数据挖掘-基于机器学习的SNS隐私策略推荐向导分类器的C++及WEKA实现与评估
本文接《基于机器学习的SNS隐私保护策略推荐向导的设计与实现》,详细解析基于机器学习的SNS隐私策略推荐向导分类器的C++及WEKA实现与评估结果,本文完整C++程序及JAVA工程下载链接见点击打开链接,对数据挖掘和SNS感兴趣的朋友可以下载跑一下,有任何问题欢迎交流:)
基于机器学习的SNS隐私策略推荐向导分类器的C++及WEKA实现与评估
1 SNS朋友数据预处理与统计
要实现对朋友访问权限的自动分类,首先需要对朋友的数据进行预处理。预处理主要包括向量化和格式化输出。格式化输出主要是针对使用的数据挖掘开源程序包,WWW10’原文中实验时采用的是RapidMiner,主要使用了其中的朴素贝叶斯、决策树及KNN算法的实现。本文中SNS隐私向导分类器的实现主要基于WEKA,同样是非常著名的数据挖掘开源程序包。WEKA支持命令行、GUI、程序API等多种调用方式。为了让WEKA成功读取样本数据,首先得知道WEKA对样本数据格式的规定,如图7-1所示,给出了本项目训练样本数据文件格式,以WEKA读取数据格式ARFF文件保存。
SNS朋友向量化的JAVA实现如下
package com.pku.yangliu; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStreamReader; import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.List; /**Compute the vector of friends in arff format * @author yangliu * @qq 772330184 * @mail [email protected] * @blog http://blog.csdn.net/yangliuy */ public class ComputeFriendsVector { public static String dataPath = "data/"; public static String resPath = "friendvec/"; public static String communityFile = "friendvec/community.out.txt"; /** * @param args * @throws IOException */ public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub File[] dataFiles = new File(dataPath).listFiles(); String line; for(int i = 0; i < dataFiles.length; i++){ BufferedReader dataFileReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(dataFiles[i]), "UTF-8")); BufferedReader communityFileReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(communityFile), "UTF-8")); String resFile = resPath +"vec_" +dataFiles[i].getName()+".arff"; FileWriter resFileWriter = new FileWriter(resFile); resFileWriter.append("@relation " + dataFiles[i].getName() + "_friends" + "\n\n"); //先写出arf文件头信息 writeArffHeader(resFileWriter); int count = 0; HashMap<String,String> userProfile = new HashMap<String,String>(); HashMap<String,String> friendProfile = new HashMap<String,String>(); HashSet<String> birthdays = new HashSet<String>(); String communityLine = communityFileReader.readLine();//第一行数据不要,是用户的圈子信息 communityLine = communityFileReader.readLine(); while((line = dataFileReader.readLine()) != null){ count++; if(count == 1){ System.out.print(count + " "); userProfile = transToMap(line); continue; }else{ friendProfile = transToMap(line); //基于frindProfile统计出现过的所有出生年份,写入arff文件头部 birthdays = countBirthdays(birthdays, friendProfile); line = generateVecLine(friendProfile, userProfile); resFileWriter.append(line + communityLine + "," + friendProfile.get("permission")+"\n"); System.out.println(line +" haha " + communityLine + "," + friendProfile.get("permission")); communityLine = communityFileReader.readLine(); } System.out.print(count + " "); } resFileWriter.flush(); resFileWriter.close(); System.out.println(birthdays.size()); for(String birth : birthdays){ System.out.print(birth + ","); } System.out.println(); } System.out.println("done"); } /**Count all the types of birthday * @param friendProfile * @param resFileWriter * @return Vector<String> * @throws IOException */ private static HashSet<String> countBirthdays(HashSet<String> birthdays, HashMap<String, String> friendProfile) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(friendProfile.containsKey("birthday")){ String year[] = friendProfile.get("birthday").split("[^0-9]"); birthdays.add(year[0]); } return birthdays; } /**Write the header of arff file * @param resFileWriter * @throws IOException */ private static void writeArffHeader(FileWriter resFileWriter) throws IOException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub resFileWriter.append("@attribute gender {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute birthday numeric\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute hometown {0,1,2}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute college {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute highschool {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute middleschool {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute primaryschool {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G1 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G2 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G3 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G4 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G5 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G6 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G7 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G8 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G9 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G10 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G11 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G12 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G13 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G14 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G15 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G16 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G17 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G18 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G19 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute G20 {0,1}\n"); resFileWriter.append("@attribute permission {0,1}\n\n"); resFileWriter.append("@data\n"); } /**Generate the line for the vector of a friend * @param friendProfile * @param userProfile * @return String the line for the vector of a friend * @throws UnsupportedEncodingException */ private static String generateVecLine( HashMap<String, String> friendProfile, HashMap<String, String> userProfile) throws UnsupportedEncodingException { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String vecLine = new String(); String[] keys = {"id", "name", "gender", "birthday", "hometown", "college", "highschool", "middleschool", "primaryschool","permission"}; for(String key : keys){ String userVal = userProfile.get(key); String friendVal = friendProfile.get(key); if(friendVal == null){//朋友缺失该项信息,向量中使用"?"表示 vecLine += "?" + ",";//arff文件分隔符为逗号 continue; } else { if(key.equals("id")){ continue; } else if(key.equals("name")){ continue; } else if(key.equals("gender")){ int flag = friendVal.trim().equals(userVal.trim()) ? 1 : 0; vecLine += String.valueOf(flag) + ","; } else if(key.equals("birthday")){ vecLine += birthdayToAge(friendVal.trim()) + ","; } else if(key.equals("hometown")){ vecLine += hometownToVecVal(userVal.trim(), friendVal.trim()) + ","; } else if(key.equals("college") ||key.equals("highschool") ||key.equals("middleschool") ||key.equals("primaryschool")){ vecLine += schoolToVecVal(userVal.trim(), friendVal.trim()) + ","; } else if(key.equals("permission")){ continue; } } } return vecLine; } /**Transfer school information to value in vector * @param userVal * @param friendVal * @return String value for school in vector */ private static String schoolToVecVal(String userVal, String friendVal) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String[] userSchools = userVal.split(" "); String[] friendSchools = friendVal.split(" "); List<String> userList = new ArrayList<String>(Arrays.asList(userSchools)); userList.retainAll(Arrays.asList(friendSchools)); if(userList.isEmpty()) return "0";//all schools has no interset else return "1"; } /**Transfer hometown information to value in vector * @param userVal * @param friendVal * @return String value for hometown in vector */ private static String hometownToVecVal(String userVal, String friendVal) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String[] userHometown = userVal.split("-"); String[] friendHometown = friendVal.split("-"); if(userHometown[0].trim().equals(friendHometown[0].trim())){ if(friendHometown.length == 1) return "1"; if(userHometown[1].trim().equals(friendHometown[1].trim())){ return "2"; } else return "1"; } else return "0"; } /**Transfer birthday information to age * @param userVal * @param friendVal * @return String age of friend */ private static String birthdayToAge(String friendVal) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub String[] birthdayInfo = friendVal.split("[^0-9]"); if(birthdayInfo.length == 0) return "?"; //Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); //int curYear = cal.get(Calendar.YEAR); //int birthYear = Integer.parseInt(birthdayInfo[0]); //改变一下生日的离散化算法,直接用生日年份来作为birthday //return String.valueOf(curYear - birthYear); return birthdayInfo[0].trim(); } /**Transfer the attribute of one friend to Map * @param line original attribute * @return HashMap<String,String> a Map to store the attribute information */ private static HashMap<String,String> transToMap(String line) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //System.out.println(line); String attri[] = line.split(";"); HashMap<String,String> profileMap = new HashMap<String,String>(); for(int i = 0; i < attri.length - 1; i++){ String keyVal[] = attri[i].split(":"); profileMap.put(keyVal[0].trim(), keyVal[1].trim()); } //最后一项是分类标签permission 0-deny 1-allow profileMap.put("permission", attri[attri.length - 1].trim()); return profileMap; } }
识别ARFF文件的重要依据是分行,因此不能在这种文件里随意的断行。整个ARFF文件可以分为两个部分。第一部分给出了头信息(Head information),包括了对关系的声明和对属性的声明。第二部分给出了数据信息(Data information),即数据集中给出的数据。从“@data”标记开始,后面的就是数据信息。 从图中的属性描述信息可知,朋友向量主要包括性别、生日、家乡、大学、高中、初中、小学以及抽取出的20个圈子属性。对该用户全部449个好友情况统计见表7-1。注意有部分朋友某些属性值无法获取,用“?”表示,表中没有统计入内。
表中最后一列用户隐私偏好(allow/deny)是用户根据自己的隐私偏好手动打算的标签,以备分类实验使用,选取的资料是用户“生日”,从表中可知,该用户只希望79位朋友看到他的生日信息。
