图的深度优先和广度优先算法(DFS递归与非递归)
本博客前面文章已对图有过简单的介绍,本文主要是重点介绍有关图的一些具体操作与应用
阅读本文前,可以先参考本博客 各种基本算法实现小结(四)—— 图及其遍历 和 图的一些基本算法
无向图——邻接矩阵的深度优先和广度优先算法实现
测试环境:VS2008(C)
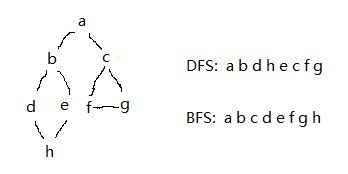
#include "stdafx.h" #include <stdlib.h> #include <malloc.h> #define INFINITY INT_MAX #define MAX_VEX 20 #define VRType int #define VertexType char #define InfoType int int *visited; /********************************/ /**** 图的结构定义 ****/ /********************************/ typedef enum { DG, DN, UDG, UDN }GraphKind; struct _ArcCell { VRType adj; /* note weight */ InfoType *info; }; typedef struct _ArcCell ArcCell, AdjMatrix[MAX_VEX][MAX_VEX]; struct _MGraph { VertexType vexs[MAX_VEX]; AdjMatrix arcs; int vexnum, arcnum; GraphKind kind; }; typedef struct _MGraph MGraph; /********************************/ /**** 栈的结构定义 ****/ /********************************/ struct _node { int ivex; struct _node *next; }; typedef struct _node node, *pnode; struct _stack { int size; pnode ptop; }; typedef struct _stack stack, *pstack; /********************************/ /**** 堆的结构定义 ****/ /********************************/ struct _queue { pnode front; pnode rear; }; typedef struct _queue queue, *pqueue; /********************************/ /**** 栈的实现 ****/ /********************************/ pstack init_stack(int size) { pnode pn=NULL; pstack ps=NULL; pn=(pnode)malloc(sizeof(node)); ps=(pstack)malloc(sizeof(stack)); pn->ivex=-1; pn->next=NULL; ps->size=size; ps->ptop=pn; return ps; } int empty_stack(pstack ps) { if(ps->ptop->next==NULL) return 1; else return 0; } void push_stack(pstack ps, int ivex) { pnode pn=NULL; pn=(pnode)malloc(sizeof(node)); pn->ivex=ivex; pn->next=ps->ptop; ps->ptop=pn; } int pop_stack(pstack ps) { int ivex=-1; pnode pn=NULL; if(!empty_stack(ps)) { pn=ps->ptop; ps->ptop=ps->ptop->next; ivex=pn->ivex; free(pn); } return ivex; } /********************************/ /**** 堆的实现 ****/ /********************************/ queue init_queue() { pnode pn=NULL; queue qu; pn=(pnode)malloc(sizeof(node)); pn->next; pn->ivex=-1; qu.front=qu.rear=pn; return qu; } int empty_queue(queue qu) { if(qu.front==qu.rear) return 1; else return 0; } void en_queue(queue qu, int ivex) { pnode pn=NULL; pn=(pnode)malloc(sizeof(node)); pn->ivex=ivex; pn->next=qu.rear->next; qu.rear=pn; } int de_queue(queue qu) { int ivex=-1; pnode pn=NULL; if(!empty_queue(qu)) { pn=qu.front; qu.front=qu.front->next; ivex=pn->ivex; free(pn); } return ivex; } /********************************/ /**** 图的实现 ****/ /********************************/ int LocateVex(MGraph g, char ch) { int i; for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) if(ch==g.vexs[i]) return i; return -1; } MGraph Create_UDG() { int i, j, w, p1, p2; char ch1, ch2; MGraph g; printf("Enter vexnum arcnum: "); scanf("%d %d", &g.vexnum, &g.arcnum); getchar(); for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) for(j=1; j<=g.vexnum; j++) g.arcs[i][j].adj=g.arcs[j][i].adj=INFINITY; /* UDG should define i-j and j-i */ printf("Enter %d vex.../n", g.vexnum); for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) { printf("vex %d: ", i); scanf("%c", &g.vexs[i]); getchar(); } printf("Enter %d arc.../n", g.arcnum); for(i=1; i<=g.arcnum; i++) { printf("arc %d: ", i); scanf("%c %c %d", &ch1, &ch2, &w); getchar(); p1=LocateVex(g, ch1); p2=LocateVex(g, ch2); g.arcs[p1][p2].adj=g.arcs[p2][p1].adj=w; } return g; } int FirstVex(MGraph g, int i) { int k; if(i>=1 && i<=g.vexnum) for(k=1; k<=g.vexnum; k++) if(g.arcs[i][k].adj!=INFINITY) return k; return -1; } int NextVex(MGraph g, int i, int j) { int k; if(i>=1 && i<=g.vexnum && j>=1 && j<=g.vexnum) for(k=j+1; k<=g.vexnum; k++) if(g.arcs[i][k].adj!=INFINITY) return k; return -1; } void DFS(MGraph g, int i) { int j; if(!visited[i]) { visited[i]=1; printf("%3c", g.vexs[i]); for(j=FirstVex(g, i); j>=1; j=NextVex(g, i, j)) if(!visited[j]) DFS(g, j); } } void DFS_Graph(MGraph g) { int i; visited=(int *)malloc((g.vexnum+1)*sizeof(int)); for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) visited[i]=0; for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) if(!visited[i]) DFS(g, i); } void DFS2_Graph(MGraph g) { int i, j, k; pstack ps=NULL; ps=init_stack(g.vexnum); visited=(int *)malloc((g.vexnum+1)*sizeof(int)); for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) visited[i]=0; for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) if(!visited[i]) { visited[i]=1; printf("%3c", g.vexs[i]); push_stack(ps, i); k=i; while (!empty_stack(ps)) { for(j=FirstVex(g, k); j>=1; j=NextVex(g, k, j)) { if(!visited[j]) { visited[j]=1; printf("%3c", g.vexs[j]); push_stack(ps, j); /* push all visited ivex */ k=j; /* newer node */ } } k=pop_stack(ps); } } } void BFS_Graph(MGraph g) { int i, j, k; queue qu; qu=init_queue(); visited=(int *)malloc((g.vexnum+1)*sizeof(int)); for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) visited[i]=0; for(i=1; i<=g.vexnum; i++) if(!visited[i]) { visited[i]=1; printf("%3c", g.vexs[i]); en_queue(qu, i); while (!empty_queue(qu)) { k=de_queue(qu); for(j=FirstVex(g, k); j>=1; j=NextVex(g, k, j)) if(!visited[j]) { visited[j]=1; printf("%3c", g.vexs[j]); en_queue(qu, j); } } } } /********************************/ /**** 主函数 ****/ /********************************/ int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { MGraph g; g=Create_UDG(); printf("/nDFS: "); DFS_Graph(g); /* recursion */ printf("/nDFS: "); DFS2_Graph(g); /* non recursion */ printf("/nBFS: "); BFS_Graph(g); printf("/n"); return 0; }
运行结果: