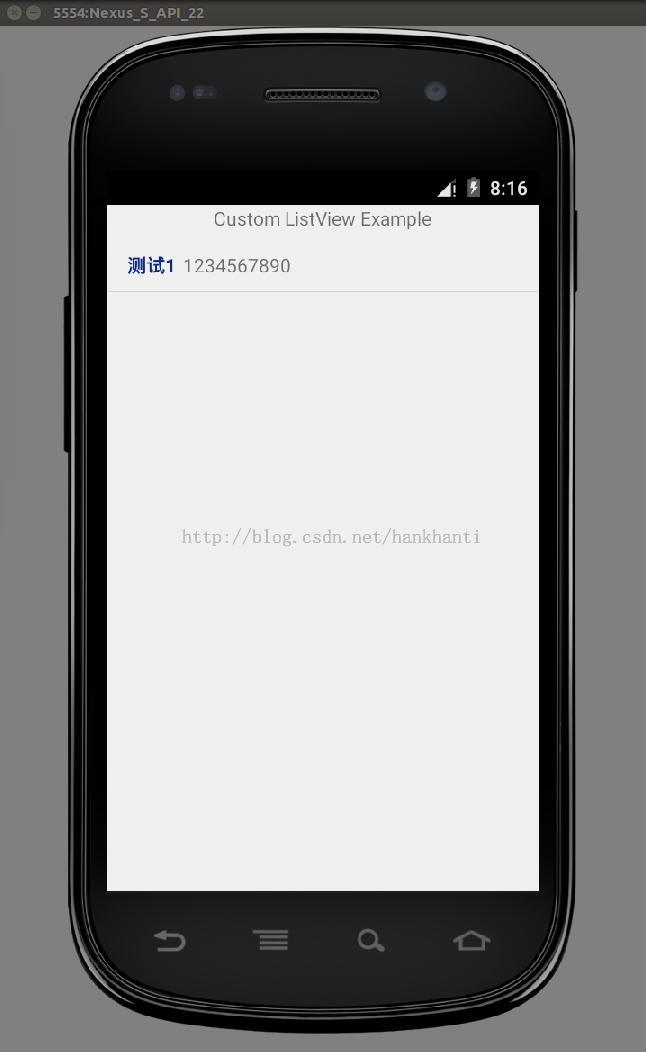
contact list app in android
前言: 好久没写文章记录写研究心得, 避免久了就忘了, 也为记忆留下点滴,开始了久违后的第一个心得.
最近在研究 Android 开发, 就先以一个小的目标写下所得.
1. To get the contact db from device:
command: adb pull /data/data/com.android.providers.contacts/databases/contact2.db
error message: permission denied.
解决办法: 进入 adb shell, 将要抓取的档案改变权限 (chmod 777)
再执行如上命令 - worked.
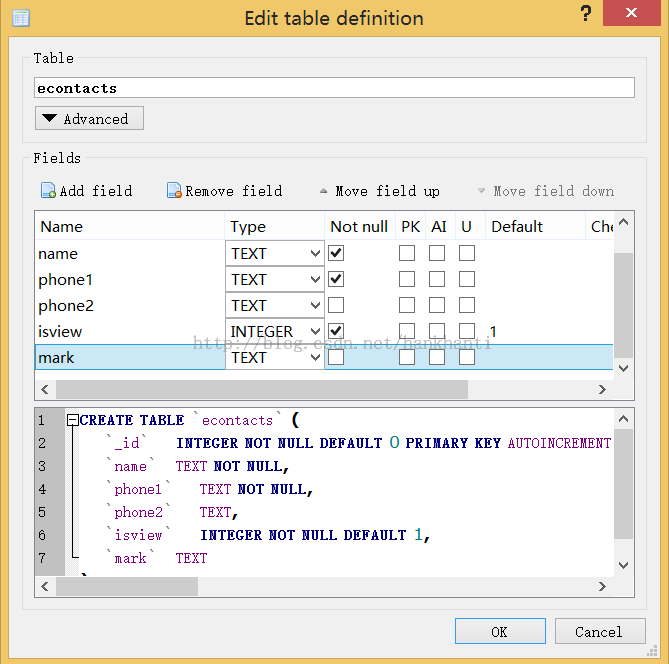
2.了解 android db file 的结构, to download sqlitebrowser. 用这个tool大概了解了一下资料结构.
