浅析 Android recovery mode
# recovery介绍
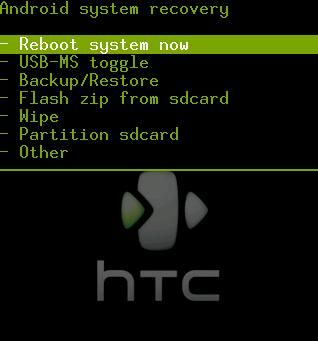
从事android的开发者对recovery一定不会陌生.它主要用来擦除数据和进行系统升级.擦除数据就是为了上层恢复出厂设置提供接口.主要有wipe data和wipe cache.升级又分为在线升级和离线升级.在线升级一般通过网络(3G,WIFI,GPRS)下载资源包,然后进入recovery进行升级.离线升级一般把下载好的update包放至SD卡,然后选择从SD卡更新的方式进行升级(我们常常说的刷机就是这样).并且recovery还可以根据自己的需求定制.下面这个是HTC早期的recovery.
# 使用recovery的不同情形
·恢复出厂设置
<1>
用户在系统设置中选择“恢复出厂设置”
<2>系统将"wipe_data"命令写入/cache/recovery/command
<2>系统将"wipe_data"命令写入/cache/recovery/command
<3>系统重启,并进入recover模式(/sbin/recovery)
<4>get_args()将"boot-recovery"和"--wipe_data"写入BCB(bootloader control block)
<5>erase_volume("/data") 格式化(擦除)DATA分区
<6>erase_volume("/cache")格式化(擦除)CACHE分区
<7>finish_recovery() 擦除BCB
<8>reboot
·刷机
<1>用户按下power+volume down键进入recovery mode
<2>用户选择Flash Zip from SD card(以上图为例)
<3>update_directory将"boot-recovery"和"recovery\n"写入BCB
<4>在really_install_package中验证更新包
<5>在try_update_binary执行2进制更新文件"/tmp/update_binary"
<6>利用pipe通信更新recovery UI
<7>finish_recovery() 擦除BCB
<8>reboot
# SD卡升级流程(也就是我们一般所说的刷机)
1.首先从main函数入手吧
<有些注释直接添加到了源代码中>
int
main(int argc, char **argv) {
time_t start = time(NULL);
// If these fail, there's not really anywhere to complain...
freopen(TEMPORARY_LOG_FILE, "a", stdout); setbuf(stdout, NULL);
freopen(TEMPORARY_LOG_FILE, "a", stderr); setbuf(stderr, NULL);
printf("Starting recovery on %s", ctime(&start));
device_ui_init(&ui_parameters);
ui_init();
ui_set_background(BACKGROUND_ICON_INSTALLING);
load_volume_table();
get_args(&argc, &argv);//write the bcb partition
int previous_runs = 0;
const char *send_intent = NULL;
const char *update_package = NULL;
int wipe_data = 0, wipe_cache = 0;
int arg;
while ((arg = getopt_long(argc, argv, "", OPTIONS, NULL)) != -1) {
switch (arg) {
case 'p': previous_runs = atoi(optarg); break;
case 's': send_intent = optarg; break;
case 'u': update_package = optarg; break;
case 'w': wipe_data = wipe_cache = 1; break;
case 'c': wipe_cache = 1; break;
case 't': ui_show_text(1); break;
case '?':
LOGE("Invalid command argument\n");
continue;
}
}
......
......//省略部分代码
......
int status = INSTALL_SUCCESS;
if (update_package != NULL) {
status = install_package(update_package);
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS) ui_print("Installation aborted.\n");
} else if (wipe_data) {
if (device_wipe_data()) status = INSTALL_ERROR;
if (erase_volume("/data")) status = INSTALL_ERROR;
if (wipe_cache && erase_volume("/cache")) status = INSTALL_ERROR;
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS) ui_print("Data wipe failed.\n");
} else if (wipe_cache) {
if (wipe_cache && erase_volume("/cache")) status = INSTALL_ERROR;
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS) ui_print("Cache wipe failed.\n");
} else {
status = INSTALL_ERROR; // No command specified
}
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS) ui_set_background(BACKGROUND_ICON_ERROR);
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS || ui_text_visible()) {
prompt_and_wait();
}
// Otherwise, get ready to boot the main system...
finish_recovery(send_intent);
ui_print("Rebooting...\n");
android_reboot(ANDROID_RB_RESTART, 0, 0);
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
while循环中读取recovery的command参数(/cache/recovery/command),在main函数中的OPTIONS中可以看到不同选项的定义
{ "send_intent", required_argument, NULL, 's' },
{ "update_package", required_argument, NULL, 'u' },
{ "wipe_data", no_argument, NULL, 'w' },
{ "wipe_cache", no_argument, NULL, 'c' },
{ "show_text", no_argument, NULL, 't' },之后根据设置的不同标志变量执行不同的操作,比如写入了"wipe_data"就调用erase_volume擦洗data和cache分区.如果没有任何标志变量被设置则
进入prompt_and_wait函数中.
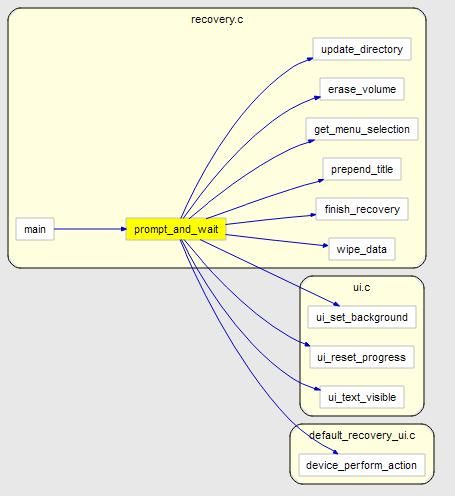
2.进入prompt_and_wait,准备接收用户按键.
static void
prompt_and_wait() {
char** headers = prepend_title((const char**)MENU_HEADERS);
for (;;) {
finish_recovery(NULL);
ui_reset_progress();
int chosen_item = get_menu_selection(headers, MENU_ITEMS, 0, 0);
//get the item of you selection in the menu
// device-specific code may take some action here. It may
// return one of the core actions handled in the switch
// statement below.
chosen_item = device_perform_action(chosen_item);
int status;
switch (chosen_item) {
case ITEM_REBOOT:
return;
case ITEM_WIPE_DATA:
wipe_data(ui_text_visible());//wipe the data partition
if (!ui_text_visible()) return;
break;
case ITEM_WIPE_CACHE://wipe cache partition
ui_print("\n-- Wiping cache...\n");
erase_volume("/cache");
ui_print("Cache wipe complete.\n");
if (!ui_text_visible()) return;
break;
case ITEM_APPLY_SDCARD://update system use the zip in the SDcard
status = update_directory(SDCARD_ROOT, SDCARD_ROOT);//both "/sdcard"
if (status >= 0) {
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS) {
ui_set_background(BACKGROUND_ICON_ERROR);
ui_print("Installation aborted.\n");
} else if (!ui_text_visible()) {
return; // reboot if logs aren't visible
} else {
ui_print("\nInstall from sdcard complete.\n");
}
}
break;
case ITEM_APPLY_CACHE:
// Don't unmount cache at the end of this.
status = update_directory(CACHE_ROOT, NULL);
if (status >= 0) {
if (status != INSTALL_SUCCESS) {
ui_set_background(BACKGROUND_ICON_ERROR);
ui_print("Installation aborted.\n");
} else if (!ui_text_visible()) {
return; // reboot if logs aren't visible
} else {
ui_print("\nInstall from cache complete.\n");
}
}
break;
}
}
}
这个函数比较简单,调用get_menu_selection进入循环等待用户按键.这里会根据用户选择进行分支处理.这段代码比较简单.就不用多介绍了.
配个简单的调用图,更直观一点
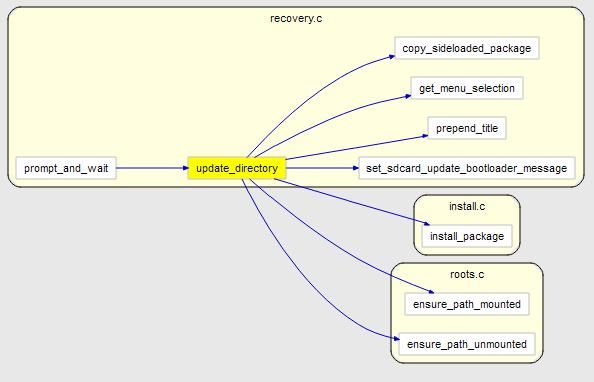
3.当我们选择从SD卡更新后,流程直接走到update_directory.
update_directory(const char* path, const char* unmount_when_done) {
ensure_path_mounted(path);//ensure the path is mounted
const char* MENU_HEADERS[] = { "Choose a package to install:",
path,
"",
NULL };
DIR* d;
struct dirent* de;
d = opendir(path);
if (d == NULL) {
LOGE("error opening %s: %s\n", path, strerror(errno));
if (unmount_when_done != NULL) {
ensure_path_unmounted(unmount_when_done);
}
return 0;
}
char** headers = prepend_title(MENU_HEADERS);//prepare the frameUI
int d_size = 0;
int d_alloc = 10;
char** dirs = malloc(d_alloc * sizeof(char*));//40 bytes 10 char * eg:char * [10]
int z_size = 1;
int z_alloc = 10;
char** zips = malloc(z_alloc * sizeof(char*));
zips[0] = strdup("../");//duplicate the string "../"
......
......//省略部分代码
......
int result;
int chosen_item = 0;
do {
chosen_item = get_menu_selection(headers, zips, 1, chosen_item);
char* item = zips[chosen_item];
int item_len = strlen(item);
if (chosen_item == 0) { // item 0 is always "../"
// go up but continue browsing (if the caller is update_directory)
result = -1;
break;
} else if (item[item_len-1] == '/') {
// recurse down into a subdirectory
char new_path[PATH_MAX];
strlcpy(new_path, path, PATH_MAX);
strlcat(new_path, "/", PATH_MAX);//append the full path
strlcat(new_path, item, PATH_MAX);
new_path[strlen(new_path)-1] = '\0'; // truncate the trailing '/'
result = update_directory(new_path, unmount_when_done);
if (result >= 0) break;
} else {
// selected a zip file: attempt to install it, and return
// the status to the caller.
char new_path[PATH_MAX];
strlcpy(new_path, path, PATH_MAX);
strlcat(new_path, "/", PATH_MAX);
strlcat(new_path, item, PATH_MAX);
ui_print("\n-- Install %s ...\n", path);
set_sdcard_update_bootloader_message();//set the boot command with boot-recovery
char* copy = copy_sideloaded_package(new_path);//copy update.zip into SIDELOAD_TEMP_DIR
if (unmount_when_done != NULL) {
ensure_path_unmounted(unmount_when_done);
}
if (copy) {
result = install_package(copy);//important function to install the update.zip file
free(copy);
} else {
result = INSTALL_ERROR;
}
break;
}
} while (true);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < z_size; ++i) free(zips[i]);
free(zips);
free(headers);
if (unmount_when_done != NULL) {
ensure_path_unmounted(unmount_when_done);
}
return result;
}
上半部分的代码就是在SD card下的文件.并把路径记录下来,然后根据名称排序.然后处理用户按键(这里powe键是确认)
·当用户选择第一个条目“../”,直接跳转到上级目录,并且继续浏览文件.
·当用户选择的条目以"/"开头,直接进入子目录
·其它情况表明,该条目就是zip包.写入BCB,copy 更新包至临时目录.直接转入install_package
实际上这里就是一个基于frameUI的一个建议文件浏览器.只能显示zip文件和目录.
老规矩,配个调用图方便理解函数
老规矩,配个调用图方便理解函数
4.进入install_package函数之前,先看看set_sdcard_update_bootloader_message
static void
set_sdcard_update_bootloader_message() {
struct bootloader_message boot;
memset(&boot, 0, sizeof(boot));
strlcpy(boot.command, "boot-recovery", sizeof(boot.command));
strlcpy(boot.recovery, "recovery\n", sizeof(boot.recovery));
set_bootloader_message(&boot);
}构造了bootloader_message结构之后,其余工作就交给set_bootloader_message去做.里面根据不同的/misc类别去
写mtd或者block.有兴趣的可以深入了解.
5.install_package只是简单的包装了一下really_install_package.在really_install_package中更新了一下背景,验证了更新包.
验证成功则转入try_update_binary函数.
static int
try_update_binary(const char *path, ZipArchive *zip) {
const ZipEntry* binary_entry =
mzFindZipEntry(zip, ASSUMED_UPDATE_BINARY_NAME);
if (binary_entry == NULL) {
mzCloseZipArchive(zip);
return INSTALL_CORRUPT;
}
char* binary = "/tmp/update_binary";
unlink(binary);
int fd = creat(binary, 0755);
if (fd < 0) {
mzCloseZipArchive(zip);
LOGE("Can't make %s\n", binary);
return 1;
}
bool ok = mzExtractZipEntryToFile(zip, binary_entry, fd);
close(fd);
mzCloseZipArchive(zip);
if (!ok) {
LOGE("Can't copy %s\n", ASSUMED_UPDATE_BINARY_NAME);
return 1;
}
int pipefd[2];
pipe(pipefd);//use pipe
// When executing the update binary contained in the package, the
// arguments passed are:
//
// - the version number for this interface
//
// - an fd to which the program can write in order to update the
// progress bar. The program can write single-line commands:
//
// progress <frac> <secs>
// fill up the next <frac> part of of the progress bar
// over <secs> seconds. If <secs> is zero, use
// set_progress commands to manually control the
// progress of this segment of the bar
//
// set_progress <frac>
// <frac> should be between 0.0 and 1.0; sets the
// progress bar within the segment defined by the most
// recent progress command.
//
// firmware <"hboot"|"radio"> <filename>
// arrange to install the contents of <filename> in the
// given partition on reboot.
//
// (API v2: <filename> may start with "PACKAGE:" to
// indicate taking a file from the OTA package.)
//
// (API v3: this command no longer exists.)
//
// ui_print <string>
// display <string> on the screen.
//
// - the name of the package zip file.
//
char** args = malloc(sizeof(char*) * 5);
args[0] = binary;
args[1] = EXPAND(RECOVERY_API_VERSION); // defined in Android.mk
args[2] = malloc(10);
sprintf(args[2], "%d", pipefd[1]);
args[3] = (char*)path;
args[4] = NULL;
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {//in child process
close(pipefd[0]);
execv(binary, args);
fprintf(stdout, "E:Can't run %s (%s)\n", binary, strerror(errno));
_exit(-1);
}
close(pipefd[1]);
char buffer[1024];
FILE* from_child = fdopen(pipefd[0], "r");
while (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), from_child) != NULL) {
char* command = strtok(buffer, " \n");
if (command == NULL) {
continue;
} else if (strcmp(command, "progress") == 0) {
char* fraction_s = strtok(NULL, " \n");
char* seconds_s = strtok(NULL, " \n");
float fraction = strtof(fraction_s, NULL);
int seconds = strtol(seconds_s, NULL, 10);
ui_show_progress(fraction * (1-VERIFICATION_PROGRESS_FRACTION),
seconds);
} else if (strcmp(command, "set_progress") == 0) {
char* fraction_s = strtok(NULL, " \n");
float fraction = strtof(fraction_s, NULL);
ui_set_progress(fraction);
} else if (strcmp(command, "ui_print") == 0) {
char* str = strtok(NULL, "\n");
if (str) {
ui_print("%s", str);
} else {
ui_print("\n");
}
} else {
LOGE("unknown command [%s]\n", command);
}
}
fclose(from_child);
int status;
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
if (!WIFEXITED(status) || WEXITSTATUS(status) != 0) {
LOGE("Error in %s\n(Status %d)\n", path, WEXITSTATUS(status));
return INSTALL_ERROR;
}
return INSTALL_SUCCESS;
}
fork了一个进程去执行update_binary,并且父进程于子进程通过管道进行通信,父进程根据子进程的数据去更新进度.
不过在android代码注释里看到有更新固件的选项.在代码中又没有发现,应该是被和谐了吧.
6.之后返回至main中,执行finish_recovery
static void
finish_recovery(const char *send_intent) {
// By this point, we're ready to return to the main system...
if (send_intent != NULL) {
FILE *fp = fopen_path(INTENT_FILE, "w");
if (fp == NULL) {
LOGE("Can't open %s\n", INTENT_FILE);
} else {
fputs(send_intent, fp);
check_and_fclose(fp, INTENT_FILE);
}
}
// Copy logs to cache so the system can find out what happened.
copy_log_file(LOG_FILE, true);
copy_log_file(LAST_LOG_FILE, false);
chmod(LAST_LOG_FILE, 0640);
// Reset to mormal system boot so recovery won't cycle indefinitely.
struct bootloader_message boot;
memset(&boot, 0, sizeof(boot));
set_bootloader_message(&boot);
// Remove the command file, so recovery won't repeat indefinitely.
if (ensure_path_mounted(COMMAND_FILE) != 0 ||
(unlink(COMMAND_FILE) && errno != ENOENT)) {
LOGW("Can't unlink %s\n", COMMAND_FILE);
}
sync(); // For good measure.
}
最后在finish_recovery中copy安装日志,清理BCB,调用sync()进行文件系统同步.