详解Linux内核红黑树算法的实现
内核源码:linux-2.6.38.8.tar.bz2
关于二叉查找树的概念请参考博文《详解二叉查找树算法的实现》。
平衡二叉树(BalancedBinary Tree或Height-Balanced Tree)又称AVL树。它或者是一棵空树,或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:它的左子树和右子树都是平衡二叉树,且左子树和右子树的深度之差的绝对值不超过1。若将二叉树上结点的平衡因子BF(BalanceFactor)定义为该结点的左子树的深度减去它的右子树的深度,则平衡二叉树上所有结点的平衡因子只可能是-1、0和1。(此段定义来自严蔚敏的《数据结构(C语言版)》)
红黑树是一种在插入或删除结点时都需要维持平衡的二叉查找树,并且每个结点都具有颜色属性:
(1)、一个结点要么是红色的,要么是黑色的。
(2)、根结点是黑色的。
(3)、如果一个结点是红色的,那么它的子结点必须是黑色的,也就是说在沿着从根结点出发的任何路径上都不会出现两个连续的红色结点。
(4)、从一个结点到一个NULL指针的每条路径上必须包含相同数目的黑色结点。
(此图片来自维基百科)
Linux内核红黑树的算法都定义在linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/rbtree.h和linux-2.6.38.8/lib/rbtree.c两个文件中。
1、结构体
- struct rb_node
- {
- unsigned long rb_parent_color;
- #define RB_RED 0
- #define RB_BLACK 1
- struct rb_node *rb_right;
- struct rb_node *rb_left;
- } __attribute__((aligned(sizeof(long))));
这里的巧妙之处是使用成员rb_parent_color同时存储两种数据,一是其双亲结点的地址,另一是此结点的着色。__attribute__((aligned(sizeof(long))))属性保证了红黑树中的每个结点的首地址都是32位对齐的(在32位机上),也就是说每个结点首地址的bit[1]和bit[0]都是0,因此就可以使用bit[0]来存储结点的颜色属性而不干扰到其双亲结点首地址的存储。
操作rb_parent_color的函数:
- #define rb_parent(r) ((struct rb_node *)((r)->rb_parent_color & ~3)) //获得其双亲结点的首地址
- #define rb_color(r) ((r)->rb_parent_color & 1) //获得颜色属性
- #define rb_is_red(r) (!rb_color(r)) //判断颜色属性是否为红
- #define rb_is_black(r) rb_color(r) //判断颜色属性是否为黑
- #define rb_set_red(r) do { (r)->rb_parent_color &= ~1; } while (0) //设置红色属性
- #define rb_set_black(r) do { (r)->rb_parent_color |= 1; } while (0) //设置黑色属性
- static inline void rb_set_parent(struct rb_node *rb, struct rb_node *p) //设置其双亲结点首地址的函数
- {
- rb->rb_parent_color = (rb->rb_parent_color & 3) | (unsigned long)p;
- }
- static inline void rb_set_color(struct rb_node *rb, int color) //设置结点颜色属性的函数
- {
- rb->rb_parent_color = (rb->rb_parent_color & ~1) | color;
- }
初始化新结点:
- static inline void rb_link_node(struct rb_node * node, struct rb_node * parent,
- struct rb_node ** rb_link)
- {
- node->rb_parent_color = (unsigned long )parent; //设置其双亲结点的首地址(根结点的双亲结点为NULL),且颜色属性设为黑色
- node->rb_left = node->rb_right = NULL; //初始化新结点的左右子树
- *rb_link = node; //指向新结点
- }
指向红黑树根结点的指针:
- struct rb_root
- {
- struct rb_node *rb_node;
- };
- #define RB_ROOT (struct rb_root) { NULL, } //初始化指向红黑树根结点的指针
- #define rb_entry(ptr, type, member) container_of(ptr, type, member) //用来获得包含struct rb_node的结构体的首地址
- #define RB_EMPTY_ROOT(root) ((root)->rb_node == NULL) //判断树是否为空
- #define RB_EMPTY_NODE(node) (rb_parent(node) == node) //判断node的双亲结点是否为自身
- #define RB_CLEAR_NODE(node) (rb_set_parent(node, node)) //设置双亲结点为自身
2、插入
首先像二叉查找树一样插入一个新结点,然后根据情况作出相应的调整,以使其满足红黑树的颜色属性(其实质是维持红黑树的平衡)。
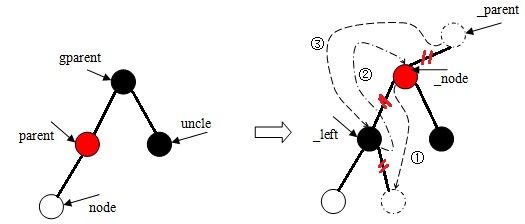
函数rb_insert_color使用while循环不断地判断双亲结点是否存在,且颜色属性为红色。
若判断条件为真,则分成两部分执行后续的操作:
(1)、当双亲结点是祖父结点左子树的根时,则:
a、存在叔父结点,且颜色属性为红色。
b、当node是其双亲结点右子树的根时,则左旋,然后执行第c步。
c、当node是其双亲结点左子树的根时。
(2)、当双亲结点是祖父结点右子树的根时的操作与第(1)步大致相同,这里略过不谈。
若为假,则始终设置根结点的颜色属性为黑色。
- void rb_insert_color(struct rb_node *node, struct rb_root *root)
- {
- struct rb_node *parent, *gparent;
- while ((parent = rb_parent(node)) && rb_is_red(parent)) //双亲结点不为NULL,且颜色属性为红色
- {
- gparent = rb_parent(parent); //获得祖父结点
- if (parent == gparent->rb_left) //双亲结点是祖父结点左子树的根
- {
- {
- register struct rb_node *uncle = gparent->rb_right; //获得叔父结点
- if (uncle && rb_is_red(uncle)) //叔父结点存在,且颜色属性为红色
- {
- rb_set_black(uncle); //设置叔父结点为黑色
- rb_set_black(parent); //设置双亲结点为黑色
- rb_set_red(gparent); //设置祖父结点为红色
- node = gparent; //node指向祖父结点
- continue; //继续下一个while循环
- }
- }
- if (parent->rb_right == node) //当node是其双亲结点右子树的根时
- {
- register struct rb_node *tmp;
