几种设计模式用到了它。状态模式,策略模式和访问者模式都依赖于它。在状态模式中,对象给状态对象授权,它可以体现对当前的状态做出回应。在策略模式中,对象授权特殊的命令给对象是为了体现策略执行命令。对象不止一个状态,对于不同的命令它可以有很多种状态。通过改变对象所授权的命令,可以改变对象的行为,这是连个模式的目的。在访问者模式中,运算在每一个对象结构元素授权给访问者对象的时候执行。
Other patterns use delegation less heavily.Mediator (305) introduces an object to mediate communication between other objects. Sometimes the Mediator object implements operations simply by forwarding them to the other objects; other times it passes along a reference to itself and thus uses true delegation. Chain of Responsibility (251) handles requests by forwarding them from one object to another along a chain of objects. Sometimes this request carries with it a reference to the original object receiving the request,in which case the pattern is using delegation. Bridge (171) decouples an abstraction from its implementation. If the abstraction and a particular implementation are closely matched, then the abstraction may simply delegate operations to that implementation. Delegation is an extreme example of object composition. It shows that you can always replace inheritance with object composition as a mechanism for code reuse.
其他的模式少量的用到了授权:中介模式介绍了对象作为和其他对象交流的中介。有时,通过发送中介对象,中介对象的运算就实现了。有时批准了随着它的引用,之后就会给予它们正确的授权。职责链模式掌控命令是通过发送命令给这条链上的一个又一个对象。有时它们携带着面向对象命令的引用来接收这些命令,在这个案例中可以用授权。桥接模式减弱了来自实现的抽象。如果抽象和特别的实现有密切的联系,那么抽象就可能简单的授权有关实现的运算。在对象的组合中,授权是一个极端的例子。作为代码复用的机制,你可以总是用对象的组合来替代继承。