scanf,fscanf,sscanf的区别----整理
scanf 从控制台输入
fscanf 从文件输入
sscanf 从指定字符串输入
1、例:使用scanf函数输入数据。
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,c;
printf("输入 a, b, c\n");
scanf("%d,%d,%d", &a, &b, &c);
printf("a = %d b = %d c = %d\n", a, b, c);
return 0;
}
2、int fscanf(
文件指针
,格式字符串,输入列表);
功 能: 从一个流中执行格式化输入,fscanf遇到空格和换行时结束,注意空格时也结束。这与 fgets有区别,fgets遇到空格不结束。
用 法: int fscanf(FILE *stream, char *format,[argument...]);
如:
FILE *fp;
char a[10];
int b;
double c;
fscanf(fp,"%s%d%lf",a,&b,&c)
返回值:整型,成功读入的参数的个数
3、大家都知道sscanf是一个很好用的函数,利用它可以从字符串中取出整数、浮点数和字符串等等。它的使用方法简单,特别对于整数和浮点数来说。但新手可能并不知道处理字符串时的一些高级用法,这里做个简要说明吧。
1. 常见用法。
char str[512] = {0};
sscanf("123456 ", "%s", str);
printf("str=%s\n", str);
2. 取指定长度的字符串。如在下例中,取最大长度为4字节的字符串。
sscanf("123456 ", "%4s", str);
printf("str=%s\n", str);//str的值为1234
3. 取到指定字符为止的字符串。如在下例中,取遇到空格为止字符串。
sscanf("123456 abcdedf", "%[^ ]", str);//注意^后面有一空格
printf("str=%s\n", str);
4. 取仅包含指定字符集的字符串。如在下例中,取仅包含1到9和小写字母的字符串。
sscanf("123456abcdedfBCDEF", "%[1-9a-z]", str);
printf("str=%s\n", str);
5. 取到指定字符集为止的字符串。如在下例中,取遇到大写字母为止的字符串。
sscanf("123456abcdedfBCDEF", "%[^A-Z]", str);
printf("str=%s\n", str);
源代码一如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
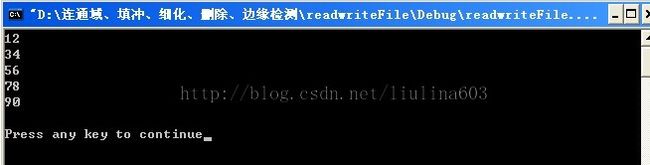
char *tokenstring = "12:34:56-7890";
char a1[3], a2[3], a3[3];
int i1, i2;
void main(void)
{
sscanf(tokenstring, "%2s:%2s:%2s-%2d%2d", a1, a2, a3, &i1, &i2);
printf("%s\n%s\n%s\n%d\n%d\n\n", a1, a2, a3, i1, i2);
getch();
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
char *tokenstring = "12:34:56-7890";
char a1[3], a2[3], a3[3],a;
int i1, i2;
void main(void)
{
sscanf(tokenstring, "%2s%1s%2s%1s%2s%1s%2d%2d", a1, &a, a2, &a3, a3, &a, &i1, &i2);
printf("%s\n%s\n%s\n%d\n%d\n\n", a1, a2, a3, i1, i2);
getch();
}
结果同上
源代码三如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
char *tokenstring = "12:34:56-7890";
char a1[3], a2[3], a3[3], a4[3], a5[3];
int i1, i2;
void main(void)
{
char a;
sscanf(tokenstring, "%2s%1s%2s%1s%2s%1s%2s%2s", a1, &a, a2, &a3, a3, &a, a4, a5);
i1 =atoi(a4);
i2 =atoi(a5);
printf("%s\n%s\n%s\n%d\n%d\n\n", a1, a2, a3, i1, i2);
getch();
}
结果同上
方法四如下(以实例说明,原理相同):
/* The following sample illustrates the use of brackets and the
caret (^) with sscanf().
Compile options needed: none
*/
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
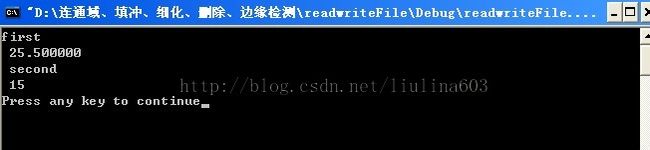
char *tokenstring = "first,25.5,second,15";
int result, i;
double fp;
char o[10], f[10], s[10], t[10];
void main()
{
result = sscanf(tokenstring, "%[^','],%[^','],%[^','],%s", o, s, t, f);
fp = atof(s);
i = atoi(f);
printf("%s\n %lf\n %s\n %d\n", o, fp, t, i);
}