Android 应用程序进程启动过程源码分析
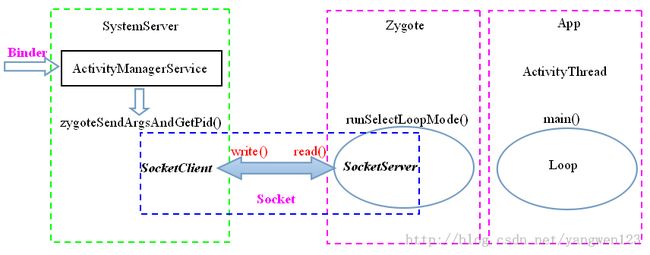
在Zygote进程启动过程的源代码分析一文中介绍到,Zygote是java世界的开创者,所有的java应用进程都是通过Zygote孵化出来的。我们知道在Android应用程序框架层中,ActivityManagerService组件负责管理Android应用程序的创建,ActivityManagerService也是运行在独立的进程SystemServer中,SystemServer进程启动过程源码分析中介绍了SystemServer进程是如果通过开启线程来启动各种服务,ActivityManagerService也是System Server启动的服务之一。
ActivityManagerService请求创建应用程序进程
当系统决定要在一个新的进程中启动一个Activity或者Service时,它就会创建一个新的进程,ActivityManagerService通过调用startProcessLocked函数来为应用程序启动新的进程。
frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,
ApplicationInfo info, boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,
String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName, boolean allowWhileBooting,
boolean isolated) {
ProcessRecord app;
//是否在现有进程中启动
if (!isolated) {
//从现有进程表mProcessNames中查找相应的进程描述符ProcessRecord
app = getProcessRecordLocked(processName, info.uid);
} else {
// If this is an isolated process, it can't re-use an existing process.
app = null;
}
// We don't have to do anything more if:
// (1) There is an existing application record; and
// (2) The caller doesn't think it is dead, OR there is no thread
// object attached to it so we know it couldn't have crashed; and
// (3) There is a pid assigned to it, so it is either starting or
// already running.
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "startProcess: name=" + processName
+ " app=" + app + " knownToBeDead=" + knownToBeDead
+ " thread=" + (app != null ? app.thread : null)
+ " pid=" + (app != null ? app.pid : -1));
if (app != null && app.pid > 0) {
if (!knownToBeDead || app.thread == null) {
// We already have the app running, or are waiting for it to
// come up (we have a pid but not yet its thread), so keep it.
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "App already running: " + app);
// If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
app.addPackage(info.packageName);
return app;
} else {
// An application record is attached to a previous process,
// clean it up now.
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "App died: " + app);
handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true);
}
}
String hostingNameStr = hostingName != null
? hostingName.flattenToShortString() : null;
if (!isolated) {
if ((intentFlags&Intent.FLAG_FROM_BACKGROUND) != 0) {
// If we are in the background, then check to see if this process
// is bad. If so, we will just silently fail.
if (mBadProcesses.get(info.processName, info.uid) != null) {
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "Bad process: " + info.uid
+ "/" + info.processName);
return null;
}
} else {
// When the user is explicitly starting a process, then clear its
// crash count so that we won't make it bad until they see at
// least one crash dialog again, and make the process good again
// if it had been bad.
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "Clearing bad process: " + info.uid
+ "/" + info.processName);
mProcessCrashTimes.remove(info.processName, info.uid);
if (mBadProcesses.get(info.processName, info.uid) != null) {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_GOOD, info.uid,info.processName);
mBadProcesses.remove(info.processName, info.uid);
if (app != null) {
app.bad = false;
}
}
}
}
if (app == null) {
//在ActivityManagerService中为新进程创建一个ProcessRecord实例
app = newProcessRecordLocked(null, info, processName, isolated);
if (app == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed making new process record for "
+ processName + "/" + info.uid + " isolated=" + isolated);
return null;
}
//添加到进程列表中
mProcessNames.put(processName, app.uid, app);
//如果当前服务运行在独立进程中,添加到独立进程表mIsolatedProcesses中
/**
* SparseArray<ProcessRecord> mIsolatedProcesses = new SparseArray<ProcessRecord>();
* The currently running isolated processes.
*/
if (isolated) {
mIsolatedProcesses.put(app.uid, app);
}
} else {
// If this is a new package in the process, add the package to the list
app.addPackage(info.packageName);
}
// If the system is not ready yet, then hold off on starting this
// process until it is.
if (!mProcessesReady && !isAllowedWhileBooting(info) && !allowWhileBooting) {
/**
* final ArrayList<ProcessRecord> mProcessesOnHold = new ArrayList<ProcessRecord>();
* List of records for processes that someone had tried to start before the
* system was ready. We don't start them at that point, but ensure they
* are started by the time booting is complete.
*/
if (!mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) {
mProcessesOnHold.add(app);
}
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG, "System not ready, putting on hold: " + app);
return app;
}
//调用startProcessLocked启动新的应用程序进程
startProcessLocked(app, hostingType, hostingNameStr);
return (app.pid != 0) ? app : null;
}在该函数里,首先在ActivityManagerService中为即将创建的新应用程序进程创建一个ProcessRecord对象,并保存到mProcessNames进程列表中,然后调用另一个重载函数startProcessLocked来请求创建一个新的应用程序进程。
frameworks\base\services\java\com\android\server\am\ActivityManagerService.java
private final void startProcessLocked(ProcessRecord app,
String hostingType, String hostingNameStr) {
if (app.pid > 0 && app.pid != MY_PID) {
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
mPidsSelfLocked.remove(app.pid);
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
}
app.pid = 0;
}
//系统准备好了,马上启动服务,因此如果mProcessesOnHold列表中包含当前启动的服务,则需移除
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES && mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) Slog.v(TAG,
"startProcessLocked removing on hold: " + app);
mProcessesOnHold.remove(app);
//唤醒进程信息收集线程
updateCpuStats();
System.arraycopy(mProcDeaths, 0, mProcDeaths, 1, mProcDeaths.length-1);
mProcDeaths[0] = 0;
try {
int uid = app.uid;
int[] gids = null;
if (!app.isolated) {
try {
gids = mContext.getPackageManager().getPackageGids(
app.info.packageName);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to retrieve gids", e);
}
}
if (mFactoryTest != SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_OFF) {
if (mFactoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL
&& mTopComponent != null
&& app.processName.equals(mTopComponent.getPackageName())) {
uid = 0;
}
if (mFactoryTest == SystemServer.FACTORY_TEST_HIGH_LEVEL
&& (app.info.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_FACTORY_TEST) != 0) {
uid = 0;
}
}
//设置应用程序进程创建方式
int debugFlags = 0;
if ((app.info.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_DEBUGGABLE) != 0) {
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER;
// Also turn on CheckJNI for debuggable apps. It's quite
// awkward to turn on otherwise.
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI;
}
// Run the app in safe mode if its manifest requests so or the
// system is booted in safe mode.
if ((app.info.flags & ApplicationInfo.FLAG_VM_SAFE_MODE) != 0 ||
Zygote.systemInSafeMode == true) {
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE;
}
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.checkjni"))) {
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI;
}
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.jni.logging"))) {
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING;
}
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.assert"))) {
debugFlags |= Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT;
}
//它调用了Process.start函数开始为应用程序创建新的进程,
//它传入一个第一个参数为"android.app.ActivityThread",这就是进程初始化时要加载的Java类了,
//把这个类加载到进程之后,就会把它里面的静态成员函数main作为进程的入口点,
Process.ProcessStartResult startResult = Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread",
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, null);
BatteryStatsImpl bs = app.batteryStats.getBatteryStats();
synchronized (bs) {
if (bs.isOnBattery()) {
app.batteryStats.incStartsLocked();
}
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_START, startResult.pid, uid,
app.processName, hostingType,
hostingNameStr != null ? hostingNameStr : "");
//如果启动的进程是一个持久进程,则添加到Watchdog中监控
if (app.persistent) {
Watchdog.getInstance().processStarted(app.processName, startResult.pid);
}
StringBuilder buf = mStringBuilder;
buf.setLength(0);
buf.append("Start proc ");
buf.append(app.processName);
buf.append(" for ");
buf.append(hostingType);
if (hostingNameStr != null) {
buf.append(" ");
buf.append(hostingNameStr);
}
buf.append(": pid=");
buf.append(startResult.pid);
buf.append(" uid=");
buf.append(uid);
buf.append(" gids={");
if (gids != null) {
for (int gi=0; gi<gids.length; gi++) {
if (gi != 0) buf.append(", ");
buf.append(gids[gi]);
}
}
buf.append("}");
Slog.i(TAG, buf.toString());
app.pid = startResult.pid;
app.usingWrapper = startResult.usingWrapper;
app.removed = false;
//将新创建的进程描述符ProcessRecord保存到mPidsSelfLocked链表中
/**
* final SparseArray<ProcessRecord> mPidsSelfLocked = new SparseArray<ProcessRecord>();
* All of the processes we currently have running organized by pid.
* The keys are the pid running the application.
*/
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
this.mPidsSelfLocked.put(startResult.pid, app);
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = app;
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, startResult.usingWrapper
? PROC_START_TIMEOUT_WITH_WRAPPER : PROC_START_TIMEOUT);
}
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
// XXX do better error recovery.
app.pid = 0;
Slog.e(TAG, "Failure starting process " + app.processName, e);
}
if (LC_RAM_SUPPORT
&& ((app.info.flags & (ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM)) == (ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM))
&& (CONTACTS_PROCESS_NAME.equals(app.processName))) {
app.isContactsProcess = true;
}
if (LC_RAM_SUPPORT && fixAdjList.containsKey(app.processName)) {
app.fixAdj = fixAdjList.get(app.processName);
Slog.v(TAG, "app[" + app.processName + "] has fix adj:" + app.fixAdj);
}
}在该函数里,首先获取即将创建的应用程序的gid和uid,并设置应用程序进程创建方式,然后调用Process类的start()函数来创建一个新的应用程序进程,同时指定新进程执行的入口为ActivityThread类的main函数。
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\Process.java
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int targetSdkVersion,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, targetSdkVersion, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException("Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}该函数直接调用startViaZygote()函数来创建一个新的应用程序进程。
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\Process.java
private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int targetSdkVersion,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
synchronized(Process.class) {
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();
// --runtime-init, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-init");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-jni-logging");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-safemode");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-checkjni");
}
if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT) != 0) {
argsForZygote.add("--enable-assert");
}
argsForZygote.add("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);
//TODO optionally enable debuger
//argsForZygote.add("--enable-debugger");
// --setgroups is a comma-separated list
if (gids != null && gids.length > 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("--setgroups=");
int sz = gids.length;
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
if (i != 0) {
sb.append(',');
}
sb.append(gids[i]);
}
argsForZygote.add(sb.toString());
}
if (niceName != null) {
argsForZygote.add("--nice-name=" + niceName);
}
argsForZygote.add(processClass);
if (extraArgs != null) {
for (String arg : extraArgs) {
argsForZygote.add(arg);
}
}
//将通过Socket方式将参数列表发送给Zygote进程
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(argsForZygote);
}
}在该函数里,首先将新的应用程序进程启动参数保存到argsForZygote列表中,然后调用zygoteSendArgsAndGetPid将应用程序进程启动参数发送到Zygote进程。
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\Process.java
private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(ArrayList<String> args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
//创建一个客户端Socket,并连接到Zygote进程的Socket服务端
openZygoteSocketIfNeeded();
try {
/**
* See com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.readArgumentList()
* Presently the wire format to the zygote process is:
* a) a count of arguments (argc, in essence)
* b) a number of newline-separated argument strings equal to count
*
* After the zygote process reads these it will write the pid of
* the child or -1 on failure, followed by boolean to
* indicate whether a wrapper process was used.
