linux core文件设置
在Linux中,一般当进程非正常退出时,会生成一个core文件,这个文件是进程猝死时内存的转储文件,也称为core dump。
查看Linux脚本解析方式:
echo $0
1.检验core是否打开
以see/see登录
csh: limit; coredumpsize = 0 , 说明没有打开core, 否则打开了。
bash: ulimit –a ; 关注红色部分。 如果是0,表示core没有打开,否则打开了。
2.开启core,设置大小
如果没有开启,永久开启
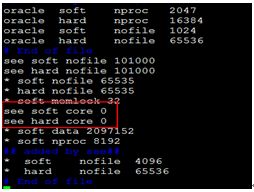
······以root/huawei用户登录,vi /etc/security/limits.conf ,注意红色部分
soft < hard大小
临时指定大小,以see/see用户登录,
csh: limit coredumpsize 4096000
bash: ulimit -c 4096000 大小低于/etc/security/limits.conf中设置的大小
注意:这些都是临时的,一旦该活跃窗口关闭后再次打开,设置的core大小就失效了。
3. core路径配置
注意:指定的core路径有写入权限
以see/see用户登录,/sbin/sysctl -a |grep core, 查看目前core文件生成的路径
然后肉眼查一下 kernel.core_pattern 和 kernel.core_uses_pid 两个配置值是多少。
kernel.core_pattern: core文件路径
kernel.core_uses_pid: 生成core文件,后缀是否带pid 1:带; 0 :不带
临时修改路径(需要root权限)
/sbin/sysctl -w kernel.core_pattern=/core/core.%e.%p
/sbin/sysctl -w kernel.core_uses_pid=0
%p – insert pid into filename --- 显示进程号
%u – insert current uid into filename --- 用户ID
%g – insert current gid into filename --- 组ID
%s – insert signal that caused the coredump into the filename ---添加导致产生core的信号
%t – insert UNIX time that the coredump occurred into filename --- 时间
%h – insert hostname where the coredump happened into filename --- 主机名
%e – insert coredumping executable name into filename --- 名字
永久修改路径(需要root权限,机器重新启动也会生效):
修改/etc/sysctl.conf,添加2行即可:
kernel.core_pattern = /core/core.%e.%p
kernel.core_uses_pid = 0
设置生效
sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
4. 产生core(用于自测试)
以see/see用户,ksh;kill -11 $$
5. 定位分析core
gdb container core文件
然后:bt
6 .关闭core
临时关闭:
csh: limit coredumpsize 0
bash: ulimit -c 0
注意:这些都是临时的,一旦该活跃窗口关闭后再次打开,设置的core大小就失效了。
永久关闭:
以root/huawei用户登录,vi /etc/security/limits.conf ,注意红色部分为0