Java:对象的强、软、弱和虚引用
1.对象的强、软、弱和虚引用
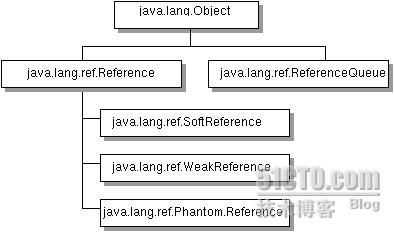
在JDK 1.2以前的版本中,若一个对象不被任何变量引用,那么程序就无法再使用这个对象。也就是说,只有对象处于可触及(reachable)状态,程序才能使用它。从JDK 1.2版本开始,把对象的引用分为4种级别,从而使程序能更加灵活地控制对象的生命周期。这4种级别由高到低依次为:强引用、软引用、弱引用和虚引用。图1为对象应用类层次。
图1
⑴强引用(StrongReference)
强引用是使用最普遍的引用。如果一个对象具有强引用,那垃圾回收器绝不会回收它。当内存空间不足,Java虚拟机宁愿抛出OutOfMemoryError错误,使程序异常终止,也不会靠随意回收具有强引用的对象来解决内存不足的问题。
⑵软引用(SoftReference)
如果一个对象只具有软引用,则内存空间足够,垃圾回收器就不会回收它;如果内存空间不足了,就会回收这些对象的内存。只要垃圾回收器没有回收它,该对象就可以被程序使用。软引用可用来实现内存敏感的高速缓存(下文给出示例)。
软引用可以和一个引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用,如果软引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收器回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个软引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
⑶弱引用(WeakReference)
弱引用与软引用的区别在于:只具有弱引用的对象拥有更短暂的生命周期。在垃圾回收器线程扫描它所管辖的内存区域的过程中,一旦发现了只具有弱引用的对象,不管当前内存空间足够与否,都会回收它的内存。不过,由于垃圾回收器是一个优先级很低的线程,因此不一定会很快发现那些只具有弱引用的对象。
弱引用可以和一个引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用,如果弱引用所引用的对象被垃圾回收,Java虚拟机就会把这个弱引用加入到与之关联的引用队列中。
⑷虚引用(PhantomReference)
“虚引用”顾名思义,就是形同虚设,与其他几种引用都不同,虚引用并不会决定对象的生命周期。如果一个对象仅持有虚引用,那么它就和没有任何引用一样,在任何时候都可能被垃圾回收器回收。
虚引用主要用来跟踪对象被垃圾回收器回收的活动。虚引用与软引用和弱引用的一个区别在于:虚引用必须和引用队列(ReferenceQueue)联合使用。当垃圾回收器准备回收一个对象时,如果发现它还有虚引用,就会在回收对象的内存之前,把这个虚引用加入到与之 关联的引用队列中。
|
MyObject
aRef
=
new
MyObject();
SoftReference
aSoftRef
=
new
SoftReference(
aRef
);
|
此时,对于这个MyObject对象,有两个引用路径,一个是来自SoftReference对象的软引用,一个来自变量aReference的强引用,所以这个MyObject对象是强可及对象。
随即,我们可以结束aReference对这个MyObject实例的强引用:
|
MyObject
anotherRef
=(MyObject)
aSoftRef
.get();
|
重新获得对该实例的强引用。而回收之后,调用get()方法就只能得到null了。
3.3 使用ReferenceQueue清除失去了软引用对象的SoftReference
作为一个Java对象,SoftReference对象除了具有保存软引用的特殊性之外,也具有Java对象的一般性。所以,当软可及对象被回收之后,虽然这个SoftReference对象的get()方法返回null,但这个SoftReference对象已经不再具有存在的价值,需要一个适当的清除机制,避免大量SoftReference对象带来的内存泄漏。在java.lang.ref包里还提供了ReferenceQueue。如果在创建SoftReference对象的时候,使用了一个ReferenceQueue对象作为参数提供给SoftReference的构造方法,如:
|
SoftReference ref =
null
;
while
((ref = (EmployeeRef)
q
.poll()) !=
null
) {
//
清除
ref
}
|
理解了ReferenceQueue的工作机制之后,我们就可以开始构造一个Java对象的高速缓存器了。
3.4通过软可及对象重获方法实现Java对象的高速缓存
利用Java2平台垃圾收集机制的特性以及前述的垃圾对象重获方法,我们通过一个雇员信息查询系统的小例子来说明如何构建一种高速缓存器来避免重复构建同一个对象带来的性能损失。我们将一个雇员的档案信息定义为一个Employee类:
|
import
java.lang.ref.ReferenceQueue;
import
java.lang.ref.SoftReference;
import
java.util.Hashtable;
public
class
EmployeeCache {
static
private
EmployeeCache
cache
;
//
一个
Cache
实例
private
Hashtable<String,EmployeeRef>
employeeRefs
;
//
用于
Chche
内容的存储
private
ReferenceQueue<Employee>
q
;
//
垃圾
Reference
的队列
//
继承
SoftReference
,使得每一个实例都具有可识别的标识。
//
并且该标识与其在
HashMap
内的
key
相同。
private
class
EmployeeRef
extends
SoftReference<Employee> {
private
String
_key
=
""
;
public
EmployeeRef(Employee em, ReferenceQueue<Employee> q) {
super
(em, q);
_key
= em.getID();
}
}
//
构建一个缓存器实例
private
EmployeeCache() {
employeeRefs
=
new
Hashtable<String,EmployeeRef>();
q
=
new
ReferenceQueue<Employee>();
}
//
取得缓存器实例
public
static
EmployeeCache getInstance() {
if
(
cache
==
null
) {
cache
=
new
EmployeeCache();
}
return
cache
;
}
//
以软引用的方式对一个
Employee
对象的实例进行引用并保存该引用
private
void
cacheEmployee(Employee em) {
cleanCache();
//
清除垃圾引用
EmployeeRef ref =
new
EmployeeRef(em,
q
);
employeeRefs
.put(em.getID(), ref);
}
//
依据所指定的
ID
号,重新获取相应
Employee
对象的实例
public
Employee getEmployee(String ID) {
Employee em =
null
;
//
缓存中是否有该
Employee
实例的软引用,如果有,从软引用中取得。
if
(
employeeRefs
.containsKey(ID)) {
EmployeeRef ref = (EmployeeRef)
employeeRefs
.get(ID);
em = (Employee) ref.get();
}
//
如果没有软引用,或者从软引用中得到的实例是
null
,重新构建一个实例,
//
并保存对这个新建实例的软引用
if
(em ==
null
) {
em =
new
Employee(ID);
System.
out
.println(
"Retrieve From EmployeeInfoCenter. ID="
+ ID);
this
.cacheEmployee(em);
}
return
em;
}
//
清除那些所软引用的
Employee
对象已经被回收的
EmployeeRef
对象
private
void
cleanCache() {
EmployeeRef ref =
null
;
while
((ref = (EmployeeRef)
q
.poll()) !=
null
) {
employeeRefs
.remove(ref.
_key
);
}
}
//
清除
Cache
内的全部内容
public
void
clearCache() {
cleanCache();
employeeRefs
.clear();
System.
gc();
System.
runFinalization();
}
}
|
4.使用弱引用构建非敏感数据的缓存
4.1全局 Map 造成的内存泄漏
无意识对象保留最常见的原因是使用Map将元数据与临时对象(transient object)相关联。假定一个对象具有中等生命周期,比分配它的那个方法调用的生命周期长,但是比应用程序的生命周期短,如客户机的套接字连接。需要将一些元数据与这个套接字关联,如生成连接的用户的标识。在创建Socket时是不知道这些信息的,并且不能将数据添加到Socket对象上,因为不能控制 Socket 类或者它的子类。这时,典型的方法就是在一个全局 Map 中存储这些信息,如下面的SocketManager 类所示:使用一个全局 Map 将元数据关联到一个对象。
|
import
java.util.WeakHashMap;
class
Element {
private
String
ident
;
public
Element(String id) {
ident
= id;
}
public
String toString() {
return
ident
;
}
public
int
hashCode() {
return
ident
.hashCode();
}
public
boolean
equals(Object obj) {
return
obj
instanceof
Element &&
ident
.equals(((Element) obj).
ident
);
}
protected
void
finalize(){
System.
out
.println(
"Finalizing "
+getClass().getSimpleName()+
" "
+
ident
);
}
}
class
Key
extends
Element{
public
Key(String id){
super
(id);
}
}
class
Value
extends
Element{
public
Value (String id){
super
(id);
}
}
public
class
CanonicalMapping {
public
static
void
main(String[] args){
int
size=1000;
Key[] keys=
new
Key[size];
WeakHashMap<Key,Value> map=
new
WeakHashMap<Key,Value>();
for
(
int
i=0;i<size;i++){
Key k=
new
Key(Integer.toString(i));
Value v=
new
Value(Integer.toString(i));
if
(i%3==0)
keys[i]=k;
map.put(k, v);
}
System.
gc();
}
}
|
从打印结果可以看出,当执行System.gc()方法后,垃圾回收器只会回收那些仅仅持有弱引用的Key对象。id可以被3整除的Key对象持有强引用,因此不会被回收。
4.3用 WeakHashMap 堵住泄漏
在 SocketManager 中防止泄漏很容易,只要用 WeakHashMap 代替 HashMap 就行了。(这里假定SocketManager不需要线程安全)。当映射的生命周期必须与键的生命周期联系在一起时,可以使用这种方法。用WeakHashMap修复SocketManager。
<td )="" 0%="" 50%;="" padding-bottom:="" 0cm;="" border-left:="" windowtext="" 1pt="" solid;="" width:="" 426.1pt;="" padding-top:="" border-bottom:="" -moz-background-clip:="" -moz-initial;="" -moz-background-origin:="" -moz-background-inline-policy:="" -moz-initial"="" valign="top" width="568" style="padding: 0px 5.4pt; margin: 0px; border-right-color: windowtext; border-right-width: 1pt; border-right-style: solid; border-top-color: windowtext; border-top-width: 1pt; border-top-style: solid; ">
public
class
SocketManager {
private
Map<Socket,User>
m
=
new
WeakHashMap<Socket,User>();
public
void
setUser(Socket s, User u) {
m
.put(s, u);
}
public
User getUser(Socket s) {
return
m
.get(s);
}
}
4.4配合使用引用队列
WeakHashMap 用弱引用承载映射键,这使得应用程序不再使用键对象时它们可以被垃圾收集,get() 实现可以根据WeakReference.get() 是否返回 null 来区分死的映射和活的映射。但是这只是防止 Map 的内存消耗在应用程序的生命周期中不断增加所需要做的工作的一半,还需要做一些工作以便在键对象被收集后从 Map 中删除死项。否则,Map 会充满对应于死键的项。虽然这对于应用程序是不可见的,但是它仍然会造成应用程序耗尽内存。
引用队列是垃圾收集器向应用程序返回关于对象生命周期的信息的主要方法。弱引用有个构造函数取引用队列作为参数。如果用关联的引用队列创建弱引用,在弱引用对象成为 GC 候选对象时,这个引用对象就在引用清除后加入到引用队列中(具体参考上文软引用示例)。
WeakHashMap 有一个名为 expungeStaleEntries() 的私有方法,大多数 Map 操作中会调用它,它去掉引用队列中所有失效的引用,并删除关联的映射。
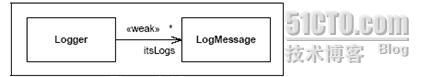
5.UML:使用关联类指明特定形式的引用
关联类能够用来指明特定形式的引用,如弱(weak)、软(soft)或虚 (phantom)引用。
也可以如下的构造型方式。
6.参考资料
[1]Thinking in Java4th
[2]孙卫琴,Java面向对象编程,电子工业出版社,2006
[3]Robert Martin,UML for java programmers,2004
[4] 通过Java软可及对象的重获提高程序性能,张立明,陈朔鹰,程序员,2003,08
[5] Monica Pawlan,Reference Objects and Garbage Collection,
[url]http://java.sun.com/developer/technicalArticles/ALT/RefObj/[/url]
[6]Brian Goetz,Java 理论与实践: 用弱引用堵住内存泄漏,
[url]http://www-128.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/java/j-jtp11225/[/url]
本文出自 “子 孑” 博客,请务必保留此出处http://zhangjunhd.blog.51cto.com/113473/53092