FZU 1977 Pandora adventure(插头DP)
Accept: 320 Submit: 1034
Time Limit: 1000 mSec Memory Limit : 32768 KB
 Problem Description
Problem Description
The pollution of the earth is so serious that people can not survive any more. Fortunately, people have found a new planet that maybe has life, and we call it "Pandora Planet".
Leonardo Da Vinci is the only astronaut on the earth. He will be sent to the Pandora Planet to gather some plant specimens and go back. The plant specimen is important to the people to decide whether the planet is fit to live or not.
Assuming that Da Vinci can only move in an N×M grid. The positions of the plant specimens he wants to collect are all marked by the satellite. His task is to find a path to collect all the plant specimens and return to the spaceship. There are some savage beasts in the planet. Da Vinci can not investigate the grid with the savage beast. These grids are also marked by the satellite. In order to save time Da Vinci could only visit each grid exactly once and also return to the start grid, that is, you can not visit a grid twice except the start grid. You should note that you can choose any grid as the start grid.
Now he wants to know the number of different paths he can collect all the plant specimens. We only care about the path and ignore where the start grid is, so the two paths in Figure 1 are considered as the same.
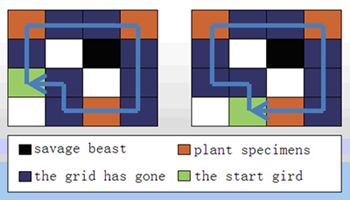 Figure 1
Figure 1
 Input
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T (T≤100), indicating the number of cases. Each case begins with a line containing two integers N and M (1≤N, M≤12), the size of the planet is N×M. Each of the following N lines contains M characters Gij(1≤i≤N, 1≤j≤M), Gij denotes the status of the grid in row i and column j, where 'X' denotes the grid with savage beast, '*' denotes the safe grid that you can decide to go or not, 'O' denotes the plant specimen you should collect. We guarantee that there are at least three plant specimens in the map.
 Output
Output
For each test case, print a line containing the test case number (beginning with 1) and the number of different paths he can collect all the plant specimens. You can make sure that the answer will fit in a 64-bit signed integer.
 Sample Input
Sample Input
 Sample Output
Sample Output
 Source
Source
The 35th ACM/ICPC Asia Regional Fuzhou Site —— Online Contest
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int HASH=10007;//哈希表的大小
const int STATE=100010;//状态数
const int MAXD=15;
int N,M,ex,ey;//ex,ey最后一个可到点
int code[MAXD],maze[MAXD][MAXD],mcod[MAXD];//编码。和存地图。最小表示法
char graph[20];
long long ans;
struct HASHMAP//哈希表结构
{
int head[HASH],next[STATE],sz;//哈希表头指针模数相同的状态用链表连接。方便状态查找和判重
long long f[STATE],state[STATE];//f记录对应状态的方法数。next指向模数相同的下一个状态。state记录状态。sz记录状态总数
void init()//哈希表初始化函数
{
sz=0;
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
}
void push(long long st,long long ans)//压入状态和方法数
{
int i,h=st%HASH;
for(i=head[h]; i!=-1; i=next[i])
if(st==state[i])//若状态已经存在。方法数增加就行
{
f[i]+=ans;
return;
}
f[sz]=ans;//存入新的可行状态
state[sz]=st;
next[sz]=head[h];
head[h]=sz++;
}
} hm[2];
void decode(int *code,int m,long long st)//编码从高位到低位m到0编码。对应从左到右的插头
{
int i;
for(i=m; i>=0; i--)
{
code[i]=st&7;
st>>=3;
}
}
long long encode(int *code,int m)//最小表示法解码到st中
{
int i,cnt=1;
long long st=0;
memset(mcod,-1,sizeof mcod);
mcod[0]=0;
for( i=0; i<=m; i++)
{
if(mcod[code[i]]==-1)
mcod[code[i]]=cnt++;
code[i]=mcod[code[i]];
st<<=3;
st|=code[i];
}
return st;
}
void init()//读数据。初始化
{
int i,j;
memset(maze,0,sizeof maze);
ex=0;
for(i=1; i<=N; i++)
{
scanf("%s",graph+1);
for( j=1; j<=M; j++)
{
if(graph[j]=='O')
{
maze[i][j]=1;
ex=i,ey=j;
}
else if(graph[j]=='*')
maze[i][j]=2;
}
}
}
void shift(int *code,int m)//换行的时候移位
{
int i;
for(i=m; i>0; i--)
code[i]=code[i-1];
code[0]=0;
}
void dpblank(int i,int j,int cur)//处理可到格的情况
{
int k,t,left,up,temp;
for(k=0; k<hm[cur].sz; k++) //遍历j格出轮廓线的状态进行状态转移
{
decode(code,M,hm[cur].state[k]);//对状态进行编码
left=code[j-1];//获取左插头状态
up=code[j];//获取上插头状态
if(left&&up)//11 -> 00
{
if(left==up)
{
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;
if(i*M+j>=ex*M+ey&&!encode(code,M))//成环且只能为一个联通分量。不加!encode(code,M)就会出现图示情况是不合法的
ans+=hm[cur].f[k];
}
else
{
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;
for(t=0; t<=M; t++)
if(code[t]==up)
{
code[t]=left;
break;
}
if(j==M)shift(code,M);//到了边界后换行
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);//压入新状态
}
}
else if((!left&&up)||(left&&!up))//01 或 10
{
if(up)
temp=up;
else
temp=left;
if(maze[i][j+1])
{
code[j-1]=0;
code[j]=temp;
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
if(maze[i+1][j])
{
code[j-1]=temp;
code[j]=0;
if(j==M)shift(code,M);
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
else
{
if(maze[i][j+1]&&maze[i+1][j])
{
code[j]=code[j-1]=13;
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
if(maze[i][j]==2)//2代表可选择点
{
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;
if(j==M)shift(code,M);
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
}
}
void dpblock(int i,int j,int cur)//处理不能到格的情况
{
int k;
for(k=0; k<hm[cur].sz; k++) //存入状态均合法不用判断
{
decode(code,M,hm[cur].state[k]);//先编码
code[j-1]=code[j]=0;//肯定不能用插头
if(j==M)shift(code,M);//转移到下一行
hm[cur^1].push(encode(code,M),hm[cur].f[k]);
}
}
void solve()
{
int i,j,cur=0;
ans=0;
hm[cur].init();//cur用于滚动数组。节约空间。cur存当前格上插头和左插头情况。cur^1用于记录转移出的新状态即下一格
hm[cur].push(0,1);
for(i=1; i<=N; i++)
for(j=1; j<=M; j++)
{
hm[cur^1].init();//初始化
if(maze[i][j])dpblank(i,j,cur);
else dpblock(i,j,cur);
cur^=1;
}
printf("%I64d\n",ans);
}
int main()
{
int t,cas=1;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&N,&M);
init();
printf("Case %d: ",cas++);
if(!ex)
printf("0\n");
else
solve();
}
return 0;
}
