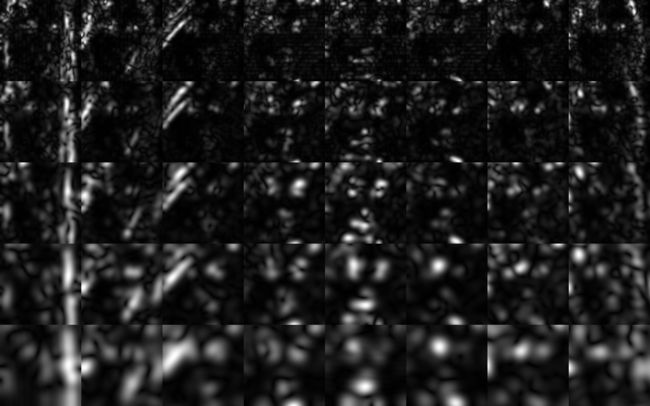
OpenCV实现Gabor滤波(2)
对上一版的Gabor滤波代码进行了修改:
1) 将filter2D函数的ddepth参数值改为CV_64, 因为输入图像的类型是CV_8U, 而gabor kernel的类型是CV_64, 如果ddepth为默认值-1,计算的结果会有误差(为什么?)。
2) 修改了garbor kernel的参数,包括kernel_size 和 v的范围,都是为了适应不同图像的大小。v 越小,Gabor函数的宽度越小,越能刻画细节信息,适应于较小的图像。按照Mian Zhou的学位论文里的推荐,v的范围选择为-1到3,而kernel_size的确定公式为:
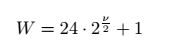 ,对应v的kernel_size大小分别为19x19, 25x25, 35x35, 49x49, 69x69.
,对应v的kernel_size大小分别为19x19, 25x25, 35x35, 49x49, 69x69.
我将所有kenel_size统一选为69x69。构建出的gabor bank如下图:
修改过的代码如下:
#include <opencv2/core/core.hpp>
#include <opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp>
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
using namespace cv;
using namespace std;
const double PI = 3.14159265;
// ref: http://blog.csdn.net/watkinsong/article/details/7876361
Mat getMyGabor(int width, int height, int U, int V, double Kmax, double f,
double sigma, int ktype, const string kernel_name)
{
//CV_ASSERT(width % 2 == 0 && height % 2 == 0);
//CV_ASSERT(ktype == CV_32F || ktype == CV_64F);
int half_width = width / 2;
int half_height = height / 2;
double Qu = PI*U/8;
double sqsigma = sigma*sigma;
double Kv = Kmax/pow(f,V);
double postmean = exp(-sqsigma/2);
Mat kernel_re(width, height, ktype);
Mat kernel_im(width, height, ktype);
Mat kernel_mag(width, height, ktype);
double tmp1, tmp2, tmp3;
for(int j = -half_height; j <= half_height; j++){
for(int i = -half_width; i <= half_width; i++){
tmp1 = exp(-(Kv*Kv*(j*j+i*i))/(2*sqsigma));
tmp2 = cos(Kv*cos(Qu)*i + Kv*sin(Qu)*j) - postmean;
tmp3 = sin(Kv*cos(Qu)*i + Kv*sin(Qu)*j);
if(ktype == CV_32F)
kernel_re.at<float>(j+half_height, i+half_width) =
(float)(Kv*Kv*tmp1*tmp2/sqsigma);
else
kernel_re.at<double>(j+half_height, i+half_width) =
(double)(Kv*Kv*tmp1*tmp2/sqsigma);
if(ktype == CV_32F)
kernel_im.at<float>(j+half_height, i+half_width) =
(float)(Kv*Kv*tmp1*tmp3/sqsigma);
else
kernel_im.at<double>(j+half_height, i+half_width) =
(double)(Kv*Kv*tmp1*tmp3/sqsigma);
}
}
magnitude(kernel_re, kernel_im, kernel_mag);
if(kernel_name.compare("real") == 0)
return kernel_re;
else if(kernel_name.compare("imag") == 0)
return kernel_im;
else{
printf("Invalid kernel name!\n");
return kernel_mag;
}
}
void construct_gabor_bank()
{
const int kernel_size = 69;
double Kmax = PI/2;
double f = sqrt(2.0);
double sigma = 2*PI;
int U = 0;
int V = 0;
int GaborH = kernel_size;
int GaborW = kernel_size;
int UStart = 0, UEnd = 8;
int VStart = -1, VEnd = 4;
Mat kernel;
Mat totalMat;
for(U = UStart; U < UEnd; U++){
Mat colMat;
for(V = VStart; V < VEnd; V++){
kernel = getMyGabor(GaborW, GaborH, U, V,
Kmax, f, sigma, CV_64F, "real");
//show gabor kernel
normalize(kernel, kernel, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX);
printf("U%dV%d\n", U, V);
if(V == VStart)
colMat = kernel;
else
vconcat(colMat, kernel, colMat);
}
if(U == UStart)
totalMat = colMat;
else
hconcat(totalMat, colMat, totalMat);
}
imshow("gabor bank", totalMat);
//normalize(totalMat, totalMat, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX);
//totalMat.convertTo(totalMat, CV_8U);
//imwrite("gabor_bank.jpg",totalMat);
waitKey(0);
}
Mat gabor_filter(Mat& img, int type)
{
// Ref: Mian Zhou. Thesis. Gabor-Boosting Face Recognition.
// https://code.google.com/p/gaborboosting/
const int kernel_size = 69; // should be odd
// variables for gabor filter
double Kmax = PI/2;
double f = sqrt(2.0);
double sigma = 2*PI;
int U = 7;
int V = 4;
int GaborH = kernel_size;
int GaborW = kernel_size;
int UStart = 0, UEnd = 8;
int VStart = -1, VEnd = 4;
//
Mat kernel_re, kernel_im;
Mat dst_re, dst_im, dst_mag;
// variables for filter2D
Point archor(-1,-1);
int ddepth = CV_64F;//CV_64F
double delta = 0;
// filter image with gabor bank
Mat totalMat, totalMat_re, totalMat_im;
for(U = UStart; U < UEnd; U++){
Mat colMat, colMat_re, colMat_im;
for(V = VStart; V < VEnd; V++){
kernel_re = getMyGabor(GaborW, GaborH, U, V,
Kmax, f, sigma, CV_64F, "real");
kernel_im = getMyGabor(GaborW, GaborH, U, V,
Kmax, f, sigma, CV_64F, "imag");
// normalize kernel ????
//normalize(kernel_re, kernel_re, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX);
//normalize(kernel_im, kernel_im, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX);
// flip kernel
// Gabor kernel is symmetric, so do not need flip
//flip(kernel_re, kernel_re, -1);
//flip(kernel_im, kernel_im, -1);
filter2D(img, dst_re, ddepth, kernel_re);
filter2D(img, dst_im, ddepth, kernel_im);
dst_mag.create(img.rows, img.cols, CV_64FC1);
magnitude(Mat_<float>(dst_re),Mat_<float>(dst_im),
dst_mag);
//show gabor kernel
normalize(dst_mag, dst_mag, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX);
normalize(dst_re, dst_re, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX);
normalize(dst_im, dst_im, 0, 1, CV_MINMAX);
if(V == VStart){
colMat = dst_mag;
colMat_re = dst_re;
colMat_im = dst_im;
}
else{
vconcat(colMat, dst_mag, colMat);
vconcat(colMat_re, dst_re, colMat_re);
vconcat(colMat_im, dst_im, colMat_im);
}
}
if(U == UStart){
totalMat = colMat;
totalMat_re = colMat_re;
totalMat_im = colMat_im;
}
else{
hconcat(totalMat, colMat, totalMat);
hconcat(totalMat_re, colMat_re, totalMat_re);
hconcat(totalMat_im, colMat_im, totalMat_im);
}
}
// return
switch(type){
case 0:
return totalMat;
case 1:
return totalMat_re;
case 2:
return totalMat_im;
default:
return totalMat;
}
}
int main( int argc, char** argv )
{
//construct_gabor_bank();
//return 0;
if(3 != argc){
printf("Usage: %s <image_path> <type>", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
string image_name(argv[1]);
int type = atoi(argv[2]);
Mat image;
image = imread(image_name, 0); // Read the file
if(! image.data ) // Check for invalid input
{
cout << "Could not open or find the image" << std::endl ;
return -1;
}
Mat filterd_image = gabor_filter(image, type);
imshow("origin image", image);
imshow("filtered image", filterd_image);
//normalize(filterd_image, filterd_image, 0, 255, CV_MINMAX);
//filterd_image.convertTo(filterd_image, CV_8U);
//imwrite("filterd_image.jpg",filterd_image);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
}
原图:
滤波结果:
可以与上一篇OpenCV实现Gabor滤波 的结果做对比
参考:Mian Zhou. Thesis. Gabor-Boosting Face Recognition. 从https://code.google.com/p/gaborboosting/source/checkout 可以下载到论文及代码。CSDN上大部分Gabor滤波代码都出自这位仁兄。
