Struts tags详解(Data tags)
*****************************************************************************************************************
@author Lue
@e-mail [email protected]
@note 本文格式排版尽量利于阅读,如果在阅读本文时有不便之处还请见谅(文中例子来源structs2文档)
*****************************************************************************************************************
struts2 tags详解之 <s:a> 和 <s:url> 标签
这两个标签用来创建一个URL 链接。所谓URL 连接,即是Web 中最常见的标签样式:
<a href=""> 标签文本</a>
但在Struts 2 中,Struts 对其做了封装,使用<s:url> 和<s:a> 来表示<a> 标签,经过Java Web 服务器的解析,客户端最终看到的还是<a> 标签。
其中<s:a> 标签支持<s:url> 标签的所有属性,包括使用<param> 来嵌套属性参数。但是如果你想在<s:a> 中添加额外的参数,这里建议使用<s:url> 来创建你的url 。然后你再将这个url 插入到<s:a> 标签中。以下这个例子就是先定义一个id 属性,id=testUriId ,然后再<s:a> 中利用%{testUrlId} 引用这个属性值。
<s:url id="testUrlId" namespace="/subscriber" action="customField" method="delete">
<s:param name="customFieldDefinition.id" value="${id}"/>
</s:url>
<s:a errorText="Sorry your request had an error." preInvokeJS="confirm('Are you sure you want to delete this item?')" href="%{testUrlId}">
<img src="<s:url value="/images/delete.gif"/>" border="none"/>
</s:a>
你可以用<param> 标签在body 中插入需要额外添加的参数,如果这个参数的值是一个数组或者iterable ,那么它们所有的值都将被添加到URL 中。默认情况下请求参数会使用& 符号分离使用( 这是XHTML 的规定) 。
当属性 includeParams的值 是' all' 或' get' ,在<PARAM> 标记中定义的 参数将 优先于 任何 参数 ,包括 includeParams 属性。例如,在 示例 3 所示:
如果 有一个 id 参数的 url 如这个标签 这样:
http://<host>:<port>/<context>/editUser.action?id=3333&name=John
生成的URL 将是
http://<host>:<port>/<context>/editUser.action?id=22&name=John ,
因为在param 标签中定义的 参数将 优先考虑 。
<-- Example 1 -->
<s:url value="editGadget.action">
<s:param name="id" value="%{selected}" />
</s:url>
<-- Example 2 -->
<s:url action="editGadget">
<s:param name="id" value="%{selected}" />
</s:url>
<-- Example 3-->
<s:url includeParams="get">
<s:param name="id" value="%{'22'}" />
</s:url>
*****************************************************************************************************************
下面的例子部分来自于:
http://www.blogjava.net/sterning/archive/2008/01/04/172644.html
在此感谢作者!!!
*****************************************************************************************************************
struts2 tags详解之<s:action>
简单描述
这个标记使开发人员直接通过指定的动作名称(action name)和可选的命名空间(optional namespace)从一个JSP页面来调用动作(actions)。
标签的参数可以通过param标签来传递到action中
Placement in context
这里需要注意的是:在<action>标签内部,action是不允许被访问的。如:
<s:action var="myAction" name="MyAction" namespace="/">
Is "myAction" null inside the tag? <s:property value="#myAction == null" />
</s:action>
Is "myAction" null outside the tag? <s:property value="#myAction == null" />
下面是它的结果:
Will print:
Is "myAction" null inside the tag? true
Is "myAction" null outside the tag? false
部分属性
Id:可选属性,作为该Action的引用ID
Name:必选属性,指定调用Action
Namespace:可选属性,指定该标签调用Action所属namespace
executeResult:可选属性,指定是否将Action的处理结果包含到本页面中.默认值为false,不包含.
ignoreContextParam:可选参数,指定该页面的请求参数是否需要传入调用的Action中,默认值是false,即传入参数.
示例
Struts2页面中需要显示动态数据时,需要将这些数据在页面文件外面获取,然后通过某种方式传到页面中,因为要避免在JSP页面中编写Java代码。比如需要从数据库中读取一系列数据,我们一般要通过action来获取这些数据,然后让页面得到action中获取的数据。(下面的例子是在网上看到的一个例子稍作修改,未做验证)
1.WebRoot/pages/dataTagssuccess.jsp处理页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Action Tag 示例</title>
</head>
<body>
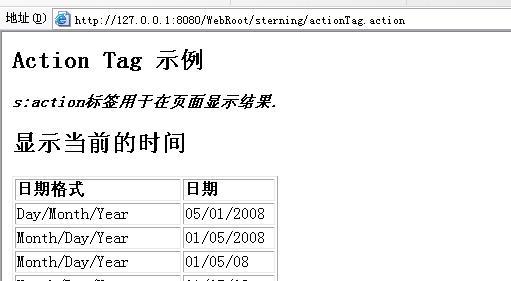
<h2>Action Tag 示例</h2>
<s:action name="dateTag" executeResult="true">
<b><i>s:action标签用于在页面显示结果.</i></b></div>
</s:action>
</body>
</html>
这里使用<s:action>标签调用action,并用于显示处理的结果。
2.先来看struts.xml中的配置:
<action name="actionTag" class="com.sterning.actionTag">
<result name="success">/pages/dataTags/success.jsp</result>
</action>
<action name="dateTag" class="com.sterning.dateTag">
<result>/pages/dataTags/dateTag.jsp</result>
</action>
3.接着创建actionTag类:代码如下:
package com.sterning;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
publicclass actionTag extends ActionSupport {
public String execute() throws Exception{
returnSUCCESS;
}
}
其实该类中没有做任何处理,只是进行页面跳转而已。
运行如下:
struts tags详解之<s:bean>
Description
Bean标签,当然需要一个JavaBean。它的属性值的操作是经由Bean标签中的参数属性来进行赋值。当然,它还有一个id属性可以进行赋值,这样就可以在上下文中使用这个Bean
如果在BeanTag中设置了var属性值,那么它将把实例化后的bean放入到stack's Context中。
Parameters
名称 |
必需 |
数据类型 |
描述 |
Id |
False |
String |
已弃用,var代替 |
Name |
true |
String |
bean的实例化类的名称(必须遵循JavaBean规范) |
Var |
False |
String |
用于引用到Value Stack中的值的名称 |
Examples
<-- in jsp form --> <s:bean name="org.apache.struts2.example.counter.SimpleCounter" var="counter"> <s:param name="foo" value="BAR" /> The value of foot is : <s:property value="foo"/>, when inside the bean tag </s:bean>
这个例子实例化了一个名叫SimpleCounter的bean,并设置foo属性(setFoo(‘BAR’))。然后将SimpleCounter对象压入值栈(Valuestack)中,这意味着我们可以调用property tag的访问方法(getFoo())来得到它的值。
在上面的例子中,id的属性值已经设为counter,这意味着SimpleCounter对象压入值栈(Valuestack)后可以通过如下标签来访问它:
<-- jsp form -->
<s:property value="#counter" />
1.WebRoot/pages/dataTags/beanTag.jsp,代码如下:
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Bean Tag 示例</title>
</head>
<body>
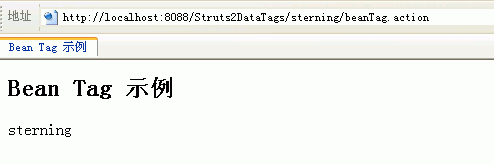
<h2>Bean Tag 示例</h2>
<s:bean name="com.sterning.companyName" id="uid">
<s:param name="name">sterning</s:param>
<s:property value="%{name}" /><br>
</s:bean>
</body>
</html>
其关联的JavaBean是com.sterning.companyName,同时参数name赋值为sterning。
2.首先创建Action进行跳转, src/com/sterning/beanTag.java,代码如下:
package com.sterning;
import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public class beanTag extends ActionSupport {
public String execute() throws Exception{
return SUCCESS;
}
}
然后创建JavaBean,src/com/sterning/companyName.java,代码如下:
package com.sterning;
public class companyName {
private String name;
public void setName(String name){
this.name =name ;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
}
3.Struts.xml的配置
这里配置很简单,与前面的例子差不多。
<action name="beanTag" class="com.sterning.beanTag">
<result name="success">/pages/dataTags/beanTag.jsp</result>
</action>
运行结果如下:
struts2 tags详解之<s:date>
Description
以不同的方式格式化日期对象。
<s:date>标记允许你以一个快速简便的方式格式化一个日期,你可以自定义日期的格式(eg. "dd/MM/yyyy hh:mm")。你也可以将日期转化成一个易读的记(like"in2hours,14minutes"),
或者你可以仅仅依靠在属性文件中预定义的”struts.date.format”的key来格式化日期。
Note: 如果请求的日期对象在堆栈找不到,那么将返回空白。
Parameters
名称 |
必需 |
默认值 |
类型 |
描述 |
format |
false |
String |
如指定该属性,将根据该属性指定的格式来格式化日期 |
|
name |
true |
String |
指定要格式化的日期 |
|
nice |
false |
false |
Boolean |
用于指定是否输出指定日期和当前时刻的时差。默认是false,即不输出 |
var |
false |
String |
如果指定了改属性,则该事件对象将被放到ValueStack中,改属性也可以用id来代替,推荐使用var |
通常,nice属性和format属性不同时指定,(不指定nice属性时,该属性值为false)。因为指定nice为true,代表输出指定日期和当前时刻的时差;指定format属性,则表明将指定日期按format指定的格式来个格式化输出。
如果即没有指定format,也没指定nice=“true”,则系统会到国际化资源文件中寻找key为struts.date.format的消息,将该消息当成格式化文本来格式化日期。如果无法找到key为struts.date.format的消息,则默认采用DateFormat.MEDIUM格式输出
Examples
<s:date name="person.birthday" format="dd/MM/yyyy" />
<s:date name="person.birthday" format="%{getText('some.i18n.key')}" />
<s:date name="person.birthday" nice="true" />
<s:date name="person.birthday" />
struts2 tags详解之<s:debug>
这个学过struts的地球人都知道:
输出值栈中的内容
Struts2 tags详解之<s:include>
Description
包含一个servlet的输入(servlet或JSP页面的结果)。
Note: 你不能通过<s:property...>来访问所包含页面的任何属性,因为没有值(valuestack)会被创建。然而,你可以通过HttpServletRequest对象在一个servlet中来访问它们,或者是通过scriptlet在jsp页面上访问它们。
How To access parameters
参数作为request参数被传递,因此可以使用$ {param.ParamName}标记来访问它们。不要使用<s:property...>标记来访问包含文件的参数。
Parameters
名称 |
必需 |
默认值 |
类型 |
描述 |
value |
true |
String |
The jsp/servlet output to include |
Example
<-- One: -->
<s:include value="myJsp.jsp" />
<-- Two: -->
<s:include value="myJsp.jsp">
<s:param name="param1" value="value2" />
<s:param name="param2" value="value2" />
</s:include>
<-- Three: -->
<s:include value="myJsp.jsp">
<s:param name="param1">value1</s:param>
<s:param name="param2">value2</s:param>
</s:include>
Example one - do an include myJsp.jsp page
Example two - do an include to myJsp.jsp page with parameters param1=value1 and param2=value2
Example three - do an include to myJsp.jsp page with parameters param1=value1 and param2=value2
struts2 tags详解之<s:property>
Description
用于获取一个属性的值。Property顾名思义,可以与<s:bean>标签结合使用,一个是给bean赋值,一个是从bean中读取值。
Examples
<s:push value="myBean">
<!-- Example 1: -->
<s:property value="myBeanProperty" />
<!-- Example 2: -->TextUtils
<s:property value="myBeanProperty" default="a default value" />
</s:push>
Example 1 prints the result of myBean's getMyBeanProperty() method.
Example 2 prints the result of myBean's getMyBeanProperty() method and if it is null, print 'a default value' instead.
Struts2 tags详解之<s:set>
以下内容来自:
http://www.blogjava.net/sterning/archive/2008/01/04/172644.html
Set标签比较简单。Set标签用户将某一值赋给某一变量,因此,任何对该项值的引用都可以通过该变量来得到该值。该变量的活动范围可自定义。如下例中,定义一健/值对,对值的引用,直接引用值就可以。。请看示例
1.WebRoot/pages/dataTags/ setTag.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html; charset=GBK" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Set Tag 示例</title>
</head>
<body>
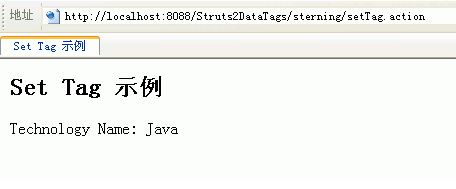
<h2>Set Tag 示例</h2>
<s:set name="technologyName" value="%{'Java'}"/>
Technology Name: <s:property value="#technologyName"/>
</body>
</html>
2.Struts.xml配置
<action name="setTag">
<result>/pages/dataTags/setTag.jsp</result>
</action>
3.运行效果