javaScript 计算网页内容的宽与高 (浏览器的标准模式与怪异模式)
标准模式与怪异模式:
由于历史的原因,各个浏览器在对页面的渲染上存在差异,甚至同一浏览器在不同版本中,对页面的渲染也不同。在W3C标准出台以前,浏览器在对页面的渲染上没有统一规范,产生了差异(Quirks mode或者称为Compatibility Mode);由于W3C标准的推出,浏览器渲染页面有了统一的标准(CSScompat或称为Strict mode也有叫做Standars mode),这就是二者最简单的区别。
W3C标准推出以后,浏览器都开始采纳新标准,但存在一个问题就是如何保证旧的网页还能继续浏览,在标准出来以前,很多页面都是根据旧的渲染方法编写的,如果用的标准来渲染,将导致页面显示异常。为保持浏览器渲染的兼容性,使以前的页面能够正常浏览,浏览器都保留了旧的渲染方法(如:微软的IE)。这样浏览器渲染上就产生了Quircks mode和Standars mode,两种渲染方法共存在一个浏览器上。
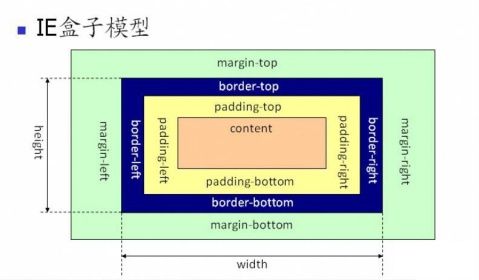
火狐一直工作在标准模式下,但IE(6,7,8)标准模式与怪异模式差别很大,主要体现在对盒子模型的解释上,这个很重要,下面就重点说这个。
那么浏览器究竟该采用哪种模式渲染呢?这就引出的DTD,既是网页的头部声明,浏览器会通过识别DTD而采用相对应的渲染模式:
1. 浏览器要使老旧的网页正常工作,但这部分网页是没有doctype声明的,所以浏览器对没有doctype声明的网页采用quirks mode解析。
2. 对于拥有doctype声明的网页,什么浏览器采用何种模式解析,这里有一张详细列表可参考:http://hsivonen.iki.fi/doctype/
3. 对于拥有doctype声明的网页,这里有几条简单的规则可用于判断:对于那些浏览器不能识别的doctype声明,浏览器采用strict mode解析
4. 在doctype声明中,没有使用DTD声明或者使用HTML4以下(不包括HTML4)的DTD声明时,基本所有的浏览器都是使用quirks mode呈现,其他的则使用strict mode解析。
5. 可以这么说,在现有有doctype声明的网页,绝大多数是采用strict mode进行解析的。
6. 在ie6中,如果在doctype声明前有一个xml声明(比如:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>),则采用quirks mode解析。这条规则在ie7中已经移除了。
如何设置为怪异模式:
方法一:在页面项部加 <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN">
我们用Eclipse的HTML模板新建的html页面,自动就有上面东东
方法二:什么也不加。
这里有一张详细列表可参考:http://hsivonen.iki.fi/doctype/
如何设置为标准模式:
加入以下任意一种:
HTML4提供了三种DOCTYPE可选择:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd">
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Frameset//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/frameset.dtd">
XHTML1.0提供了三种DOCTYPE可选择:
(1)过渡型(Transitional )
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
(2)严格型(Strict )
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-strict.dtd">
(3)框架型(Frameset )
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Frameset//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-frameset.dtd">
这里有一张详细列表可参考:http://hsivonen.iki.fi/doctype/
如何判定现在是标准模式还是怪异模式:
方法一:执行以下代码
alert(window.top.document.compatMode) ;
//BackCompat 表示怪异模式
//CSS1Compat 表示标准模式
方法二:jquery为我们提供的方法,如下:
alert($.boxModel)
alert($.support.boxModel)
IE6,7,8浏览器的标准模式还是怪异模式 盒子模型的 差异
(由于火狐的始终表现的很一致,不种我们操心。所以这里我们重点说IE浏览器)
-------------------------------------------------模态窗口----------------------------------------------------
我们想做一个DIV蒙层,中间放一个iframe,做一个像模态窗口的dialog工具
思路如下:
取出页面 网页可见区域 的宽与高, 进行蒙层,
通过CSS的固定定位属性{position:fixed}来实现,可以让HTML元素脱离文档流固定在浏览器的某个位置,
这样拖动滚动条时, 蒙层不会移动,一直在中心位置。
中心位置放一个iframe,用来显示其它网页,并可以提交表单。
可以用以下代码计算 蒙层的宽与高:
- //计算窗口的高宽和滚动条的位置
- alert(window.top.document.compatMode) ;//区分怪异模式或标准模式
- var cw = window.top.document.compatMode == "BackCompat" ?window.top.document.body.clientWidth:window.top.document.documentElement.clientWidth;//窗体高度
- var ch = window.top.document.compatMode == "BackCompat" ?window.top.document.body.clientHeight:window.top.document.documentElement.clientHeight;//窗体宽度//必须考虑文本框处于页面边缘处,控件显示不全的问题
- var sw = Math.max(window.top.document.documentElement.scrollLeft, window.top.document.body.scrollLeft);//横向滚动条位置
- var sh = Math.max(window.top.document.documentElement.scrollTop, window.top.document.body.scrollTop);//纵向滚动条位置//考虑滚动的情况
- alert("cw:"+cw+" ch:"+ch+" sw:"+sw+" sh"+sh);
----------------------------------------------参考 1-----------------------------------------------------
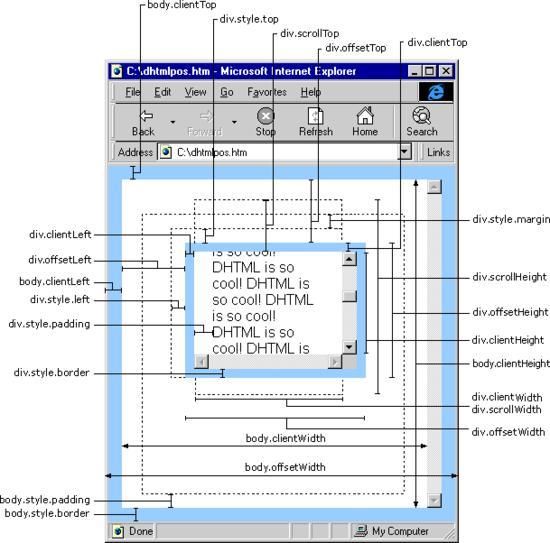
我们先来认识一下有哪些属性可以使用:
scrollLeft:设置或获取位于对象左边界和窗口中目前可见内容的最左端之间的距离
scrollTop:设置或获取位于对象最顶端和窗口中可见内容的最顶端之间的距离
scrollWidth:获取对象的滚动宽度
scrollHeight: 获取对象的滚动高度。
obj.offsetTop 指 obj 相对于版面或由 offsetParent 属性指定的父坐标的计算上侧位置,整型,单位像素。
obj.offsetLeft 指 obj 相对于版面或由 offsetParent 属性指定的父坐标的计算左侧位置,整型,单位像素。
obj.offsetWidth 指 obj 控件自身的绝对宽度,不包括因 overflow 而未显示的部分,也就是其实际占据的宽度,整型,单位像素。
obj.offsetHeight 指 obj 控件自身的绝对高度,不包括因 overflow 而未显示的部分,也就是其实际占据的高度,整型,单位像素
event.clientX 相对文档的水平座标
event.clientY 相对文档的垂直座标
event.offsetX 相对容器的水平坐标
event.offsetY 相对容器的垂直坐标
clientWidth 内容可视区域的宽度
clientHeight 内容可视区域的高度
clientTop 内容可视区域相对容器的垂直坐标
clientLeft 内容可视区域相对容器的水平坐标
参考图片:
----------------------------------------------参考 2-----------------------------------------------------
- var Width_1=document.body.scrollWidth; //body滚动条总宽
- var Height_1=document.body.scrollHeight; //body滚动条总高
- var Width_2=document.documentElement.scrollWidth; //documentElement滚动条总宽
- var Height_2=document.documentElement.scrollHeight; //documentElement滚动条总宽
- //------------------------------
- var Width_3=document.body.clientWidth; //body网页可见区域宽,滚动条隐藏部分不算
- var Height_3=document.body.clientHeight; //body网页可见区域高,滚动条隐藏部分不算
- var Width_4=document.documentElement.clientWidth; //documentElement网页可见区域宽,滚动条隐藏部分不算
- var Height_4=document.documentElement.clientHeight; //documentElement网页可见区域高,滚动条隐藏部分不算
- //------------------------------
- var Width_5=window.screen.availWidth; //屏幕可用工作区宽度(用处不大)
- var Height_5=window.screen.availHeight;//屏幕可用工作区高度
- //------------------------------
- var scrollLeft_7=window.top.document.body.scrollLeft;//body水平滚动条位置
- var scrollTop_7=window.top.document.body.scrollTop;//body垂直滚动条位置
- var scrollLeft_8=window.top.document.documentElement.scrollLeft;//documentElement水平滚动条位置
- var scrollTop_8=window.top.document.documentElement.scrollTop;//documentElement垂直滚动条位置
- alert(" body滚动条总宽:"+Width_1+",body滚动条总高:"+Height_1+
- ",/n documentElement滚动条总宽:"+Width_2+",documentElement滚动条总高:"+Height_2+
- ",/n"+
- "/n body网页可见区域宽:"+Width_3+",body网页可见区域高:"+Height_3+
- ",/n documentElement网页可见区域宽:"+ Width_4+",documentElement网页可见区域高:"+Height_4+
- ",/n"+
- "/n 屏幕可用工作区宽度:"+Width_5+", 屏幕可用工作区高度:"+Height_5+
- ",/n"+
- "/n body水平滚动条位置:"+scrollLeft_7+",body垂直滚动条位置:"+scrollTop_7+
- ",/n documentElement水平滚动条位置:"+scrollLeft_8+",documentElement垂直滚动条位置:"+scrollTop_8
- );
(需要提一下:CSS中的margin属性,与clientWidth、offsetWidth、clientHeight、offsetHeight均无关)
下面是从w3school查到的,说的不是很详细
根节点
有两种特殊的文档属性可用来访问根节点:
document.documentElement
document.body
第一个属性可返回存在于 XML 以及 HTML 文档中的文档根节点。
第二个属性是对 HTML 页面的特殊扩展,提供了对 <body> 标签的直接访问。
http://www.w3school.com.cn/htmldom/dom_nodes_access.asp
收集整理于互联网
参考:
http://cavonchen.javaeye.com/blog/738423
http://hsivonen.iki.fi/doctype/