*/
//将应用程序启动参数列表写入到Socket
sZygoteWriter.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
sZygoteWriter.newLine();
int sz = args.size();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
if (arg.indexOf('\n') >= 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(
"embedded newlines not allowed");
}
sZygoteWriter.write(arg);
sZygoteWriter.newLine();
}
sZygoteWriter.flush();
//读取Zygote进程返回来的结果
ProcessStartResult result = new ProcessStartResult();
result.pid = sZygoteInputStream.readInt();
if (result.pid < 0) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("fork() failed");
}
result.usingWrapper = sZygoteInputStream.readBoolean();
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
try {
if (sZygoteSocket != null) {
sZygoteSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex2) {
// we're going to fail anyway
Log.e(LOG_TAG,"I/O exception on routine close", ex2);
}
sZygoteSocket = null;
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}该函数首先在SystemServer进程中创建一个客户端LocalSocket,并连接到Zygote进程的名为"zygote"的服务端Socket
private static void openZygoteSocketIfNeeded()
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
int retryCount;
if (sPreviousZygoteOpenFailed) {
/*
* If we've failed before, expect that we'll fail again and
* don't pause for retries.
*/
retryCount = 0;
} else {
retryCount = 10;
}
/*
* See bug #811181: Sometimes runtime can make it up before zygote.
* Really, we'd like to do something better to avoid this condition,
* but for now just wait a bit...
*/
for (int retry = 0; (sZygoteSocket == null) && (retry < (retryCount + 1)); retry++ ) {
if (retry > 0) {
try {
Log.i("Zygote", "Zygote not up yet, sleeping...");
Thread.sleep(ZYGOTE_RETRY_MILLIS);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
// should never happen
}
}
try {
sZygoteSocket = new LocalSocket();
//连接到Zygote进程的服务端zygote Socket
sZygoteSocket.connect(new LocalSocketAddress(ZYGOTE_SOCKET, LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED));
sZygoteInputStream = new DataInputStream(sZygoteSocket.getInputStream());
sZygoteWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
sZygoteSocket.getOutputStream()),256);
Log.i("Zygote", "Process: zygote socket opened");
sPreviousZygoteOpenFailed = false;
break;
} catch (IOException ex) {
//Socket操作失败,关闭该Socket
if (sZygoteSocket != null) {
try {
sZygoteSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ex2) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,"I/O exception on close after exception",ex2);
}
}
sZygoteSocket = null;
}
}
if (sZygoteSocket == null) {
sPreviousZygoteOpenFailed = true;
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("connect failed");
}
}最后将参数列表写入到创建的客户端Socket中,从而将应用程序启动参数发送给Zygote进程,启动参数包括:
"--runtime-init"
"--setuid=x"
"--setgid=x"
"--enable-safemode"
"--enable-debugger"
"--enable-checkjni"
"--enable-assert"
"--setgroups=x"
"--nice-name=x"
"android.app.ActivityThread"
要启动一个新的应用程序进程,应用程序不能直接请求Zygote来fork出新进程,而是要通过SystemServer进程中的ActivityManagerService服务来请求Zygote进程。
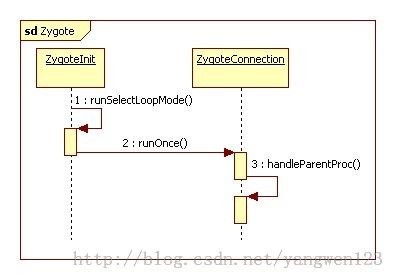
Zygote进程孵化应用程序进程
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteInit.java
private static void runSelectLoopMode() throws MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList();
FileDescriptor[] fdArray = new FileDescriptor[4];
fds.add(sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
int loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
while (true) {
int index;
/*
* Call gc() before we block in select().
* It's work that has to be done anyway, and it's better
* to avoid making every child do it. It will also
* madvise() any free memory as a side-effect.
*
* Don't call it every time, because walking the entire
* heap is a lot of overhead to free a few hundred bytes.
*/
if (loopCount <= 0) {
gc();
loopCount = GC_LOOP_COUNT;
} else {
loopCount--;
}
try {
fdArray = fds.toArray(fdArray);
//监听zygote Socket是否有客户端连接
index = selectReadable(fdArray);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()", ex);
}
if (index < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("Error in select()");
//zygote socket句柄中有事件到来,表示有客户端的socket连接
} else if (index == 0) {
//接收客户端连接请求,并将客户端请求添加到句柄池中监控
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer();
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
//客户端连接Socket有事件到来,表示SystemServer进程正在发送应用程序启动参数
} else {
boolean done;
//孵化一个新的应用程序进程
done = peers.get(index).runOnce();
//从socket句柄池中移除客户连接socket句柄
if (done) {
peers.remove(index);
fds.remove(index);
}
}
}
}当接收到新的客户端socket连接请求时,函数从selectReadable中返回,并为该客户端连接创建一个ZygoteConnection实例;当Zygote接收到SystemServer进程发送过来的应用程序进程启动参数时,就会调用相应ZygoteConnection实例的runOnce()函数来启动一个新的进程。
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteConnection.java
boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
//读取参数
args = readArgumentList();
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());
closeSocket();
return true;
}
if (args == null) {
// EOF reached.
closeSocket();
return true;
}
/** the stderr of the most recent request, if avail */
PrintStream newStderr = null;
if (descriptors != null && descriptors.length >= 3) {
newStderr = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(descriptors[2]));
}
int pid = -1;
FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
try {
parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);
applyUidSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyRlimitSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyCapabilitiesSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyInvokeWithSecurityPolicy(parsedArgs, peer);
applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
int[][] rlimits = null;
if (parsedArgs.rlimits != null) {
rlimits = parsedArgs.rlimits.toArray(intArray2d);
}
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit && parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
FileDescriptor[] pipeFds = Libcore.os.pipe();
childPipeFd = pipeFds[1];
serverPipeFd = pipeFds[0];
ZygoteInit.setCloseOnExec(serverPipeFd, true);
}
//创建子进程,而且有两个返回值,一个是在当前进程中返回的,一个是在新创建的进程中返回,
//即在当前进程的子进程中返回,在当前进程中的返回值就是新创建的子进程的pid值,而在子进程中的返回值是0。
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids, parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits);
} catch (IOException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Exception creating pipe", ex);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Invalid zygote arguments", ex);
} catch (ZygoteSecurityException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,
"Zygote security policy prevents request: ", ex);
}
try {
//父子进程运行分界线
if (pid == 0) {
//子进程执行过程
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
//父进程,也就是Zygote进程执行过程
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}函数首先调用readArgumentList读取ActivityManagerService发送过来的应用程序启动参数,接着根据参数调用forkAndSpecialize函数fork一个新的应用程序进程,就是复制一份Zygote进程地址空间,当返回的pid=0时,表示当前是新创建的应用程序进程,否则为Zygote进程的函数执行返回。首先来分析Zygote进程返回后执行的工作:
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteConnection.java
private boolean handleParentProc(int pid,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, Arguments parsedArgs) {
if (pid > 0) {
setChildPgid(pid);
}
if (descriptors != null) {
for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd);
}
}
boolean usingWrapper = false;
if (pipeFd != null && pid > 0) {
DataInputStream is = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream(pipeFd));
int innerPid = -1;
try {
innerPid = is.readInt();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "Error reading pid from wrapped process, child may have died", ex);
} finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
}
}
// Ensure that the pid reported by the wrapped process is either the
// child process that we forked, or a descendant of it.
if (innerPid > 0) {
int parentPid = innerPid;
while (parentPid > 0 && parentPid != pid) {
parentPid = Process.getParentPid(parentPid);
}
if (parentPid > 0) {
Log.i(TAG, "Wrapped process has pid " + innerPid);
pid = innerPid;
usingWrapper = true;
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "Wrapped process reported a pid that is not a child of "
+ "the process that we forked: childPid=" + pid
+ " innerPid=" + innerPid);
}
}
}
//将创建的应用程序进程ID返回给SystemServer进程的ActivityManagerService服务
try {
mSocketOutStream.writeInt(pid);
mSocketOutStream.writeBoolean(usingWrapper);
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reading from command socket", ex);
return true;
}
/*
* If the peer wants to use the socket to wait on the
* newly spawned process, then we're all done.
*/
if (parsedArgs.peerWait) {
try {
mSocket.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote: error closing sockets", ex);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}Zygote进程将新创建的应用程序进程写回到SystemServer进程后,从函数handleParentProc一路返回到runSelectLoopMode(),继续监听客户端进程的Socket连接请求。
Zygote孵化出新的应用程序进程后,新的应用程序进程将执行handleChildProc函数,从此与其父进程Zygote分道扬镳。
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteConnection.java
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
/*
* Close the socket, unless we're in "peer wait" mode, in which
* case it's used to track the liveness of this process.
*/
if (parsedArgs.peerWait) {
try {
ZygoteInit.setCloseOnExec(mSocket.getFileDescriptor(), true);
sPeerWaitSocket = mSocket;
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote Child: error setting peer wait "
+ "socket to be close-on-exec", ex);
}
} else {//关闭从Zygote进程复制过来的Socket连接
closeSocket();
ZygoteInit.closeServerSocket();
}
if (descriptors != null) {
try {
//为新创建的应用程序进程重新打开标准输入输出控制台
ZygoteInit.reopenStdio(descriptors[0],descriptors[1], descriptors[2]);
for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors) {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(fd);
}
newStderr = System.err;
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error reopening stdio", ex);
}
}
//设置新进程名称
if (parsedArgs.niceName != null) {
Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.niceName);
}
//重新初始化Runtime
if (parsedArgs.runtimeInit) {
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.invokeWith,
parsedArgs.niceName, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
pipeFd, parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
} else {
//为应用程序进程启动Binder线程池
RuntimeInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,parsedArgs.remainingArgs);
}
} else {
String className;
try {
//读取新进程执行的类名,在Process.start()函数中,传过来的类名为:"android.app.ActivityThread"
className = parsedArgs.remainingArgs[0];
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr,"Missing required class name argument", null);
return;
}
String[] mainArgs = new String[parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length - 1];
System.arraycopy(parsedArgs.remainingArgs, 1,mainArgs, 0, mainArgs.length);
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
WrapperInit.execStandalone(parsedArgs.invokeWith,parsedArgs.classpath, className, mainArgs);
} else {
//获取类加载器
ClassLoader cloader;
if (parsedArgs.classpath != null) {
cloader = new PathClassLoader(parsedArgs.classpath,ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
} else {
cloader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
//加载并执行"android.app.ActivityThread"类
try {
ZygoteInit.invokeStaticMain(cloader, className, mainArgs);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
logAndPrintError(newStderr, "Error starting.", ex);
}
}
}
}由于应用程序启动参数中已经设置了"--runtime-init"标志位,因此新创建的应用程序进程将调用RuntimeInit.zygoteInit()函数来初始化运行时库,为应用程序启动Binder线程池,完成这些准备工作后,调用应用程序进程的入口函数ActivityThread.main()为应用程序进程创建消息循环。
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\RuntimeInit.java
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
//重定向Log输出流
redirectLogStreams();
//初始化运行环境
commonInit();
//启动Binder线程池
nativeZygoteInit();
//调用程序入口函数
applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv);
}1. 初始化Log输出流
/**
* Redirect System.out and System.err to the Android log.
