hbase源码学习之put操作
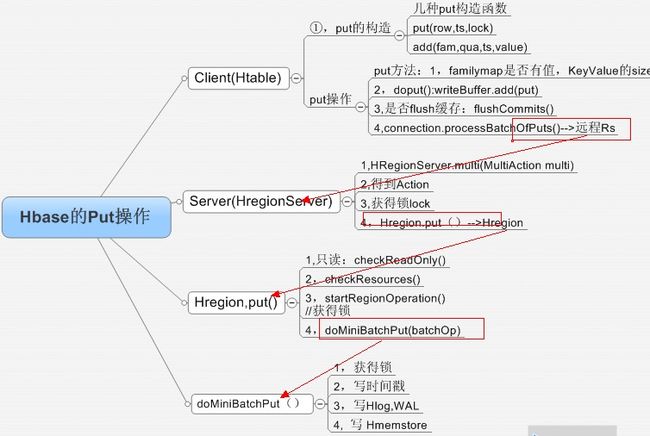
整理了下大致流程图:Client--->Htable---->Hmastermanager/ZK(获取-root-,--meta--)------>HregionServer----->Hregion------>Hlog/Hmemstore----->HFile
customHBase.put(table, row, fam, qual, val);
Result result = customHBase.get(table, row);
System.out.println("-------------------"+result);
customHBase.put(table, row, fam, null, 12);
Result result1 = customHBase.get(table, row);
System.out.println("-------------------"+result1);-------------------keyvalues={testrow_1/c:testqual_1/1356586011766/Put/vlen=8/ts=0}
-------------------keyvalues={testrow_1/c:/1356586011781/Put/vlen=8/ts=0, testrow_1/c:testqual_1/1356586011766/Put/vlen=8/ts=0}
故意写了个不存在的fam然后put:customHBase.put(table, lprow, lpfam, null, 12); 看着过程很明显了,好看源码
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.regionserver.HRegionServer.multi(HRegionServer.java:3089)
at sun.reflect.GeneratedMethodAccessor24.invoke(Unknown Source)
at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:25)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:597)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.WritableRpcEngine$Server.call(WritableRpcEngine.java:364)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.HBaseServer$Handler.run(HBaseServer.java:1326)
: 1 time, servers with issues:
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation.processBatchCallback(HConnectionManager.java:1591)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HConnectionManager$HConnectionImplementation.processBatch(HConnectionManager.java:1367)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable.flushCommits(HTable.java:945)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable.doPut(HTable.java:801)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTable.put(HTable.java:776)
at org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.HTablePool$PooledHTable.put(HTablePool.java:397)
hbase-0.90.5
一,首先来看下put的构造函数:ts为时间戳
①,public Put(byte [] row) {
this(row, null);
}
②, public Put(byte [] row, RowLock rowLock) {
this(row, HConstants.LATEST_TIMESTAMP, rowLock);
}
③, public Put(byte [] row, RowLock rowLock) {
this(row, HConstants.LATEST_TIMESTAMP, rowLock);
}
④,public Put(byte[] row, long ts) {
this(row, ts, null);
}
⑤,
public Put(byte [] row, long ts, RowLock rowLock) {
if(row == null || row.length > HConstants.MAX_ROW_LENGTH) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Row key is invalid");
}
this.row = Arrays.copyOf(row, row.length);
this.timestamp = ts;
if(rowLock != null) {
this.lockId = rowLock.getLockId();
}
}
看到⑤的时候很明显了,
①,有传入的参数key
②,如果时间戳为空,则为null
③,如果传入的rowlock不为空,那么就通过rowLock.getLockId()拿到lockId,赋值给当前lockid.