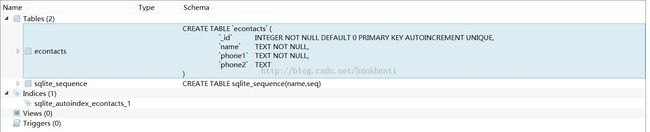
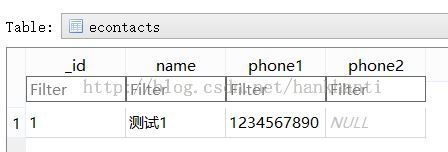
会用到的资料格式大概为 integer,TEXT. 为此建了一个 table 如下所示:
独立开了一个 db, 命名为 econtacts.db.
3. 开始进入正式 App 开发, 分为以下几个小功能进行研究:
1> Android to access SQLite.
Add below content into AndroidManifest.xml
android:name=".ApplicationContextProvider"
So AndroidManifest.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.xxx.test04" >
<application
android:name=".ApplicationContextProvider"
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
To create the class "ApplicationContextProvider":
package com.example.xxx.test04;
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Context;
public class ApplicationContextProvider extends Application {
/**
* Keeps a reference of the application context
*/
private static Context sContext;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
sContext = getApplicationContext();
}
/**
* Returns the application context
*
* @return application context
*/
public static Context getContext() {
return sContext;
}
}
接下来就是重头戏 - to create the database connection/access class "DBHelper"
其中利用 select(String query) 中的 Cursor 把资料读出来,这边要特别注意到一个细节,一定要做到
Cursor.close(), 否则 Android 会有内存泄漏的报错.
public ArrayList<Contacts> select(String query) throws SQLException {
//Cursor c=null;
ArrayList<Contacts> objects = new ArrayList<Contacts>();
Log.d("select()", query);
Cursor c=null;
try {
c = mDataBase.rawQuery(query, null);
int id[]=new int[c.getCount()];
int i=0;
if (c.getCount() > 0)
{
c.moveToFirst();
do {
id[i]=c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex("name"));
Log.d("name", c.getString(1));
i++;
Contacts cons = new Contacts(c.getString(1), c.getString(2), c.getString(3));
objects.add(cons);
//cursor = c;
} while (c.moveToNext());
c.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
c.close();
} finally {
if(c!=null) {
c.close();
}
}
Log.d("Test Name in DBHelper", objects.get(0).getName());
c.close();
return objects;
}
细心的读者会注意到上面这个函数中的 Contacts 还没有定义, 没有错我们还需要定义它,而他就是用来作
画面显示所需要模板(Android称为Adapter)会用到的物件,注意到返回的是
ArrayList<Contacts>
这个就是我们从SQLite DB 获取到的内容就会存放在这个物件阵列中. 在看 Contacts 定义之前, 先把 DBHelper.java 描述出来.
package com.example.xxx.test04;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
import android.database.Cursor;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import android.database.SQLException;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper {
private final static String DATABASE_NAME = "econtacts.db";
private final static String DATABASE_FILE = "econtacts.db";
private final static int DATABASE_VERSION = 1;
private static final String DATABASE_PATH = "/data/data/com.example.xxx.test04/databases/";
private static final String TABLE_CONTACT = "econtacts";
private static SQLiteDatabase mDataBase;
//private Cursor cursor=null;
private static final String KEY_ID = "_id";
private static final String KEY_NAME = "name";
private static final String KEY_PH1 = "phone1";
private static final String KEY_PH2 = "phone2";
private static DBHelper sInstance = null;
private static String TAG = "DataBaseHelper"; // Tag just for the LogCat window
//Context ctx;
public DBHelper() {
super(ApplicationContextProvider.getContext(), DATABASE_NAME, null, DATABASE_VERSION);
try {
createDataBase();
openDataBase();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static DBHelper instance() {
if (sInstance == null) {
sInstance = new DBHelper();
}
return sInstance;
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db) {
}
/*
public void onStop() {
if (cursor != null) {
cursor.close();
}
}
*/
private boolean checkDataBase() {
File dbFile = ApplicationContextProvider.getContext().getDatabasePath(DATABASE_NAME);
return dbFile.exists();
/*
SQLiteDatabase checkDB = null;
try {
String myPath = DATABASE_PATH + DATABASE_NAME;
checkDB = SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase(myPath, null,
SQLiteDatabase.OPEN_READONLY);
} catch (SQLiteException e) {
// database doesn't exist yet.
