poj 2046 Gap(dfs&hash&壮压)
题意:
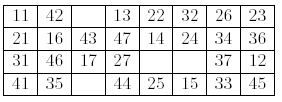
如图分部这的卡片,每次移动一个空格,让比空格左边的数大一的数移动到空格。最后达到目标状态。问最少的步数。
思路:
关键在于hash。然后就是简单的bfs和判重了。。。
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<sstream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<set>
#include<map>
//#pragma comment(linker,"/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
using namespace std;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const double eps=1e-8;
const double PI=acos(-1.0);
const int maxn=100010;
const int mod=1000007;
typedef __int64 ll;
/*
int aim[4][8]=
{
{11,12,13,14,15,16,17,0},
{21,22,23,24,25,26,27,0},
{31,32,33,34,35,36,37,0},
{41,42,43,44,45,46,47,0}
};
*/
ll over=98430874871LL;//最终状态值
ll base[33];
struct yb
{
int bx[4],by[4],maze[4][8];//四个空格的位置和整个图
ll step;
ll cod;//状态值
} tmp;
struct HASHMAP//hash结构体
{
int head[mod],next[mod],sz;
ll st[mod];
void init()
{
sz=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof head);
}
bool Insert(ll code)
{
int i,h=code%mod;
for(i=head[h];i!=-1;i=next[i])
{
if(st[i]==code)
return true;
}
st[sz]=code;
next[sz]=head[h];
head[h]=sz++;
return false;
}
} hm;
queue<yb> q;
ll getcode(int st[][8])//壮压
{
int i,j;
ll tp=0;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<8;j++)
tp+=st[i][j]*base[i*8+j];//都这么压。表示怀疑。
return tp;
}
ll bfs()
{
int x,y,i,j,k;
yb tt;
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
q.push(tmp);
while(!q.empty())
{
tt=q.front();
if(tt.cod==over)
return tt.step;
for(k=0;k<4;k++)
{
tmp=tt;
x=tmp.bx[k];
y=tmp.by[k];
if(tmp.maze[x][y-1]==0)
continue;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<8;j++)
{
if(tmp.maze[i][j]!=tmp.maze[x][y-1]+1)//连续空格
continue;
tmp.maze[x][y]=tmp.maze[i][j];
tmp.maze[i][j]=0;
tmp.bx[k]=i;
tmp.by[k]=j;
if(!hm.Insert(tmp.cod=getcode(tmp.maze)))
{
tmp.step++;
q.push(tmp);
}
}
}
}
q.pop();
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,k,n,tt,cnt;
base[0]=1;
for(i=1;i<=33;i++)
base[i]=base[i-1]<<1;
while(~scanf("%d",&n))
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
{
hm.init();
cnt=0;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
tmp.maze[i][0]=(i+1)*10+1;
for(j=1;j<8;j++)
{
scanf("%d",&tt);
if(tt%10==1)
{
tmp.maze[i][j]=0;
tmp.bx[cnt]=i;
tmp.by[cnt++]=j;
}
else
tmp.maze[i][j]=tt;
}
}
tmp.step=0;
tmp.cod=getcode(tmp.maze);
printf("%I64d\n",bfs());
}
}
return 0;
}