另外还有个
public Put(Put putToCopy)
Copy constructor. Creates a Put operation cloned from the specified Put.
this.writeToWAL = putToCopy.writeToWAL;
二,add操作:
public Put add(byte [] family, byte [] qualifier, long ts, byte [] value) {
List<KeyValue> list = getKeyValueList(family);
KeyValue kv = createPutKeyValue(family, qualifier, ts, value);
list.add(kv);
familyMap.put(kv.getFamily(), list);
return this;List<KeyValue> list
}
先取出依据family从familyMap拿到List<KeyValue> list,如果list为空,则创建一个list,然后依据参数family, qualifier, ts, value生成一个KeyValue
然后将KeyValue放入familyMap中
private List<KeyValue> getKeyValueList(byte[] family) {
List<KeyValue> list = familyMap.get(family);
if(list == null) {
list = new ArrayList<KeyValue>(0);
}
return list;
}
再来看下htable的put方法:
主要工作:
①,验证:验证put的familyMap是否有值,验证KeyValue的size是否在hbase,client.keyvalue,maxsize的范围之内
②,将put放入缓冲区,当currentWriteBufferSize > writeBufferSize (由hbase.client.write.buffer来确定),则刷新缓冲区,而且当autoFlush=true时,会立刻刷新缓冲区
private void doPut(final List<Put> puts) throws IOException {
int n = 0;
for (Put put : puts) {
validatePut(put);
writeBuffer.add(put);
currentWriteBufferSize += put.heapSize();
// we need to periodically see if the writebuffer is full instead of waiting until the end of the List
n++;
if (n % DOPUT_WB_CHECK == 0 && currentWriteBufferSize > writeBufferSize) {
flushCommits();
}
if (autoFlush || currentWriteBufferSize > writeBufferSize) {
flushCommits();
}
}
如果currentWriteBufferSize > writeBufferSize,此时就会调用 flushCommits()方法
//将row与action组装起来
@Override
public void flushCommits() throws IOException {
try {
connection.processBatchOfPuts(writeBuffer, tableName, pool);
} finally {
if (clearBufferOnFail) {
writeBuffer.clear();
currentWriteBufferSize = 0;
} else {
// the write buffer was adjusted by processBatchOfPuts
currentWriteBufferSize = 0;
for (Put aPut : writeBuffer) {
currentWriteBufferSize += aPut.heapSize();
}
}
}
}
-----------------------------------------------HConnectionManager.class-------------------------------------------------------------
connection.processBatchOfPuts(writeBuffer, tableName, pool);
最终调用的是 processBatch((List) list, tableName, pool, results);方法
processBatch内部有retry机制,// sleep first, if this is a retry
sleep时间: long sleepTime = getPauseTime(tries);
此后回依据参数调用locateRegion的去定位Region
HRegionLocation loc = locateRegion(tableName, row.getRow(), true);
private HRegionLocation locateRegion(final byte [] tableName,
final byte [] row, boolean useCache)
在这个函数中:
if (Bytes.equals(tableName, HConstants.ROOT_TABLE_NAME)) {
try {
HServerAddress hsa =
this.rootRegionTracker.waitRootRegionLocation(this.rpcTimeout);
LOG.debug("Lookedup root region location, connection=" + this +
"; hsa=" + hsa);
if (hsa == null) return null;
return new HRegionLocation(HRegionInfo.ROOT_REGIONINFO, hsa);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
return null;
}
} else if (Bytes.equals(tableName, HConstants.META_TABLE_NAME)) {
return locateRegionInMeta(HConstants.ROOT_TABLE_NAME, tableName, row,
useCache, metaRegionLock);
} else {
// Region not in the cache - have to go to the meta RS
return locateRegionInMeta(HConstants.META_TABLE_NAME, tableName, row,
useCache, userRegionLock);
}
①, 如果tableName == -ROOT- 就会调用waitRootRegionLocation方法,通过zookeeper得到rootregion的地址。返回一个new HRegionLocation(HRegionInfo.ROOT_REGIONINFO, hsa);
通过zookeeper得到rootregion的地址:
-----------------------------------------------RootRegionTracker.class--------------------
public HServerAddress waitRootRegionLocation(long timeout)
throws InterruptedException {
return dataToHServerAddress(super.blockUntilAvailable(timeout));
ZooKeeperNodeTracker.class中:
public synchronized byte [] blockUntilAvailable(long timeout)
throws InterruptedException {