2 SNS隐私向导分类器的实现
本项目隐私向导分类器的实现基于ID3和C4.5两种算法,ID3是自己用C++实现的,C4.5及决策树可视化主要基于数据挖掘开源程序包WEKA,主要是在训练样本的不定抽样阶段使用朴素贝叶斯算法进行每轮迭代分类计算熵值;在分类阶段使用决策树算法。本项目分类器的实现采取了基于WEKA实现和全部自己开发两种途径,下面重点介绍分类器中使用的决策树算法。
决策树算法是非常常用的分类算法,是逼近离散目标函数的方法,学习得到的函数以决策树的形式表示。其基本思路是不断选取产生信息增益最大的属性来划分样例集和,构造决策树。决策树的构造过程不依赖领域知识,它使用属性选择度量来选择将元组最好地划分成不同的类的属性。所谓决策树的构造就是进行属性选择度量确定各个特征属性之间的拓扑结构。构造决策树的关键步骤是分裂属性。所谓分裂属性就是在某个节点处按照某一特征属性的不同划分构造不同的分支,其目标是让各个分裂子集尽可能地“纯”。尽可能“纯”就是尽量让一个分裂子集中待分类项属于同一类别。
属性选择度量算法有很多,一般使用自顶向下递归分治法,并采用不回溯的贪心策略。基于WEKA的分类器主要使用C4.5算法,而自己开发的决策树分类器基于ID3算法。下面简要说明这两种算法的原理。
2.1 基于决策树ID3算法的分类器
从信息论知识中我们知道,期望信息越小,信息增益越大,从而纯度越高。所以ID3算法的核心思想就是以信息增益度量属性选择,选择分裂后信息增益最大的属性进行分裂。而信息纯度可以用熵来度量。信息熵是香农提出的,用于描述信息不纯度(不稳定性)。 设D为用类别对训练元组进行的划分,则D的熵(entropy)表示为:
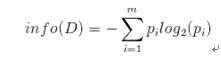
其中pi表示第i个类别在整个训练元组中出现的概率,可以用属于此类别元素的数量除以训练元组元素总数量作为估计。熵的实际意义表示是D中元组的类标号所需要的平均信息量。现在我们假设将训练元组D按属性A进行划分,则A对D划分的期望信息为:
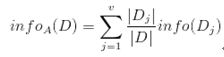
而信息增益即为两者的差值:![]()
ID3算法就是在每次需要分裂时,计算每个属性的增益率,然后选择增益率最大的属性进行分裂。
自己开发的基于ID3算法的SNS隐私向导的C++实现如下:
#include <iostream> #include <string> #include <vector> #include <map> #include <algorithm> #include <cmath> using namespace std; #define MAXLEN 9//输入每行的数据个数 /**基于决策树ID3的隐私向导分类器的C++实现 * @author yangliu * @qq 772330184 * @mail [email protected] * @blog http://blog.csdn.net/yangliuy */ vector <vector <string> > state;//实例集 vector <string> item(MAXLEN);//对应一行实例集 vector <string> attribute_row;//保存首行即属性行数据 string end("end");//输入结束 string yes("1"); string no("0"); string blank(""); map<string,vector < string > > map_attribute_values;//存储属性对应的所有的值 int tree_size = 0; struct Node{//决策树节点 string attribute;//属性值 string arrived_value;//到达的属性值 vector<Node *> childs;//所有的孩子 Node(){ attribute = blank; arrived_value = blank; } }; Node * root; //根据数据实例计算属性与值组成的map void ComputeMapFrom2DVector(){ unsigned int i,j,k; bool exited = false; vector<string> values; for(i = 1; i < MAXLEN-1; i++){//按照列遍历 for (j = 1; j < state.size(); j++){ for (k = 0; k < values.size(); k++){ if(!values[k].compare(state[j][i])) exited = true; } if(!exited){ values.push_back(state[j][i]);//注意Vector的插入都是从前面插入的,注意更新it,始终指向vector头 } exited = false; } map_attribute_values[state[0][i]] = values; values.erase(values.begin(), values.end()); } } //根据具体属性和值来计算熵 double ComputeEntropy(vector <vector <string> > remain_state, string attribute, string value,bool ifparent){ vector<int> count (2,0); unsigned int i,j; bool done_flag = false;//哨兵值 for(j = 1; j < MAXLEN; j++){ if(done_flag) break; if(!attribute_row[j].compare(attribute)){ for(i = 1; i < remain_state.size(); i++){ if((!ifparent&&!remain_state[i][j].compare(value)) || ifparent){//ifparent记录是否算父节点 if(!remain_state[i][MAXLEN - 1].compare(yes)){ count[0]++; } else count[1]++; } } done_flag = true; } } if(count[0] == 0 || count[1] == 0 ) return 0;//全部是正实例或者负实例 //具体计算熵 根据[+count[0],-count[1]],log2为底通过换底公式换成自然数底数 double sum = count[0] + count[1]; double entropy = -count[0]/sum*log(count[0]/sum)/log(2.0) - count[1]/sum*log(count[1]/sum)/log(2.0); return entropy; } //计算按照属性attribute划分当前剩余实例的信息增益 double ComputeGain(vector <vector <string> > remain_state, string attribute){ unsigned int j,k,m; //首先求不做划分时的熵 double parent_entropy = ComputeEntropy(remain_state, attribute, blank, true); double children_entropy = 0; //然后求做划分后各个值的熵 vector<string> values = map_attribute_values[attribute]; vector<double> ratio; vector<int> count_values; int tempint; for(m = 0; m < values.size(); m++){ tempint = 0; for(k = 1; k < MAXLEN - 1; k++){ if(!attribute_row[k].compare(attribute)){ for(j = 1; j < remain_state.size(); j++){ if(!remain_state[j][k].compare(values[m])){ tempint++; } } } } count_values.push_back(tempint); } for(j = 0; j < values.size(); j++){ ratio.push_back((double)count_values[j] / (double)(remain_state.size()-1)); } double temp_entropy; for(j = 0; j < values.size(); j++){ temp_entropy = ComputeEntropy(remain_state, attribute, values[j], false); children_entropy += ratio[j] * temp_entropy; } return (parent_entropy - children_entropy); } int FindAttriNumByName(string attri){ for(int i = 0; i < MAXLEN; i++){ if(!state[0][i].compare(attri)) return i; } cerr<<"can't find the numth of attribute"<<endl; return 0; } //找出样例中占多数的正/负性 string MostCommonLabel(vector <vector <string> > remain_state){ int p = 0, n = 0; for(unsigned i = 0; i < remain_state.size(); i++){ if(!remain_state[i][MAXLEN-1].compare(yes)) p++; else n++; } if(p >= n) return yes; else return no; } //判断样例是否正负性都为label bool AllTheSameLabel(vector <vector <string> > remain_state, string label){ int count = 0; for(unsigned int i = 0; i < remain_state.size(); i++){ if(!remain_state[i][MAXLEN-1].compare(label)) count++; } if(count == remain_state.size()-1) return true; else return false; } //计算信息增益,DFS构建决策树 //current_node为当前的节点 //remain_state为剩余待分类的样例 //remian_attribute为剩余还没有考虑的属性 //返回根结点指针 Node * BulidDecisionTreeDFS(Node * p, vector <vector <string> > remain_state, vector <string> remain_attribute){ if (p == NULL) p = new Node(); //先看搜索到树叶的情况 if (AllTheSameLabel(remain_state, yes)){ p->attribute = yes; return p; } if (AllTheSameLabel(remain_state, no)){ p->attribute = no; return p; } if(remain_attribute.size() == 0){//所有的属性均已经考虑完了,还没有分尽 string label = MostCommonLabel(remain_state); p->attribute = label; return p; } double max_gain = 0, temp_gain; vector <string>::iterator max_it = remain_attribute.begin(); vector <string>::iterator it1; for(it1 = remain_attribute.begin(); it1 < remain_attribute.end(); it1++){ temp_gain = ComputeGain(remain_state, (*it1)); if(temp_gain > max_gain) { max_gain = temp_gain; max_it = it1; } } //下面根据max_it指向的属性来划分当前样例,更新样例集和属性集 vector <string> new_attribute; vector <vector <string> > new_state; for(vector <string>::iterator it2 = remain_attribute.begin(); it2 < remain_attribute.end(); it2++){ if((*it2).compare(*max_it)) new_attribute.push_back(*it2); } //确定了最佳划分属性,注意保存 p->attribute = *max_it; vector <string> values = map_attribute_values[*max_it]; int attribue_num = FindAttriNumByName(*max_it); new_state.push_back(attribute_row); for(vector <string>::iterator it3 = values.begin(); it3 < values.end(); it3++){ for(unsigned int i = 1; i < remain_state.size(); i++){ if(!remain_state[i][attribue_num].compare(*it3)){ new_state.push_back(remain_state[i]); } } Node * new_node = new Node(); new_node->arrived_value = *it3; if(new_state.size() == 0){//表示当前没有这个分支的样例,当前的new_node为叶子节点 new_node->attribute = MostCommonLabel(remain_state); } else BulidDecisionTreeDFS(new_node, new_state, new_attribute); //递归函数返回时即回溯时需要1 将新结点加入父节点孩子容器 2清除new_state容器 p->childs.push_back(new_node); new_state.erase(new_state.begin()+1,new_state.end());//注意先清空new_state中的前一个取值的样例,准备遍历下一个取值样例 } return p; } void Input(){ string s; while(cin>>s,s.compare(end) != 0){//-1为输入结束 item[0] = s; for(int i = 1;i < MAXLEN; i++){ cin>>item[i]; } state.push_back(item);//注意首行信息也输入进去,即属性 } for(int j = 0; j < MAXLEN; j++){ attribute_row.push_back(state[0][j]); } } void PrintTree(Node *p, int depth){ for (int i = 0; i < depth; i++) cout << '\t';//按照树的深度先输出tab if(!p->arrived_value.empty()){ cout<<p->arrived_value<<endl; for (int i = 0; i < depth+1; i++) cout << '\t';//按照树的深度先输出tab } cout<<p->attribute<<endl; for (vector<Node*>::iterator it = p->childs.begin(); it != p->childs.end(); it++){ PrintTree(*it, depth + 1); } } void FreeTree(Node *p){ if (p == NULL) return; for (vector<Node*>::iterator it = p->childs.begin(); it != p->childs.end(); it++){ FreeTree(*it); } delete p; tree_size++; } int main(){ Input(); vector <string> remain_attribute; string gender("gender"); string birthday("birthday"); string hometown("hometown"); string college("college"); string highschool("highschool"); string middleschool("middleschool"); string primaryschool("primaryschool"); remain_attribute.push_back(gender); remain_attribute.push_back(birthday); remain_attribute.push_back(hometown); remain_attribute.push_back(college); remain_attribute.push_back(highschool); remain_attribute.push_back(middleschool); remain_attribute.push_back(primaryschool); vector <vector <string> > remain_state; for(unsigned int i = 0; i < state.size(); i++){ remain_state.push_back(state[i]); } ComputeMapFrom2DVector(); root = BulidDecisionTreeDFS(root,remain_state,remain_attribute); cout<<"the decision tree is :"<<endl; PrintTree(root,0); FreeTree(root); cout<<endl; cout<<"tree_size:"<<tree_size<<endl; return 0; }训练数据如下
id gender birthday hometown college highschool middleschool primaryschool permission 18 1 1987 1 0 0 0 0 0 19 1 1989 0 1 0 0 0 0 20 1 1984 0 0 0 0 0 0 21 1 1984 0 0 0 0 0 0 22 1 1984 0 1 0 0 0 0 23 1 1991 0 0 0 0 0 0 24 1 1988 1 1 0 0 0 1 25 1 1985 0 0 0 0 0 0 26 1 1987 0 0 0 0 0 0 27 1 1988 0 0 0 0 0 0 28 0 1988 1 0 0 0 0 0 29 1 1988 1 0 0 0 0 0 30 0 1984 0 0 0 0 0 0 31 0 1988 0 0 0 0 0 1 32 0 1989 0 1 0 0 0 1 end
程序根据朋友向量信息及用户标签训练数据输出的隐私向导决策树如下,当然如果训练数据越多,决策树中的结点就会越多,所得到的分类结果也就越精确。
2.2 基于决策树C4.5算法的分类器
ID3算法存在一个问题,就是偏向于多值属性,例如,如果存在唯一标识属性ID,则ID3会选择它作为分裂属性,这样虽然使得划分充分纯净,但这种划分对分类几乎毫无用处。ID3的后继算法C4.5使用增益率(gain ratio)的信息增益扩充,试图克服这个偏倚。
C4.5算法首先定义了“分裂信息”,其定义可以表示成:
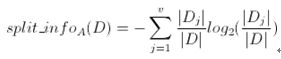
其中各符号意义与ID3算法相同,然后,增益率被定义为:![]()
C4.5选择具有最大增益率的属性作为分裂属性,其余建树及分类的过程和ID3类似。
3 分类器决策树可视化
本项目基于C4.5算法的决策树分类器实现主要基于WEKA,主要JAVA程序如下:
package com.pku.yangliu; import java.io.File; import java.util.Random; import weka.classifiers.Classifier; import weka.classifiers.Evaluation; import weka.classifiers.trees.J48; import weka.core.Instances; import weka.core.converters.ArffLoader; /**A Classifer for access control privilege of SNS friends * @author yangliu * @qq 772330184 * @mail [email protected] * @blog http://blog.csdn.net/yangliuy */ public class DecisionTreeClassifer { /** * @param args * @throws Exception */ public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Classifier m_classifier = new J48();//基于C4.5决策树的实现 //随机抽样实验 File inputFile = new File("friendvec/vec_profile.txt2.txt-train.arff");//训练样例 ArffLoader atf = new ArffLoader(); atf.setFile(inputFile); Instances instancesTrain = atf.getDataSet(); inputFile = new File("friendvec/vec_profile.txt2.txt-test.arff");//测试样例 atf.setFile(inputFile); Instances instancesTest = atf.getDataSet(); instancesTest.setClassIndex(instancesTrain.numAttributes() - 1); double testAmount = instancesTest.numInstances();//测试样本总数 double rightAmount = 0.0f;//分类正确的样本总数 instancesTrain.setClassIndex(instancesTrain.numAttributes() - 1); m_classifier.buildClassifier(instancesTrain);//基于决策树C4.5算法训练 //统计正确分类的结果 for(int i = 0; i < testAmount; i++){ if(m_classifier.classifyInstance(instancesTest.instance(i)) == instancesTest.instance(i).classValue()) { rightAmount++; } } System.out.println("Trian and test evaluateModel Results\nSNS Wizard random samples classification accuaracy:" + (rightAmount / testAmount * 100) + "00%"); //交叉验证法实验 inputFile = new File("friendvec/vec_profile.txt2.txt-whole.arff");//训练样例 atf.setFile(inputFile); instancesTrain = atf.getDataSet(); instancesTrain.setClassIndex(instancesTrain.numAttributes() - 1); //10组交叉验证评估分类器性能 Evaluation eval = new Evaluation(instancesTrain); J48 tree = new J48(); eval.crossValidateModel(tree, instancesTrain, 10, new Random(1)); System.out.println(eval.toSummaryString("\n\nSNS Wizard crossValidateModel classification accuaracy:", false)); // train classifier //J48 cls = new J48(); //cls.buildClassifier(instancesTrain); //evaluate classifier and print some statistics //Evaluation eval2 = new Evaluation(instancesTrain); //eval2.evaluateModel(cls, instancesTest); //System.out.println(eval.toSummaryString("\n trian and test evaluateModel Results\n\n", false)); } }
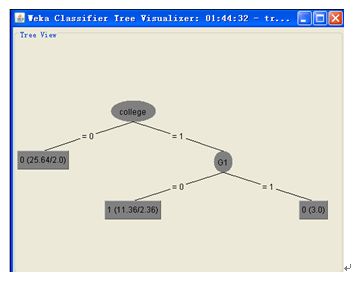
同时WEKA还良好支持了数据可视化,可以将训出的决策树可视化给SNS用户,其可视化的决策树见图7-2所示。
4 实验设计
SNS关系隐私向导分类实验结果的主要评价标准是分类的准确率,即隐私向导推荐设置准确率,主要描述了分类器计算出的隐私设置结果与用户实际隐私偏好的符合程度。其计算公式如下
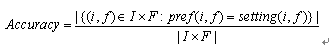
影响隐私向导推荐设置准确率的主要因素及主要实验设计思路如下:
1) 朋友向量的组成。是否加入了抽取的圈子信息属性,一般而言,准确抽取的圈子信息会有助于提高分类准确率;但是如果圈子信息提取误差很大,则可能起相反的作用。本项目设计实验对比了加入抽取圈子信息前后隐私设置准确率的变化情况。
2) 训练样本抽样方法。主要有随机抽样、交叉验证、基于圈子信息的抽样和不定抽样等方法,WWW10’论文里面使用的是不定抽样法,在本文的第5部分有介绍。本项目中主要采用了随机抽样和交叉验证法。
3) 分类算法。主要的分类算法有决策树、朴素贝叶斯、KNN等,不同分类算法的分类准确率和速度也会有差异,本项目实现主要对比了决策树和朴素贝叶斯算法的分类准确率。
5 实验结果及分类器评价
基于对圈子信息、抽样方法、分类算法对隐私向导推荐设置准确率的影响的分析,设计对比实验得出的隐私设置准确率见表7-2所示。
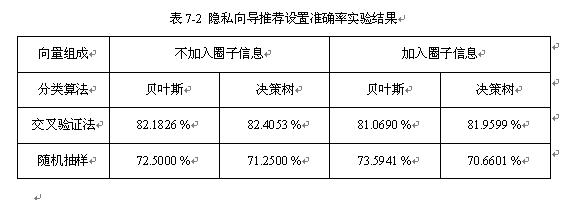
基于对实验结果的观察可以得出如下结论:
1) 朋友向量组成方面,一般而言,准确抽取的圈子信息会有助于提高分类准确率;但是在本项目实验中圈子信息提取误差很大,使得加入圈子信息后分类器的准确率下降。
2) 训练样本抽样方法方面,交叉验证法优于随机抽样法。
3) 分类算法方面,在SNS隐私策略向导分类应用上朴素贝叶斯算法和决策树算法没有显著分类准确率差异,由于数据量比较小,分类时间都很短。可以看出分类算法的选择对于隐私向导设置准确率没有显著影响。
本文完整C++程序及JAVA工程下载链接见点击打开链接,对数据挖掘和SNS感兴趣的朋友可以下载跑一下,有任何问题欢迎交流:)