- __rb_rotate_left(parent, root); //左旋
- tmp = parent; //调整parent和node指针的指向
- parent = node;
- node = tmp;
- }
- rb_set_black(parent); //设置双亲结点为黑色
- rb_set_red(gparent); //设置祖父结点为红色
- __rb_rotate_right(gparent, root); //右旋
- } else { // !(parent == gparent->rb_left)
- {
- register struct rb_node *uncle = gparent->rb_left;
- if (uncle && rb_is_red(uncle))
- {
- rb_set_black(uncle);
- rb_set_black(parent);
- rb_set_red(gparent);
- node = gparent;
- continue;
- }
- }
- if (parent->rb_left == node)
- {
- register struct rb_node *tmp;
- __rb_rotate_right(parent, root);
- tmp = parent;
- parent = node;
- node = tmp;
- }
- rb_set_black(parent);
- rb_set_red(gparent);
- __rb_rotate_left(gparent, root);
- } //end if (parent == gparent->rb_left)
- } //end while ((parent = rb_parent(node)) && rb_is_red(parent))
- rb_set_black(root->rb_node);
- }
3、删除
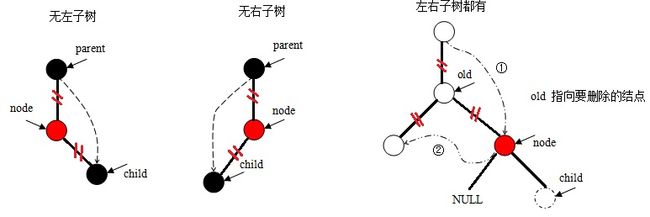
像二叉查找树的删除操作一样,首先需要找到所需删除的结点,然后根据该结点左右子树的有无分为三种情形:
若node结点的颜色属性为黑色,则需要调用__rb_erase_color函数来进行调整。
- void rb_erase(struct rb_node *node, struct rb_root *root)
- {
- struct rb_node *child, *parent;
- int color;
- if (!node->rb_left) //删除结点无左子树
- child = node->rb_right;
- else if (!node->rb_right) //删除结点无右子树
- child = node->rb_left;
- else //左右子树都有
- {
- struct rb_node *old = node, *left;
- node = node->rb_right;
- while ((left = node->rb_left) != NULL)
- node = left;
- if (rb_parent(old)) {
- if (rb_parent(old)->rb_left == old)
- rb_parent(old)->rb_left = node;
- else
- rb_parent(old)->rb_right = node;
- } else
- root->rb_node = node;
- child = node->rb_right;
- parent = rb_parent(node);
- color = rb_color(node);
- if (parent == old) {
- parent = node;
- } else {
- if (child)
- rb_set_parent(child, parent);
- parent->rb_left = child;
- node->rb_right = old->rb_right;
- rb_set_parent(old->rb_right, node);
- }
- node->rb_parent_color = old->rb_parent_color;
- node->rb_left = old->rb_left;
- rb_set_parent(old->rb_left, node);
- goto color;
- } //end else
- parent = rb_parent(node); //获得删除结点的双亲结点
- color = rb_color(node); //获取删除结点的颜色属性
- if (child)
- rb_set_parent(child, parent);
- if (parent)
- {
- if (parent->rb_left == node)
- parent->rb_left = child;
- else
- parent->rb_right = child;
- }
- else
- root->rb_node = child;
- color:
- if (color == RB_BLACK) //如果删除结点的颜色属性为黑色,则需调用__rb_erase_color函数来进行调整
- __rb_erase_color(child, parent, root);
- }
4、遍历
rb_first和rb_next函数可组成中序遍历,即以升序遍历红黑树中的所有结点。
- struct rb_node *rb_first(const struct rb_root *root)
- {
- struct rb_node *n;
- n = root->rb_node;
- if (!n)
- return NULL;
- while (n->rb_left)
- n = n->rb_left;
- return n;
- }
- struct rb_node *rb_next(const struct rb_node *node)
- {
- struct rb_node *parent;
- if (rb_parent(node) == node)
- return NULL;
- /* If we have a right-hand child, go down and then left as far
- as we can. */
- if (node->rb_right) {
- node = node->rb_right;
- while (node->rb_left)
- node=node->rb_left;
- return (struct rb_node *)node;
- }
- /* No right-hand children. Everything down and left is
- smaller than us, so any 'next' node must be in the general
- direction of our parent. Go up the tree; any time the
- ancestor is a right-hand child of its parent, keep going
- up. First time it's a left-hand child of its parent, said
- parent is our 'next' node. */
- while ((parent = rb_parent(node)) && node == parent->rb_right)
- node = parent;
- return parent;
- }
5、在应用程序中使用
Linux内核中红黑树算法的实现非常通用、巧妙,而且免费又开源,因此完全可以把它运用到自己的应用程序中。
(1)、从内核中拷贝源文件:
- $ mkdir redblack
- $ cd redblack/
- $ cp ../linux-2.6.38.8/lib/rbtree.c .
- $ cp ../linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/rbtree.h .
(2)、修改源文件:
a、C文件rbtree.c
修改包含头文件的代码
- //删除以下两行代码
- #include <linux/rbtree.h>
- #include <linux/module.h>
- //新增以下代码,即包含当前目录中的头文件rbtree.h
- #include "rbtree.h"
删除所有的EXPORT_SYMBOL宏
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_insert_color);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_erase);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_augment_insert);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_augment_erase_begin);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_augment_erase_end);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_first);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_last);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_next);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_prev);
- EXPORT_SYMBOL(rb_replace_node);
b、头文件rbtree.h
删除包含头文件的代码,并添加三个宏定义
- //删除以下两行代码
- #include <linux/kernel.h>
- #include <linux/stddef.h>
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/stddef.h */
- #undef NULL
- #if defined(__cplusplus)
- #define NULL 0
- #else
- #define NULL ((void *)0)
- #endif
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/stddef.h */
- #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
- /* linux-2.6.38.8/include/linux/kernel.h */
- #define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
- const typeof( ((type *)0)->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
- (type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
(3)、示例代码
Linux内核红黑树的使用方法请参考linux-2.6.38.8/Documentation/rbtree.txt文件。
- /* test.c */
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include "rbtree.h"
- struct mytype {
- struct rb_node my_node;
- int num;
- };
- struct mytype *my_search(struct rb_root *root, int num)
- {
- struct rb_node *node = root->rb_node;
- while (node) {
- struct mytype *data = container_of(node, struct mytype, my_node);
- if (num < data->num)
- node = node->rb_left;
- else if (num > data->num)
- node = node->rb_right;
- else
- return data;
- }
- return NULL;
- }
- int my_insert(struct rb_root *root, struct mytype *data)
- {
- struct rb_node **tmp = &(root->rb_node), *parent = NULL;
- /* Figure out where to put new node */
- while (*tmp) {
- struct mytype *this = container_of(*tmp, struct mytype, my_node);
- parent = *tmp;
- if (data->num < this->num)
- tmp = &((*tmp)->rb_left);
- else if (data->num > this->num)
- tmp = &((*tmp)->rb_right);
- else
- return -1;
- }
- /* Add new node and rebalance tree. */
- rb_link_node(&data->my_node, parent, tmp);
- rb_insert_color(&data->my_node, root);
- return 0;
- }
- void my_delete(struct rb_root *root, int num)
- {
- struct mytype *data = my_search(root, num);
- if (!data) {
- fprintf(stderr, "Not found %d.\n", num);
- return;
- }
- rb_erase(&data->my_node, root);
- free(data);
- }
- void print_rbtree(struct rb_root *tree)
- {
- struct rb_node *node;
- for (node = rb_first(tree); node; node = rb_next(node))
- printf("%d ", rb_entry(node, struct mytype, my_node)->num);
- printf("\n");
- }
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- struct rb_root mytree = RB_ROOT;
- int i, ret, num;
- struct mytype *tmp;
- if (argc < 2) {
- fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s num\n", argv[0]);
- exit(-1);
- }
- num = atoi(argv[1]);
- printf("Please enter %d integers:\n", num);
- for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
- tmp = malloc(sizeof(struct mytype));
- if (!tmp)
- perror("Allocate dynamic memory");
- scanf("%d", &tmp->num);
- ret = my_insert(&mytree, tmp);
- if (ret < 0) {
- fprintf(stderr, "The %d already exists.\n", tmp->num);
- free(tmp);
- }
- }
- printf("\nthe first test\n");
- print_rbtree(&mytree);
- my_delete(&mytree, 21);
- printf("\nthe second test\n");
- print_rbtree(&mytree);
- return 0;
- }
编译并执行:
- $ gcc rbtree.c test.c -o test
- richard@tanglinux:~/algorithm/redblack$ ./test 10
- Please enter 10 integers:
- 23
- 4
- 56
- 32
- 89
- 122
- 12
- 21
- 45
- 23
- The 23 already exists.
- the first test
- 4 12 21 23 32 45 56 89 122
- the second test
- 4 12 23 32 45 56 89 122