}
if (checkDB != null) {
checkDB.close();
}
return checkDB != null;
*/
}
@Override
public synchronized void close() {
if (mDataBase != null)
mDataBase.close();
super.close();
}
private void createDataBase() throws IOException {
boolean dbExist = checkDataBase();
if (dbExist) {
// do nothing - database already exist
Log.d("DB", "Have existed");
} else {
// By calling this method an empty database will be created into
// the default system path
// of your application so we are gonna be able to overwrite that
// database with our database.
this.getReadableDatabase();
this.close();
try {
copyDataBase();
Log.e(TAG, "createDatabase database created");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new Error("Error copying database");
}
}
}
public void copyDataBase() throws IOException {
// Open your local db as the input stream
InputStream myInput = ApplicationContextProvider.getContext().getAssets().open(DATABASE_NAME);
// Path to the just created empty db
String outFileName = DATABASE_PATH + DATABASE_FILE;
// Open the empty db as the output stream
OutputStream myOutput = new FileOutputStream(outFileName);
// transfer bytes from the inputfile to the outputfile
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = myInput.read(buffer)) > 0) {
myOutput.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
// Close the streams
myOutput.flush();
myOutput.close();
myInput.close();
}
private void openDataBase() throws SQLException {
// Open the database
String myPath = DATABASE_PATH + DATABASE_NAME;
Log.d("DB PATH", myPath);
mDataBase = SQLiteDatabase.openDatabase(myPath, null,
SQLiteDatabase.OPEN_READWRITE);
}
/*
public Cursor getCursor() {
return cursor;
}
*/
public ArrayList<Contacts> select(String query) throws SQLException {
//Cursor c=null;
ArrayList<Contacts> objects = new ArrayList<Contacts>();
Log.d("select()", query);
Cursor c=null;
try {
c = mDataBase.rawQuery(query, null);
int id[]=new int[c.getCount()];
int i=0;
if (c.getCount() > 0)
{
c.moveToFirst();
do {
id[i]=c.getInt(c.getColumnIndex("name"));
Log.d("name", c.getString(1));
i++;
Contacts cons = new Contacts(c.getString(1), c.getString(2), c.getString(3));
objects.add(cons);
//cursor = c;
} while (c.moveToNext());
c.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
c.close();
} finally {
if(c!=null) {
c.close();
}
}
Log.d("Test Name in DBHelper", objects.get(0).getName());
c.close();
return objects;
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
}
}
public class Contacts {
public String name = "";
public String ph1 = "";
public String ph2 = "";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPhone1() {
return ph1;
}
public void setPhone1(String ph1) {
this.ph1 = ph1;
}
public String getPhone2() {
return ph2;
}
public void setPhone2(String ph2) {
this.ph2 = ph2;
}
// constructor
public Contacts (String name,String ph1,String ph2){
this.ph1 = ph1;
this.ph2 = ph2;
this.name = name;
}
public Contacts (){
}
}
2. 现在我们可以读出数据库的资料也把资料记录在变数上,后面来看看根据这个变数配合模板将结果显示出来
(Based on fragment)
fragment_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_vertical|center_horizontal"
android:text="Custom ListView Example" />
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listitem"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingLeft="10dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#ff112b7d"
android:textSize="14sp"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:textStyle="bold" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item_ph1"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/item_ph2"
android:layout_marginLeft="5dp"
android:layout_marginTop="5dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</LinearLayout>
建置模板适配器 MyAdapter.java
package com.example.xxx.test04;
import android.widget.ArrayAdapter;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter {
private static ArrayList<Contacts> searchArrayList;
private LayoutInflater mInflater;
public MyAdapter(Context context, ArrayList<Contacts> results) {
searchArrayList = results;
mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(context);
}
public int getCount() {
return searchArrayList.size();
}
public Object getItem(int position) {
return searchArrayList.get(position);
}
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder holder;
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = mInflater.inflate(R.layout.listitem, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.tv_name = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.item_name);
holder.tv_ph1 = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.item_ph1);
holder.tv_ph2 = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.item_ph2);
convertView.setTag(holder);
} else {
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
Log.d("View", searchArrayList.get(position).getName());
holder.tv_name.setText(searchArrayList.get(position).getName());
holder.tv_ph1.setText(searchArrayList.get(position).getPhone1());
holder.tv_ph2.setText(searchArrayList.get(position).getPhone2());
return convertView;
}
static class ViewHolder {
TextView tv_name;
TextView tv_ph1;
TextView tv_ph2;
}
}
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View V=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false);
Log.d("CreateView", "The view was created.");
dbhelper = DBHelper.instance();
Log.d("DATABASE", "The databases was created.");
ArrayList<Contacts> objects = dbhelper.select("SELECT * FROM " + TABLE_NAME);
Log.d("DATABASE", "List table - Done.");
//Log.d("Test Name", objects.get(0).getName());
final ListView itemList= (ListView) V.findViewById(R.id.listitem);
MyAdapter customAdapter = new MyAdapter(getActivity(), objects);
itemList.setAdapter(customAdapter);
//dbhelper.onStop();
return V;
}
MainActivityFragment.java 完整源码
package com.example.elvis.test04;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import java.io.IOException;
import android.util.Log;
import android.database.Cursor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.widget.GridView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.os.Bundle;
/**
* A placeholder fragment containing a simple view.
*/
public class MainActivityFragment extends Fragment {
private DBHelper dbhelper = null;
public static final String TABLE_NAME = "econtacts";
public MainActivityFragment() {
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container,
Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View V=inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_main, container, false);
Log.d("CreateView", "The view was created.");
dbhelper = DBHelper.instance();
Log.d("DATABASE", "The databases was created.");
ArrayList<Contacts> objects = dbhelper.select("SELECT * FROM " + TABLE_NAME);
Log.d("DATABASE", "List table - Done.");
//Log.d("Test Name", objects.get(0).getName());
final ListView itemList= (ListView) V.findViewById(R.id.listitem);
MyAdapter customAdapter = new MyAdapter(getActivity(), objects);
itemList.setAdapter(customAdapter);
//dbhelper.onStop();
return V;
}
}
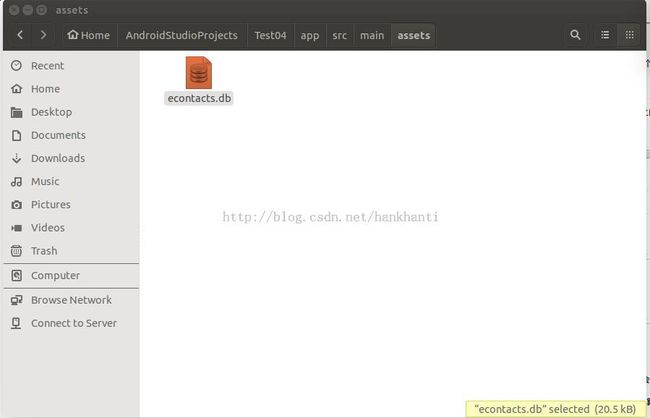
额外提一下如何将 econtacts.db 加入到 apk 中: 将 econtacts.db 放置到以下路径
且参考 DBHelper.java copyDataBase()
public void copyDataBase() throws IOException {
// Open your local db as the input stream
InputStream myInput = ApplicationContextProvider.getContext().getAssets().open(DATABASE_NAME);
// Path to the just created empty db
String outFileName = DATABASE_PATH + DATABASE_FILE;
// Open the empty db as the output stream
OutputStream myOutput = new FileOutputStream(outFileName);
// transfer bytes from the inputfile to the outputfile
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = myInput.read(buffer)) > 0) {
myOutput.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
// Close the streams
myOutput.flush();
myOutput.close();
myInput.close();
}