if (timeout < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
boolean notimeout = timeout == 0;
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long remaining = timeout;
while (!this.stopped && (notimeout || remaining > 0) && this.data == null) {
if (notimeout) {
wait();
continue;
}
wait(remaining);
remaining = timeout - (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
}
return data;
}
在start方法中可以看到data:
byte [] data = ZKUtil.getDataAndWatch(watcher, node);
②, 如果tableName == .META.,就会调用locateRegionInMeta方法,
locateRegionInMeta(HConstants.ROOT_TABLE_NAME, tableName, row,useCache, metaRegionLock);
locateRegionInMeta中:
if (useCache) {
location = getCachedLocation(tableName, row);
}
先去从缓存中拿,如果缓存中没有,得到metakey,依据这个key首先定位root和meta region,然后
HRegionInterface server =
getHRegionConnection(metaLocation.getServerAddress());
通过去定位serveraddress,首先是通过regionInfoRow = server.getClosestRowBefore得到一个regionInfoRow,在得到一个value,regionInfoRow.getValue,最终得到serveraddress:serverAddress = Bytes.toString(value);
③, 如果不是.META.表也不是-ROOT-表,那么也会调用locateRegionInMeta方法,
// Region not in the cache - have to go to the meta RS
return locateRegionInMeta(HConstants.META_TABLE_NAME, tableName, row,
useCache, userRegionLock);
传入meta表,定位获得serveraddress
之后组装actions,即put,get,delete,等操作
之后交给线程池一步来处理:
public MultiResponse call() throws IOException {
return server.multi(multi);
}
------------------------------------------------------------------HRegionServer.java ------------------------------------------
public MultiResponse multi(MultiAction multi)方法,到这里终于看到HRegionInterface了。。。
for (Action a : actionsForRegion) {
action = a.getAction();
int originalIndex = a.getOriginalIndex();
try {
if (action instanceof Delete) {
delete(regionName, (Delete) action);
response.add(regionName, originalIndex, new Result());
} else if (action instanceof Get) {
response.add(regionName, originalIndex, get(regionName, (Get) action));
} else if (action instanceof Put) {
puts.add(a); // wont throw.
} else {
LOG.debug("Error: invalid Action, row must be a Get, Delete or Put.");
throw new DoNotRetryIOException("Invalid Action, row must be a Get, Delete or Put.");
}
} 这个太明显了。。主要是想睡觉了。。。明天再来看看MultiResponse,add()干了啥
/放假回来精力好了。。。/接上回,
还是HRegionServer.java的multi()方法public MultiResponse multi(MultiAction multi){}
重点是这两行代码:
1): HRegion region = getRegion(regionName);根据regionName获取HRegion
2): OperationStatus[] codes = region.put(putsWithLocks.toArray(new Pair[]{}));
调用 HRegion的put方法
--------------------------------------------------------------来看看HRegion.java--------------------------------------------------------------
put方法:
public void put(Put put) throws IOException {
this.put(put, null, put.getWriteToWAL());
}
/**
* @param put
* @param writeToWAL
* @throws IOException
*/
public void put(Put put, boolean writeToWAL) throws IOException {
this.put(put, null, writeToWAL);
}
/**
* @param put
* @param lockid
* @throws IOException
*/
public void put(Put put, Integer lockid) throws IOException {
this.put(put, lockid, put.getWriteToWAL());
}
/**
* @param put
* @param lockid
* @param writeToWAL
* @throws IOException
*/
public void put(Put put, Integer lockid, boolean writeToWAL)
throws IOException {
checkReadOnly();
// Do a rough check that we have resources to accept a write. The check is
// 'rough' in that between the resource check and the call to obtain a
// read lock, resources may run out. For now, the thought is that this
// will be extremely rare; we'll deal with it when it happens.
checkResources();
startRegionOperation();
try {
// We obtain a per-row lock, so other clients will block while one client
// performs an update. The read lock is released by the client calling
// #commit or #abort or if the HRegionServer lease on the lock expires.
// See HRegionServer#RegionListener for how the expire on HRegionServer
// invokes a HRegion#abort.
byte [] row = put.getRow();
// If we did not pass an existing row lock, obtain a new one
Integer lid = getLock(lockid, row, true);
try {
// All edits for the given row (across all column families) must happen atomically.
put(put.getFamilyMap(), writeToWAL);
} finally {
if(lockid == null) releaseRowLock(lid);
}
} finally {
closeRegionOperation();
}
}/**
* Struct-like class that tracks the progress of a batch operation,
* accumulating status codes and tracking the index at which processing
* is proceeding.
*/
private static class BatchOperationInProgress<T> {
T[] operations;
int nextIndexToProcess = 0;
OperationStatus[] retCodeDetails;
public BatchOperationInProgress(T[] operations) {
this.operations = operations;
this.retCodeDetails = new OperationStatus[operations.length];
Arrays.fill(this.retCodeDetails, new OperationStatus(
OperationStatusCode.NOT_RUN));
}
public boolean isDone() {
return nextIndexToProcess == operations.length;
}
}
/**
* Perform a batch put with no pre-specified locks
* @see HRegion#put(Pair[])
*/
public OperationStatus[] put(Put[] puts) throws IOException {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Pair<Put, Integer> putsAndLocks[] = new Pair[puts.length];
for (int i = 0; i < puts.length; i++) {
putsAndLocks[i] = new Pair<Put, Integer>(puts[i], null);
}
return put(putsAndLocks);
}
/**
* Perform a batch of puts.
*
* @param putsAndLocks
* the list of puts paired with their requested lock IDs.
* @return an array of OperationStatus which internally contains the
* OperationStatusCode and the exceptionMessage if any.
* @throws IOException
*/
public OperationStatus[] put(
Pair<Put, Integer>[] putsAndLocks) throws IOException {
BatchOperationInProgress<Pair<Put, Integer>> batchOp =
new BatchOperationInProgress<Pair<Put,Integer>>(putsAndLocks);
while (!batchOp.isDone()) {
checkReadOnly();
checkResources();
long newSize;
startRegionOperation();
try {
long addedSize = doMiniBatchPut(batchOp);
newSize = memstoreSize.addAndGet(addedSize);
} finally {
closeRegionOperation();
}
if (isFlushSize(newSize)) {
requestFlush();
}
}
return batchOp.retCodeDetails;
}
最终来看看 doMiniBatchPut()方法了:
主要步骤:
①:获得锁
②,写时间戳
③,写Hlog(预写日志)
④,写memstore
private long doMiniBatchPut(
BatchOperationInProgress<Pair<Put, Integer>> batchOp) throws IOException {
long now = EnvironmentEdgeManager.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] byteNow = Bytes.toBytes(now);
boolean locked = false;
/** Keep track of the locks we hold so we can release them in finally clause */
List<Integer> acquiredLocks = Lists.newArrayListWithCapacity(batchOp.operations.length);
// We try to set up a batch in the range [firstIndex,lastIndexExclusive)
int firstIndex = batchOp.nextIndexToProcess;
int lastIndexExclusive = firstIndex;
boolean success = false;
try {
// ------------------------------------
// STEP 1. Try to acquire as many locks as we can, and ensure
// we acquire at least one.
// ----------------------------------
int numReadyToWrite = 0;
while (lastIndexExclusive < batchOp.operations.length) {
Pair<Put, Integer> nextPair = batchOp.operations[lastIndexExclusive];
Put put = nextPair.getFirst();
Integer providedLockId = nextPair.getSecond();
// Check the families in the put. If bad, skip this one.
try {
checkFamilies(put.getFamilyMap().keySet());
} catch (NoSuchColumnFamilyException nscf) {
LOG.warn("No such column family in batch put", nscf);
batchOp.retCodeDetails[lastIndexExclusive] = new OperationStatus(
OperationStatusCode.BAD_FAMILY, nscf.getMessage());
lastIndexExclusive++;
continue;
}
// If we haven't got any rows in our batch, we should block to
// get the next one.
boolean shouldBlock = numReadyToWrite == 0;
Integer acquiredLockId = getLock(providedLockId, put.getRow(), shouldBlock);
if (acquiredLockId == null) {
// We failed to grab another lock
assert !shouldBlock : "Should never fail to get lock when blocking";
break; // stop acquiring more rows for this batch
}
if (providedLockId == null) {
acquiredLocks.add(acquiredLockId);
}
lastIndexExclusive++;
numReadyToWrite++;
}
// Nothing to put -- an exception in the above such as NoSuchColumnFamily?
if (numReadyToWrite <= 0) return 0L;
// We've now grabbed as many puts off the list as we can
// ------------------------------------
// STEP 2. Update any LATEST_TIMESTAMP timestamps
// ----------------------------------
for (int i = firstIndex; i < lastIndexExclusive; i++) {
updateKVTimestamps(
batchOp.operations[i].getFirst().getFamilyMap().values(),
byteNow);
}
this.updatesLock.readLock().lock();
locked = true;
// ------------------------------------
// STEP 3. Write to WAL :写memsotre之前先写WAL,类似innodb的redo log
// ----------------------------------
WALEdit walEdit = new WALEdit();
for (int i = firstIndex; i < lastIndexExclusive; i++) {
// Skip puts that were determined to be invalid during preprocessing
if (batchOp.retCodeDetails[i].getOperationStatusCode() != OperationStatusCode.NOT_RUN) {
continue;
}
Put p = batchOp.operations[i].getFirst();
if (!p.getWriteToWAL()) continue;
addFamilyMapToWALEdit(p.getFamilyMap(), walEdit);
}
// Append the edit to WAL
this.log.append(regionInfo, regionInfo.getTableDesc().getName(),
walEdit, now);
// ------------------------------------
// STEP 4. Write back to memstore
// ----------------------------------
long addedSize = 0;
for (int i = firstIndex; i < lastIndexExclusive; i++) {
if (batchOp.retCodeDetails[i].getOperationStatusCode() != OperationStatusCode.NOT_RUN) {
continue;
}
Put p = batchOp.operations[i].getFirst();
addedSize += applyFamilyMapToMemstore(p.getFamilyMap());//这里才算是put入memstore
batchOp.retCodeDetails[i] = new OperationStatus(
OperationStatusCode.SUCCESS);
}
success = true;
return addedSize;
} finally {
if (locked)
this.updatesLock.readLock().unlock();
for (Integer toRelease : acquiredLocks) {
releaseRowLock(toRelease);
}
if (!success) {
for (int i = firstIndex; i < lastIndexExclusive; i++) {
if (batchOp.retCodeDetails[i].getOperationStatusCode() == OperationStatusCode.NOT_RUN) {
batchOp.retCodeDetails[i] = new OperationStatus(
OperationStatusCode.FAILURE);
}
}
}
batchOp.nextIndexToProcess = lastIndexExclusive;
}
}
applyFamilyMapToMemstore:
private long applyFamilyMapToMemstore(Map<byte[], List<KeyValue>> familyMap) {
ReadWriteConsistencyControl.WriteEntry w = null;
long size = 0;
try {
w = rwcc.beginMemstoreInsert();//ReadWriteConsistencyControl
for (Map.Entry<byte[], List<KeyValue>> e : familyMap.entrySet()) {
byte[] family = e.getKey();
List<KeyValue> edits = e.getValue();
//得到一个store实例,通过store实例的store.add(kv)添加到store
Store store = getStore(family);
for (KeyValue kv: edits) {
kv.setMemstoreTS(w.getWriteNumber());
size += store.add(kv);
}
}
} finally {
rwcc.completeMemstoreInsert(w);
//其中twcc的作用:
//rwcc: private final ReadWriteConsistencyControl rwcc =
// new ReadWriteConsistencyControl();//Use RWCC to make this set of increments atomic to reads
}
return size;
}
public WriteEntry beginMemstoreInsert() {
synchronized (writeQueue) {
long nextWriteNumber = ++memstoreWrite;
WriteEntry e = new WriteEntry(nextWriteNumber);
writeQueue.add(e);//队列操作
return e;
}
}
// This is the pending queue of writes.
private final LinkedList<WriteEntry> writeQueue =
new LinkedList<WriteEntry>();