*/
public static void redirectLogStreams() {
System.out.close();
System.setOut(new AndroidPrintStream(Log.INFO, "System.out"));
System.err.close();
System.setErr(new AndroidPrintStream(Log.WARN, "System.err"));
}
2.初始化运行环境
private static final void commonInit() {
if (DEBUG) Slog.d(TAG, "Entered RuntimeInit!");
/* set default handler; this applies to all threads in the VM */
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new UncaughtHandler());
/*
* Install a TimezoneGetter subclass for ZoneInfo.db
*/
TimezoneGetter.setInstance(new TimezoneGetter() {
@Override
public String getId() {
return SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
}
});
TimeZone.setDefault(null);
/*
* Sets handler for java.util.logging to use Android log facilities.
* The odd "new instance-and-then-throw-away" is a mirror of how
* the "java.util.logging.config.class" system property works. We
* can't use the system property here since the logger has almost
* certainly already been initialized.
*/
LogManager.getLogManager().reset();
new AndroidConfig();
/*
* Sets the default HTTP User-Agent used by HttpURLConnection.
*/
String userAgent = getDefaultUserAgent();
System.setProperty("http.agent", userAgent);
/*
* Wire socket tagging to traffic stats.
*/
NetworkManagementSocketTagger.install();
/*
* If we're running in an emulator launched with "-trace", put the
* VM into emulator trace profiling mode so that the user can hit
* F9/F10 at any time to capture traces. This has performance
* consequences, so it's not something you want to do always.
*/
String trace = SystemProperties.get("ro.kernel.android.tracing");
if (trace.equals("1")) {
Slog.i(TAG, "NOTE: emulator trace profiling enabled");
Debug.enableEmulatorTraceOutput();
}
initialized = true;
}
3.启动Binder线程池
关于Binder线程池的启动过程请参考Android应用程序启动Binder线程源码分析
4.调用进程入口函数
static void invokeStaticMain(ClassLoader loader,
String className, String[] argv)
throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {
//加载"android.app.ActivityThread"类
Class<?> cl;
try {
cl = loader.loadClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
//通过类反射机制查找ActivityThread类中的main函数
Method m;
try {
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Missing static main on " + className, ex);
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
}
//获取main函数的修饰符
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
//进程入口函数必须为静态Public类型
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
throw new RuntimeException("Main method is not public and static on " + className);
}
/*
* This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
* by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
* clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
* up the process.
*/
throw new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
抛出MethodAndArgsCaller异常,并在ZygoteInit.main()函数中捕获该异常,这样就可以清除应用程序进程创建过程的调用栈,将应用程序启动的入口函数设置为ActivityThread.main()
frameworks\base\core\java\com\android\internal\os\ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
try {
...
//捕获MethodAndArgsCaller异常
} catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "Zygote died with exception", ex);
closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}在该函数里,捕获了MethodAndArgsCaller异常,并调用MethodAndArgsCaller类的run()方法来处理异常:
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}这里通过反射机制调用ActivityThread类的main函数,到此新的应用程序进程就创建完毕,同时新的应用程序从ActivityThread.main()函数中开始运行。
frameworks\base\core\java\android\app\ActivityThread.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
SamplingProfilerIntegration.start();
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");
//为新的应用程序创建消息队列
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = new Handler();
}
//创建一个ActivityThread对象,初始化应用程序运行环境,每一个进程对应一个ActivityThread实例
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
//建立与ActivityManagerService之间的Binder通信通道
thread.attach(false);
AsyncTask.init();
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(newLogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
//为新的应用程序进程启动消息循环,这个消息循环就是应用程序主线程消息循环
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
至此,Android应用程序进程启动过程的源代码就分析完成了,以下是android应用进程的启动过程的时序图: