看书小记4(《C专家编程》)
日期与时间
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* 秒 – 取值区间为[0,59] */
int tm_min; /* 分 - 取值区间为[0,59] */
int tm_hour; /* 时 - 取值区间为[0,23] */
int tm_mday; /* 一个月中的日期 - 取值区间为[1,31] */
int tm_mon; /* 月份(从一月开始,0代表一月) - 取值区间为[0,11] */
int tm_year; /* 年份,其值等于实际年份减去1900 */
int tm_wday; /* 星期 – 取值区间为[0,6],其中0代表星期天,1代表星期一,以此类推 */
int tm_yday; /* 从每年的1月1日开始的天数 – 取值区间为[0,365],其中0代表1月1日,1代表1月2日,以此类推 */
int tm_isdst; /* 夏令时标识符,实行夏令时的时候,tm_isdst为正。不实行夏令时的进候,tm_isdst为0;不了解情况时,tm_isdst()为负。*/
};
通过time()函数来获得日历时间,如果参数为NULL,函数将只通过返回值返回现在的日历时间:
struct tm* ptr = NULL;
time_t t = time(NULL);
cout<<t<<endl;
gmtime()函数是将日历时间转化为世界标准时间(即格林尼治时间),而localtime()函数是将日历时间转化为本地时间:
ptr = gmtime(&t);
cout<<ptr->tm_hour<<endl;
ptr = localtime(&t);
cout<<ptr->tm_hour<<endl;
可以通过asctime()函数和ctime()函数将时间以固定的格式显示出来:
printf(asctime(ptr));
可以使用strftime()函数将时间格式化为我们想要的格式,格式命令忒多:
char str[128];
strftime( str, sizeof(str), "Today is %A, day %d of %B in the year %Y.\n", ptr);
printf(str);
计时函数是clock(),返回从“开启这个程序进程”到“程序中调用clock()函数”时之间的CPU时钟计时tick数:
long i = 10000000L;
clock_t start, finish;
double duration;
printf( "Time to do %ld empty loops is ", i );
start = clock();
while( i-- ) ;
finish = clock();
duration = (double)(finish - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
printf( "%f seconds\n", duration );
使用mktime()函数将用tm结构表示的时间转化为日历时间:
time_t t_of_day;
ptr->tm_year=1997-1900;
ptr->tm_mon=6;
ptr->tm_mday=1;
ptr->tm_hour=0;
ptr->tm_min=0;
ptr->tm_sec=1;
ptr->tm_isdst=0;
t_of_day=mktime(ptr);
printf(ctime(&t_of_day));
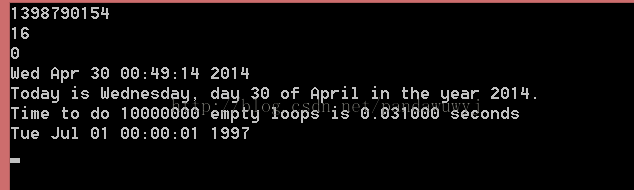
最后附上当前的执行结果和参考(http://www.cnblogs.com/Wiseman/archive/2005/10/24/260576.html)