API Demos 2.3 学习笔记 (17)-- Views->Tabs
更多精彩内容,请点击阅读:《API Demos 2.3 学习笔记》
TabHost有两种实现方式,一种是继承TabActivity,另一种是自己定义TabHost,不继承TabActivity。APIDemo中的三个实例都是第一种。想了解TabHost的第二种实现方式,请参考以下内容:
TabHost两种实现方式 http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-35836-1-1.html
下面我们逐一介绍APIDemo实例中TabHost的三种实现方法:
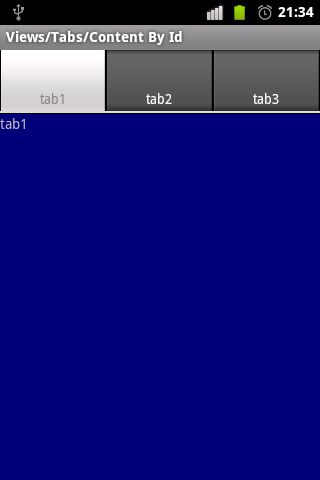
方法一、Content By Id
1、在一个FrameLayout内定义几个控件/布局,每个布局用作一个Tab的内容。
在这个实例中,FrameLayout内定义三个不同背景颜色的TextView对象view1,view2以及view3。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<!-- 一个TextView对象,背景色为蓝色 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/blue"
android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_1" />
<!-- 一个TextView对象,背景色为红色 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/red"
android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_2" />
<!-- 一个TextView对象,背景色为绿色 -->
<TextView
android:id="@+id/view3"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/green"
android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_3" />
</FrameLayout>
2、新建一个 Activity,继承自 TabActivity
public class Tabs1 extends TabActivity {
3、通过getTabHost()函数,获得TabActivity内置的TabHost对象。将样式R.layout.tabs1解压出来,并应用于TabHost对象。最后根据三个TextView控件创建了三个Tab选项卡。
//获取TabActivity内置的TabHost对象
TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
//将样式R.layout.tabs1解压出来,并应用于TabHost对象
LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabs1, tabHost.getTabContentView(), true);
//新建选项卡
//tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 新建一个以“tab1”为标记的选项卡
//setIndicator("tab1") 设置选项卡标签标题为 tab1
//setContent(R.id.view1)) 设置选项卡内容为 R.id.view1
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1")
.setIndicator("tab1")
.setContent(R.id.view1));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3")
.setIndicator("tab2")
.setContent(R.id.view2));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3")
.setIndicator("tab3")
.setContent(R.id.view3));
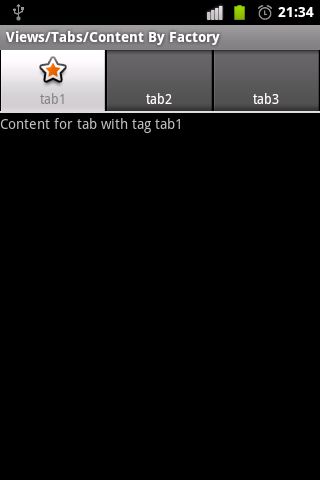
方法二、Content By Factory
1、新建一个 Activity,继承自 TabActivity,并且继承 TabHost.TabContentFactory接口。
public class Tabs2 extends TabActivity implements TabHost.TabContentFactory {
2、通过getTabHost()函数,获得TabActivity内置的TabHost对象。和上面的例子比较,发现这里创建的三个选项卡使用的代码是:setContent(this))。这里的选项卡内容就得通过实现TabHost.TabContentFactory接口来创建了。
//获取TabActivity内置的TabHost对象
final TabHost tabHost = getTabHost();
//新建选项卡
//tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 新建一个以“tab1”为标记的选项卡
//setIndicator("tab1") 设置选项卡标签标题为 tab1 ,图标为 getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.star_big_on)
//setContent(this)) 由于该TabActivity继承了 TabHost.TabContentFactory 接口,因此,点击选项卡标签时,会调用
// public View createTabContent(String tag)来创建每个选项卡内容。该函数中的参数tag和newTabSpec中的参数是一样的。
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1")
.setIndicator("tab1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.star_big_on))
.setContent(this));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2")
.setIndicator("tab2")
.setContent(this));
tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3")
.setIndicator("tab3")
.setContent(this));
3、实现TabHost.TabContentFactory接口。这样,每点击一个选项卡,该接口就会根据选项卡标记(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 中的参数 "tab1")来创建对应的View。
//每次点击选项卡标签时,根据选项卡tag标记来创建具体内容。
/** {@inheritDoc} */
public View createTabContent(String tag) {
final TextView tv = new TextView(this);
tv.setText("Content for tab with tag " + tag);
return tv;
}
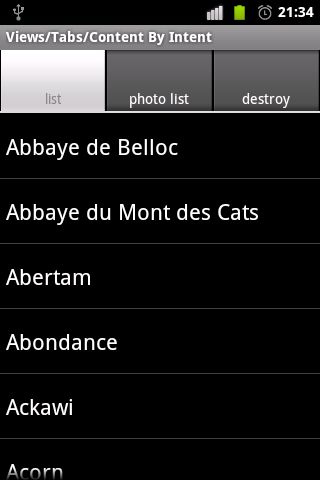
方法三、Content By Intent
1、新建一个 Activity,继承自 TabActivity。
public class Tabs3 extends TabActivity {
2、通过getTabHost()函数,获得TabActivity内置的TabHost对象。和以上两个实例比较,发现这里创建的三个选项卡使用的代码是:setContent(Intent))。点击每个选项卡,便会根据intent,跳转到对应的Activity界面。例如:点击 "tab1" 选项卡,便会跳转到 List1界面。
//获取TabActivity内置的TabHost对象 final TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //新建选项卡 //tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 新建一个以“tab1”为标记的选项卡 //setIndicator("tab1") 设置选项卡标签标题为 list //setContent(new Intent(this, List1.class))) 点击该选项卡时,通过Intent,跳转到List1界面 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") .setIndicator("list") .setContent(new Intent(this, List1.class))); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2") .setIndicator("photo list") .setContent(new Intent(this, List8.class))); // 这个选项卡设置 Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP 标记,是为了 每次点击该选项卡时,重新创建选项卡内容。 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3") .setIndicator("destroy") .setContent(new Intent(this, Controls2.class) .addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP)));
以上只是TabHost的一些基本用法,如果你想了解更多有关TabHost的知识,请点击参考以下帖子:《史上最全的Android的Tab与TabHost讲解》
http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-1035-1-1.html
下面我们进行实例代码解析:实例一、Content By Idres-layout-tabs1.xml<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" > <!-- 一个TextView对象,背景色为蓝色 --> <TextView android:id="@+id/view1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@drawable/blue" android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_1" /> <!-- 一个TextView对象,背景色为红色 --> <TextView android:id="@+id/view2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@drawable/red" android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_2" /> <!-- 一个TextView对象,背景色为绿色 --> <TextView android:id="@+id/view3" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:background="@drawable/green" android:text="@string/tabs_1_tab_3" /> </FrameLayout>
src-com.example.android.apis.view-Tabs1.java
package com.example.android.apis.view; import android.app.TabActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.TabHost; import android.view.LayoutInflater; import com.example.android.apis.R; /** * 演示如何使用TabHost * */ public class Tabs1 extends TabActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //获取TabActivity内置的TabHost对象 TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //将样式R.layout.tabs1解压出来,并应用于TabHost对象 LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.tabs1, tabHost.getTabContentView(), true); //新建选项卡 //tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 新建一个以“tab1”为标记的选项卡 //setIndicator("tab1") 设置选项卡标签标题为 tab1 //setContent(R.id.view1)) 设置选项卡内容为 R.id.view1 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") .setIndicator("tab1") .setContent(R.id.view1)); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3") .setIndicator("tab2") .setContent(R.id.view2)); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3") .setIndicator("tab3") .setContent(R.id.view3)); } }
实例二、Content By Factory
src-com.example.android.apis.view-Tabs2.java
package com.example.android.apis.view; import android.app.TabActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.TabHost; import android.widget.TextView; import android.view.View; import com.example.android.apis.R; /** * 演示如何使用TabHost * */ public class Tabs2 extends TabActivity implements TabHost.TabContentFactory { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //获取TabActivity内置的TabHost对象 final TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //新建选项卡 //tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 新建一个以“tab1”为标记的选项卡 //setIndicator("tab1") 设置选项卡标签标题为 tab1 ,图标为 getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.star_big_on) //setContent(this)) 由于该TabActivity继承了 TabHost.TabContentFactory 接口,因此,点击选项卡标签时,会调用 // public View createTabContent(String tag)来创建每个选项卡内容。该函数中的参数tag和newTabSpec中的参数是一样的。 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") .setIndicator("tab1", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.star_big_on)) .setContent(this)); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2") .setIndicator("tab2") .setContent(this)); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3") .setIndicator("tab3") .setContent(this)); } //每次点击选项卡标签时,根据选项卡tag标记来创建具体内容。 /** {@inheritDoc} */ public View createTabContent(String tag) { final TextView tv = new TextView(this); tv.setText("Content for tab with tag " + tag); return tv; } }
实例三、Content By Intent
src-com.example.android.apis.view-Tabs3.java
package com.example.android.apis.view; import android.app.TabActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.widget.TabHost; import android.content.Intent; /** * 演示如何使用TabHost * */ public class Tabs3 extends TabActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //获取TabActivity内置的TabHost对象 final TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //新建选项卡 //tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") 新建一个以“tab1”为标记的选项卡 //setIndicator("tab1") 设置选项卡标签标题为 list //setContent(new Intent(this, List1.class))) 点击该选项卡时,通过Intent,跳转到List1界面 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1") .setIndicator("list") .setContent(new Intent(this, List1.class))); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2") .setIndicator("photo list") .setContent(new Intent(this, List8.class))); // 这个选项卡设置 Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP 标记,是为了 每次点击该选项卡时,重新创建选项卡内容。 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3") .setIndicator("destroy") .setContent(new Intent(this, Controls2.class) .addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_CLEAR_TOP))); } }
预览效果: