ACPI Overview
最近有些时间,重温了一下ACPI SPEC Rev4.0,发现之前无法理解的东西,现在也不是那么难懂了。现整理一下笔记。
先来明确两个概念:ACPI,OSPM
ACPI:Advanced Configuration and Power Interface 高级配置和电源接口
OSPM:Operation System directed configuration and Power Management 操作系统直接电源管理
在ACPI SPEC中,随处可见OSPM,那么OSPM到底是什么呢?
原来,在早期的电脑中,电源管理完全是由通过APM(Advanced Power Management)来实现的,OS对此一无所知也无从干预。这种管理方式存在很多的缺陷,且BIOS维护APM代码和功能需要非常大的精力。ACPI规范就是为了解决APM的缺陷而问世的,它允许操作系统来控制电源管理,从而解放了BIOS。但是ACPI只是一个接口规范,除了硬件Support、BIOS support之外,OS 也需要support。支持ACPI的OS就可以叫做OSPM。 OSPM的最低要求如下:
1). 在Intel架构的系统上使用system address map reporting interface来得到system address map
a. INT15H,E820H
b. EFI GetMemoryMap() Boot Service Function
2).Find and consume the ACPI System Description Tables.
3). 安装启用一个支持所有已定义的AML语法元素的AML interpreter(翻译器)。
4). 支持ACPI Event programming model,包含handing SCI interrupt,managing fixed events/general-propose events/embedded controller interrupt /dynamic device support.
5). 枚举和配置ACPI Namespace中描述的主板设备。
6). 实现以下ACPI devices的支持:Embedded Controller Device/GPE Block Device/Module Device。
7). 安装ACPI Thermal Model。
8). 支持acquisition(获得) and release(释放) Global Lock。
9). 支持OS-directed power management.(设备驱动负责维护device context)。
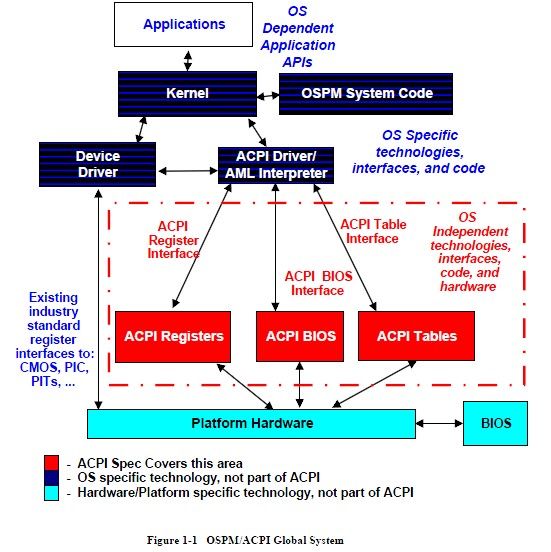
ACPI的结构
ACPI包含三个run-time Components:
1. ACPI Tables
主要描述一个Platform上的硬件界面资讯,这些描述包含了一些固定的寄存器的位置,或是说明一些Register Blocks,另外ACPI Tables还包含了一些OS可以执行的AML Code,OS会透过自己的AML Interpreter来执行这些AML Code。
2. ACPI Registers
在ACPI Register中是实体的硬件界面,这些寄存器就是被描述在ACPI Tables中的那些。
3. ACPI BIOS
符合ACPI规范的BIOS,典型情况下,他会做系统开关机的动作以及实做Sleep界面的支援(BIOS支援S3/S4/…)。
ACPI可以实现的功能
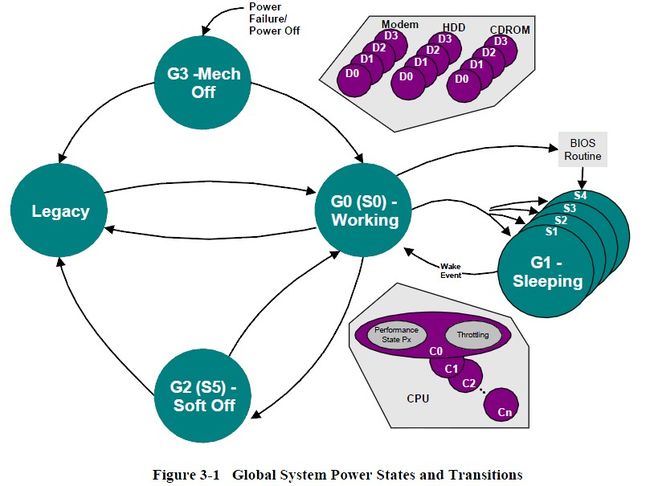
1. 系统电源管理 System Power Management
Global Power State:
G0: Working –S0
G1: Sleeping --S1/S3/S4
G2: Soft off –S5
G3: Mechanical off
2. 设备电源管理 Device Power Management
PCI, PCI Express, CardBus, USB, IEEE 1394
Device Power State:
D0: fully on 设备可以完全回应,正常工作
D1: 不同Device Class有不同规范,一般会节省一些电源
D2: 不同Device Class有不同规范,但并非大多数设备都有支援,比D1更省电,通常会关闭一些设备上的功能来达到省电的目的。
D3hot: 不同Device Class有不同规范,当要转到D0 状态是,OS SW要重新初始化该设备
D3: off 电源完全从设备移除
3. 处理器电源管理 Processor Power Management
在G0状态下,Processor Power State:C0, C1, C2, C3…
4. 设备和处理器性能管理 Device and Processor Performance Management
在C0/D0状态下,Device/Processor Performance State: P0, P1, P2, P3…
5. 配置/即插即用 Configuration/Plug and Play
6. 系统事件 System Events
7. 电池管理 Battery Management
8. 温度管理 Thermal Management
9. 嵌入式控制器 Embedded Controller
10. SMBus控制器 SMBus Controller