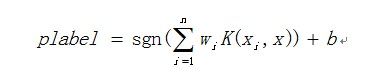libsvm 多分类中model参数
一、先看REDEME中的介绍
struct svm_model
{
struct svm_parameter param; /* parameter */int nr_class; /* number of classes, = 2 in regression/one class svm */
int l; /* total #SV */
struct svm_node **SV; /* SVs (SV[l]) */
double **sv_coef; /* coefficients for SVs in decision functions (sv_coef[k-1][l]) */
double *rho; /* constants in decision functions (rho[k*(k-1)/2]) */
double *probA; /* pairwise probability information */
double *probB;
int *sv_indices; /* sv_indices[0,...,nSV-1] are values in [1,...,num_traning_data] to indicate SVs in the training set */
/* for classification only */
int *label; /* label of each class (label[k]) */
int *nSV; /* number of SVs for each class (nSV[k]) */
/* nSV[0] + nSV[1] + ... + nSV[k-1] = l */
/* XXX */
int free_sv; /* 1 if svm_model is created by svm_load_model*/
/* 0 if svm_model is created by svm_train */
};
param describes the parameters used to obtain the model.
nr_class is the number of classes. It is 2 for regression and one-class SVM.
l is the number of support vectors. SV and sv_coef are support
vectors and the corresponding coefficients, respectively. Assume there are
k classes. For data in class j, the corresponding sv_coef includes (k-1) y*alpha vectors,
where alpha's are solutions of the following two class problems:
1 vs j, 2 vs j, ..., j-1 vs j, j vs j+1, j vs j+2, ..., j vs k
and y=1 for the first j-1 vectors, while y=-1 for the remaining k-j
vectors. For example, if there are 4 classes, sv_coef and SV are like:
+-+-+-+--------------------+
|1|1|1| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 1 |
|2|3|4| |
+-+-+-+--------------------+
|1|2|2| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 2 |
|2|3|4| |
+-+-+-+--------------------+
|1|2|3| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 3 |
|3|3|4| |
+-+-+-+--------------------+
|1|2|3| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 4 |
|4|4|4| |
+-+-+-+--------------------+
rho is the bias term (-b). probA and probB are parameters used in
probability outputs. If there are k classes, there are k*(k-1)/2
binary problems as well as rho, probA, and probB values. They are
aligned in the order of binary problems:
1 vs 2, 1 vs 3, ..., 1 vs k, 2 vs 3, ..., 2 vs k, ..., k-1 vs k.
sv_indices[0,...,nSV-1] are values in [1,...,num_traning_data] to
indicate support vectors in the training set.
label contains labels in the training data.
nSV is the number of support vectors in each class.
二、基本概念
什么是支持向量? 存在y = +1 的支持向量 y=-1的支持向量
svm对多分类支持?用1vs1加上投票的方法来确定
三、二分类和多分类model参数
对于二分类
SV用于保持支持向量
sv_coef用于保存支持向量对应的系数yi*alpha
因为C-SVC 的决策函数如下:可以看到wi是标量,Xi是 支持向量
因此 SV 和 SV_coef的行数是相同的,假设为M,则SV 为M *(fetures个数) SV_coef 为 M * 1,注意这里的支持向量分正支持向量和 负支持向量,由nSV指出个数,这个概念在推广到多分类是很有用。
+-+-+-+--------------------+
|1| |
|v| SVs from class 1 |
|2| |
+-+-+-+--------------------+
对于多分类
SV用于保持支持向量
sv_coef用于保存支持向量对应的系数yi*alpha
因为C-SVC 的决策函数如下:可以看到wi是标量,Xi是 支持向量
k -1 fetures 个数
+-+-+-+ -------------------+
|1|1|1| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 1 | 假设这里有 nSV[0]个支持向量
|2|3|4| |
| | | | | |
+-+-+ |+ --------------------+
|1|2|2| |
|v|v|v| S Vs from class 2 | nSV[1]个支持向量
|2|3|4| |
+-+-+-+-- ------------------+
|1|2|3| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 3 | nSV[2]个支持向量
|3|3|4| |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
+-+-+-+--- -----------------+
|1|2|3| |
|v|v|v| SVs from class 4 | nSV[3]个支持向量
|4|4|4| |
+-+-+-+---- ----------------+
For data in class j, the corresponding sv_coef includes (k-1) y*alpha vectors,
where alpha's are solutions of the following two class problems:
1 vs j, 2 vs j, ..., j-1 vs j, j vs j+1, j vs j+2, ..., j vs k
and y=1 for the first j-1 vectors, while y=-1 for the remaining k-j
vectors.
因此 SV 和 SV_coef的行数是相同的,注意由于使用1VS1 策略,需要分别计算
由于有k个分类器,因此对每个类需要(k-1)个 (y*alpha vectors)。
在这个k-1个系数向量中,有j-1个 是i vs j and i < j 的 ,此时,i中有正支持向量,有 k-j 个是 i vs j and i>j 的,此时i中有负支持向量。因此假如要计算 i vs j 分类器的w 系数,需要 class i中的 i vs j 系数向量,class i中的 支持向量 ,也需要 class j中的 j vs i系数向量,class j中的支持向量 ,注意这两个向量是互补的,一个在分类线左边,一个在右边,也就是上面说的正支持向量和负的支持向量。只要组合这些向量就能恢复出二分类中的中的系数向量和支持向量。
Q:libsvm 文档摘要
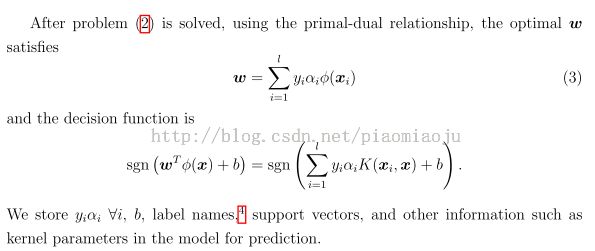
Q:How could i generate the primal variable w oflinear svm?
Let's start from the binary class and assume you have two labels -1 and +1. After obtaining the model from calling svmtrain, do the following to have w and b:
w = model.SVs' * model.sv_coef; b = -model.rho; if model.Label(1) == -1 w = -w; b = -b; endIf you do regression or one-class SVM, then the if statement is not needed.
For multi-class SVM, we illustrate the setting in the following example of running the iris data, which have 3 classes
> [y, x] = libsvmread('../../htdocs/libsvmtools/datasets/multiclass/iris.scale');
> m = svmtrain(y, x, '-t 0')
m =
Parameters: [5x1 double]
nr_class: 3
totalSV: 42
rho: [3x1 double]
Label: [3x1 double]
ProbA: []
ProbB: []
nSV: [3x1 double]
sv_coef: [42x2 double]
SVs: [42x4 double]
sv_coef is like:
+-+-+--------------------+ |1|1| | |v|v| SVs from class 1 | |2|3| | +-+-+--------------------+ |1|2| | |v|v| SVs from class 2 | |2|3| | +-+-+--------------------+ |1|2| | |v|v| SVs from class 3 | |3|3| | +-+-+--------------------+so we need to see nSV of each classes.
> m.nSV
ans =
3
21
18
Suppose the goal is to find the vector w of classes 1 vs 3. Then y_i alpha_i of training 1 vs 3 are
> coef = [m.sv_coef(1:3,2); m.sv_coef(25:42,1)];and SVs are:
> SVs = [m.SVs(1:3,:); m.SVs(25:42,:)];Hence, w is
> w = SVs'*coef;For rho,
> m.rho
ans =
1.1465
0.3682
-1.9969
> b = -m.rho(2);
because rho is arranged by 1vs2 1vs3 2vs3.