struts2 分析
转自:http://www.javaeye.com/topic/450979
1. Struts2架构图 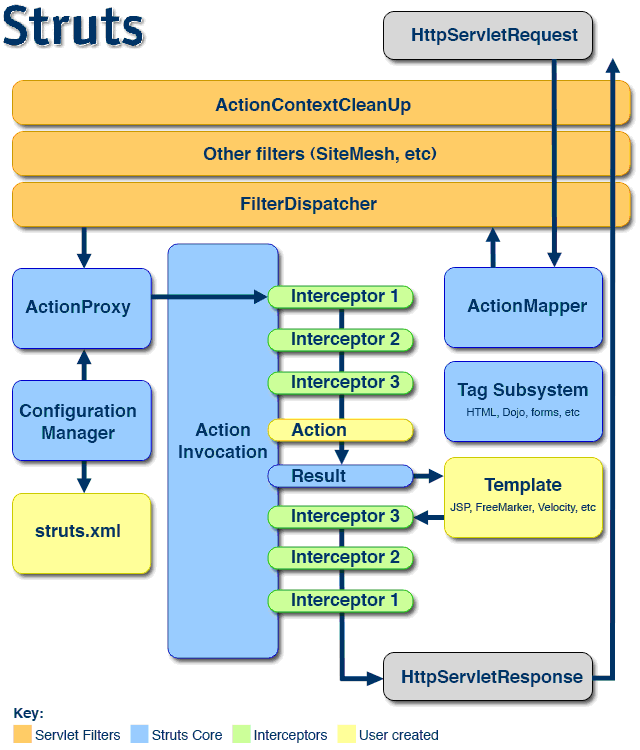
请求首先通过Filter chain,Filter主要包括ActionContextCleanUp,它主要清理当前线程的ActionContext和Dispatcher;FilterDispatcher主要通过AcionMapper来决定需要调用哪个Action。
ActionMapper取得了ActionMapping后,在Dispatcher的serviceAction方法里创建ActionProxy,ActionProxy创建ActionInvocation,然后ActionInvocation调用Interceptors,执行Action本身,创建Result并返回,当然,如果要在返回之前做些什么,可以实现PreResultListener。
2. Struts2部分类介绍
这部分从Struts2参考文档中翻译就可以了。
ActionMapper
ActionMapper其实是HttpServletRequest和Action调用请求的一个映射,它屏蔽了Action对于Request等java Servlet类的依赖。Struts2中它的默认实现类是DefaultActionMapper,ActionMapper很大的用处可以根据自己的需要来设计url格式,它自己也有Restful的实现,具体可以参考文档的docs/actionmapper.html。
ActionProxy&ActionInvocation
Action的一个代理,由ActionProxyFactory创建,它本身不包括Action实例,默认实现DefaultActionProxy是由ActionInvocation持有Action实例。ActionProxy作用是如何取得Action,无论是本地还是远程。而ActionInvocation的作用是如何执行Action,拦截器的功能就是在ActionInvocation中实现的。
ConfigurationProvider&Configuration
ConfigurationProvider就是Struts2中配置文件的解析器,Struts2中的配置文件主要是尤其实现类XmlConfigurationProvider及其子类StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider来解析。
3. Struts2请求流程
1、客户端发送请求
2、请求先通过ActionContextCleanUp-->FilterDispatcher
3、FilterDispatcher通过ActionMapper来决定这个Request需要调用哪个Action
4、如果ActionMapper决定调用某个Action,FilterDispatcher把请求的处理交给ActionProxy,这儿已经转到它的Delegate--Dispatcher来执行
5、ActionProxy根据ActionMapping和ConfigurationManager找到需要调用的Action类
6、ActionProxy创建一个ActionInvocation的实例
7、ActionInvocation调用真正的Action,当然这涉及到相关拦截器的调用
8、Action执行完毕,ActionInvocation创建Result并返回,当然,如果要在返回之前做些什么,可以实现PreResultListener。添加PreResultListener可以在Interceptor中实现,不知道其它还有什么方式?
4. Struts2(2.1.2)部分源码阅读
从org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher开始
- //创建Dispatcher,此类是一个Delegate,它是真正完成根据url解析,读取对应Action的地方
- public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
- try {
- this.filterConfig = filterConfig;
- initLogging();
- dispatcher = createDispatcher(filterConfig);
- dispatcher.init();
- dispatcher.getContainer().inject(this);
- //读取初始参数pakages,调用parse(),解析成类似/org/apache/struts2/static,/template的数组
- String param = filterConfig.getInitParameter("packages");
- String packages = "org.apache.struts2.static template org.apache.struts2.interceptor.debugging";
- if (param != null) {
- packages = param + " " + packages;
- }
- this.pathPrefixes = parse(packages);
- } finally {
- ActionContext.setContext(null);
- }
- }
顺着流程我们看Disptcher的init方法。init方法里就是初始读取一些配置文件等,先看init_DefaultProperties,主要是读取properties配置文件。
- private void init_DefaultProperties() {
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new DefaultPropertiesProvider());
- }
打开DefaultPropertiesProvider
- public void register(ContainerBuilder builder, LocatableProperties props)
- throws ConfigurationException {
- Settings defaultSettings = null;
- try {
- defaultSettings = new PropertiesSettings("org/apache/struts2/default");
- } catch (Exception e) {
- throw new ConfigurationException("Could not find or error in org/apache/struts2/default.properties", e);
- }
- loadSettings(props, defaultSettings);
- }
- //PropertiesSettings
- //读取org/apache/struts2/default.properties的配置信息,如果项目中需要覆盖,可以在classpath里的struts.properties里覆写
- public PropertiesSettings(String name) {
- URL settingsUrl = ClassLoaderUtils.getResource(name + ".properties", getClass());
- if (settingsUrl == null) {
- LOG.debug(name + ".properties missing");
- settings = new LocatableProperties();
- return;
- }
- settings = new LocatableProperties(new LocationImpl(null, settingsUrl.toString()));
- // Load settings
- InputStream in = null;
- try {
- in = settingsUrl.openStream();
- settings.load(in);
- } catch (IOException e) {
- throw new StrutsException("Could not load " + name + ".properties:" + e, e);
- } finally {
- if(in != null) {
- try {
- in.close();
- } catch(IOException io) {
- LOG.warn("Unable to close input stream", io);
- }
- }
- }
- }
再来看init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations方法,这个是读取struts-default.xml和Struts.xml的方法。
- private void init_TraditionalXmlConfigurations() {
- //首先读取web.xml中的config初始参数值
- //如果没有配置就使用默认的"struts-default.xml,struts-plugin.xml,struts.xml",
- //这儿就可以看出为什么默认的配置文件必须取名为这三个名称了
- //如果不想使用默认的名称,直接在web.xml中配置config初始参数即可
- String configPaths = initParams.get("config");
- if (configPaths == null) {
- configPaths = DEFAULT_CONFIGURATION_PATHS;
- }
- String[] files = configPaths.split("//s*[,]//s*");
- //依次解析配置文件,xwork.xml单独解析
- for (String file : files) {
- if (file.endsWith(".xml")) {
- if ("xwork.xml".equals(file)) {
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new XmlConfigurationProvider(file, false));
- } else {
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(new StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider(file, false, servletContext));
- }
- } else {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid configuration file name");
- }
- }
- }
对于其它配置文件只用StrutsXmlConfigurationProvider,此类继承XmlConfigurationProvider,而XmlConfigurationProvider又实现ConfigurationProvider接口。类XmlConfigurationProvider负责配置文件的读取和解析,addAction()方法负责读取<action>标签,并将数据保存在ActionConfig中;addResultTypes()方法负责将<result-type>标签转化为ResultTypeConfig对象;loadInterceptors()方法负责将<interceptor>标签转化为InterceptorConfi对象;loadInterceptorStack()方法负责将<interceptor-ref>标签转化为InterceptorStackConfig对象;loadInterceptorStacks()方法负责将<interceptor-stack>标签转化成InterceptorStackConfig对象。而上面的方法最终会被addPackage()方法调用,将所读取到的数据汇集到PackageConfig对象中。来看XmlConfigurationProvider的源代码,详细的我自己也就大体浏览了一下,各位可以自己研读。
- protected PackageConfig addPackage(Element packageElement) throws ConfigurationException {
- PackageConfig.Builder newPackage = buildPackageContext(packageElement);
- if (newPackage.isNeedsRefresh()) {
- return newPackage.build();
- }
- .
- addResultTypes(newPackage, packageElement);
- loadInterceptors(newPackage, packageElement);
- loadDefaultInterceptorRef(newPackage, packageElement);
- loadDefaultClassRef(newPackage, packageElement);
- loadGlobalResults(newPackage, packageElement);
- loadGobalExceptionMappings(newPackage, packageElement);
- NodeList actionList = packageElement.getElementsByTagName("action");
- for (int i = 0; i < actionList.getLength(); i++) {
- Element actionElement = (Element) actionList.item(i);
- addAction(actionElement, newPackage);
- }
- loadDefaultActionRef(newPackage, packageElement);
- PackageConfig cfg = newPackage.build();
- configuration.addPackageConfig(cfg.getName(), cfg);
- return cfg;
- }
这儿发现一个配置上的小技巧,我的xwork2.0.*是没有的,但是看源码是看到xwork2.1.*是可以的。继续看XmlConfigurationProvider的源代码:
- private List loadConfigurationFiles(String fileName, Element includeElement) {
- List<Document> docs = new ArrayList<Document>();
- if (!includedFileNames.contains(fileName)) {
- Element rootElement = doc.getDocumentElement();
- NodeList children = rootElement.getChildNodes();
- int childSize = children.getLength();
- for (int i = 0; i < childSize; i++) {
- Node childNode = children.item(i);
- if (childNode instanceof Element) {
- Element child = (Element) childNode;
- final String nodeName = child.getNodeName();
- //解析每个action配置是,对于include文件可以使用通配符*来进行配置
- //如Struts.xml中可配置成<include file="actions_*.xml"/>
- if (nodeName.equals("include")) {
- String includeFileName = child.getAttribute("file");
- if(includeFileName.indexOf('*') != -1 ) {
- ClassPathFinder wildcardFinder = new ClassPathFinder();
- wildcardFinder.setPattern(includeFileName);
- Vector<String> wildcardMatches = wildcardFinder.findMatches();
- for (String match : wildcardMatches) {
- docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(match, child));
- }
- }
- else {
- docs.addAll(loadConfigurationFiles(includeFileName, child));
- }
- }
- }
- }
- docs.add(doc);
- loadedFileUrls.add(url.toString());
- }
- }
- return docs;
- }
init_CustomConfigurationProviders方式初始自定义的Provider,配置类全名和实现ConfigurationProvider接口,用逗号隔开即可。
- private void init_CustomConfigurationProviders() {
- String configProvs = initParams.get("configProviders");
- if (configProvs != null) {
- String[] classes = configProvs.split("//s*[,]//s*");
- for (String cname : classes) {
- try {
- Class cls = ClassLoaderUtils.loadClass(cname, this.getClass());
- ConfigurationProvider prov = (ConfigurationProvider)cls.newInstance();
- configurationManager.addConfigurationProvider(prov);
- }
- }
- }
- }
好了,现在再回到FilterDispatcher,每次发送一个Request,FilterDispatcher都会调用doFilter方法。
- public void doFilter(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
- HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) req;
- HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) res;
- ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext();
- String timerKey = "FilterDispatcher_doFilter: ";
- try {
- ValueStack stack = dispatcher.getContainer().getInstance(ValueStackFactory.class).createValueStack();
- ActionContext ctx = new ActionContext(stack.getContext());
- ActionContext.setContext(ctx);
- UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
- //根据content type来使用不同的Request封装,可以参见Dispatcher的wrapRequest
- request = prepareDispatcherAndWrapRequest(request, response);
- ActionMapping mapping;
- try {
- //根据url取得对应的Action的配置信息--ActionMapping,actionMapper是通过Container的inject注入的
- mapping = actionMapper.getMapping(request, dispatcher.getConfigurationManager());
- } catch (Exception ex) {
- log.error("error getting ActionMapping", ex);
- dispatcher.sendError(request, response, servletContext, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, ex);
- return;
- }
- //如果找不到对应的action配置,则直接返回。比如你输入***.jsp等等
- //这儿有个例外,就是如果path是以“/struts”开头,则到初始参数packages配置的包路径去查找对应的静态资源并输出到页面流中,当然.class文件除外。如果再没有则跳转到404
- if (mapping == null) {
- // there is no action in this request, should we look for a static resource?
- String resourcePath = RequestUtils.getServletPath(request);
- if ("".equals(resourcePath) && null != request.getPathInfo()) {
- resourcePath = request.getPathInfo();
- }
- if (serveStatic && resourcePath.startsWith("/struts")) {
- String name = resourcePath.substring("/struts".length());
- findStaticResource(name, request, response);
- } else {
- chain.doFilter(request, response);
- }
- return;
- }
- //正式开始Action的方法了
- dispatcher.serviceAction(request, response, servletContext, mapping);
- } finally {
- try {
- ActionContextCleanUp.cleanUp(req);
- } finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
- }
- }
- }
Dispatcher类的serviceAction方法:
- public void serviceAction(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, ServletContext context,ActionMapping mapping) throws ServletException {
- Map<String, Object> extraContext = createContextMap(request, response, mapping, context);
- // If there was a previous value stack, then create a new copy and pass it in to be used by the new Action
- ValueStack stack = (ValueStack) request.getAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY);
- if (stack != null) {
- extraContext.put(ActionContext.VALUE_STACK, valueStackFactory.createValueStack(stack));
- }
- String timerKey = "Handling request from Dispatcher";
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
- String namespace = mapping.getNamespace();
- String name = mapping.getName();
- String method = mapping.getMethod();
- Configuration config = configurationManager.getConfiguration();
- ActionProxy proxy = config.getContainer().getInstance(ActionProxyFactory.class).createActionProxy(
- namespace, name, method, extraContext, true, false);
- request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, proxy.getInvocation().getStack());
- // if the ActionMapping says to go straight to a result, do it!
- if (mapping.getResult() != null) {
- Result result = mapping.getResult();
- result.execute(proxy.getInvocation());
- } else {
- proxy.execute();
- }
- // If there was a previous value stack then set it back onto the request
- if (stack != null) {
- request.setAttribute(ServletActionContext.STRUTS_VALUESTACK_KEY, stack);
- }
- } catch (ConfigurationException e) {
- LOG.error("Could not find action or result", e);
- sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND, e);
- } catch (Exception e) {
- sendError(request, response, context, HttpServletResponse.SC_INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR, e);
- } finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
- }
- }
第一句createContextMap()方法,该方法主要把Application、Session、Request的key value值拷贝到Map中,并放在HashMap<String,Object>中,可以参见createContextMap方法:
- public Map<String,Object> createContextMap(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
- ActionMapping mapping, ServletContext context) {
- // request map wrapping the http request objects
- Map requestMap = new RequestMap(request);
- // parameters map wrapping the http parameters. ActionMapping parameters are now handled and applied separately
- Map params = new HashMap(request.getParameterMap());
- // session map wrapping the http session
- Map session = new SessionMap(request);
- // application map wrapping the ServletContext
- Map application = new ApplicationMap(context);
- Map<String,Object> extraContext = createContextMap(requestMap, params, session, application, request, response, context);
- extraContext.put(ServletActionContext.ACTION_MAPPING, mapping);
- return extraContext;
- }
后面才是最主要的--ActionProxy,ActionInvocation。ActionProxy是Action的一个代理类,也就是说Action的调用是通过ActionProxy实现的,其实就是调用了ActionProxy.execute()方法,而该方法又调用了ActionInvocation.invoke()方法。归根到底,最后调用的是DefaultActionInvocation.invokeAction()方法。先看DefaultActionInvocation的init方法。
- public void init(ActionProxy proxy) {
- this.proxy = proxy;
- Map contextMap = createContextMap();
- // Setting this so that other classes, like object factories, can use the ActionProxy and other
- // contextual information to operate
- ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
- if(actionContext != null) {
- actionContext.setActionInvocation(this);
- }
- //创建Action,可Struts2里是每次请求都新建一个Action
- createAction(contextMap);
- if (pushAction) {
- stack.push(action);
- contextMap.put("action", action);
- }
- invocationContext = new ActionContext(contextMap);
- invocationContext.setName(proxy.getActionName());
- // get a new List so we don't get problems with the iterator if someone changes the list
- List interceptorList = new ArrayList(proxy.getConfig().getInterceptors());
- interceptors = interceptorList.iterator();
- }
- protected void createAction(Map contextMap) {
- // load action
- String timerKey = "actionCreate: "+proxy.getActionName();
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
- //这儿默认建立Action是StrutsObjectFactory,实际中我使用的时候都是使用Spring创建的Action,这个时候使用的是SpringObjectFactory
- action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap);
- }
- ..
- } finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
- }
- if (actionEventListener != null) {
- action = actionEventListener.prepare(action, stack);
- }
- }
接下来看看DefaultActionInvocation 的invoke方法。
- public void init(ActionProxy proxy) {
- this.proxy = proxy;
- Map contextMap = createContextMap();
- // Setting this so that other classes, like object factories, can use the ActionProxy and other
- // contextual information to operate
- ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext();
- if(actionContext != null) {
- actionContext.setActionInvocation(this);
- }
- //创建Action,可Struts2里是每次请求都新建一个Action
- createAction(contextMap);
- if (pushAction) {
- stack.push(action);
- contextMap.put("action", action);
- }
- invocationContext = new ActionContext(contextMap);
- invocationContext.setName(proxy.getActionName());
- // get a new List so we don't get problems with the iterator if someone changes the list
- List interceptorList = new ArrayList(proxy.getConfig().getInterceptors());
- interceptors = interceptorList.iterator();
- }
- protected void createAction(Map contextMap) {
- // load action
- String timerKey = "actionCreate: "+proxy.getActionName();
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
- //这儿默认建立Action是StrutsObjectFactory,实际中我使用的时候都是使用Spring创建的Action,这个时候使用的是SpringObjectFactory
- action = objectFactory.buildAction(proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getNamespace(), proxy.getConfig(), contextMap);
- }
- ..
- } finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
- }
- if (actionEventListener != null) {
- action = actionEventListener.prepare(action, stack);
- }
- }
- //接下来看看DefaultActionInvocation 的invoke方法。
- public String invoke() throws Exception {
- String profileKey = "invoke: ";
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(profileKey);
- if (executed) {
- throw new IllegalStateException("Action has already executed");
- }
- //先执行interceptors
- if (interceptors.hasNext()) {
- final InterceptorMapping interceptor = (InterceptorMapping) interceptors.next();
- UtilTimerStack.profile("interceptor: "+interceptor.getName(),
- new UtilTimerStack.ProfilingBlock<String>() {
- public String doProfiling() throws Exception {
- resultCode = interceptor.getInterceptor().intercept(DefaultActionInvocation.this);
- return null;
- }
- });
- } else {
- //interceptor执行完了之后执行action
- resultCode = invokeActionOnly();
- }
- // this is needed because the result will be executed, then control will return to the Interceptor, which will
- // return above and flow through again
- if (!executed) {
- //在Result返回之前调用preResultListeners
- if (preResultListeners != null) {
- for (Iterator iterator = preResultListeners.iterator();
- iterator.hasNext();) {
- PreResultListener listener = (PreResultListener) iterator.next();
- String _profileKey="preResultListener: ";
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(_profileKey);
- listener.beforeResult(this, resultCode);
- }
- finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(_profileKey);
- }
- }
- }
- // now execute the result, if we're supposed to
- if (proxy.getExecuteResult()) {
- executeResult();
- }
- executed = true;
- }
- return resultCode;
- }
- finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(profileKey);
- }
- }
看程序中的if(interceptors.hasNext())语句,当然,interceptors里存储的是interceptorMapping列表(它包括一个Interceptor和一个name),所有的截拦器必须实现Interceptor的intercept方法,而该方法的参数恰恰又是ActionInvocation,在intercept方法中还是调用invocation.invoke(),从而实现了一个Interceptor链的调用。当所有的Interceptor执行完,最后调用invokeActionOnly方法来执行Action相应的方法。
- protected String invokeAction(Object action, ActionConfig actionConfig) throws Exception {
- String methodName = proxy.getMethod();
- String timerKey = "invokeAction: "+proxy.getActionName();
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
- boolean methodCalled = false;
- Object methodResult = null;
- Method method = null;
- try {
- //获得需要执行的方法
- method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(methodName, new Class[0]);
- } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
- //如果没有对应的方法,则使用do+Xxxx来再次获得方法
- try {
- String altMethodName = "do" + methodName.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase() + methodName.substring(1);
- method = getAction().getClass().getMethod(altMethodName, new Class[0]);
- } catch (NoSuchMethodException e1) {
- // well, give the unknown handler a shot
- if (unknownHandler != null) {
- try {
- methodResult = unknownHandler.handleUnknownActionMethod(action, methodName);
- methodCalled = true;
- } catch (NoSuchMethodException e2) {
- // throw the original one
- throw e;
- }
- } else {
- throw e;
- }
- }
- }
- if (!methodCalled) {
- methodResult = method.invoke(action, new Object[0]);
- }
- //根据不同的Result类型返回不同值
- //如输出流Result
- if (methodResult instanceof Result) {
- this.explicitResult = (Result) methodResult;
- return null;
- } else {
- return (String) methodResult;
- }
- } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
- throw new IllegalArgumentException("The " + methodName + "() is not defined in action " + getAction().getClass() + "");
- } catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
- // We try to return the source exception.
- Throwable t = e.getTargetException();
- if (actionEventListener != null) {
- String result = actionEventListener.handleException(t, getStack());
- if (result != null) {
- return result;
- }
- }
- if (t instanceof Exception) {
- throw(Exception) t;
- } else {
- throw e;
- }
- } finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
- }
- }
好了,action执行完了,还要根据ResultConfig返回到view,也就是在invoke方法中调用executeResult方法。
- private void executeResult() throws Exception {
- //根据ResultConfig创建Result
- result = createResult();
- String timerKey = "executeResult: "+getResultCode();
- try {
- UtilTimerStack.push(timerKey);
- if (result != null) {
- //这儿正式执行:)
- //可以参考Result的实现,如用了比较多的ServletDispatcherResult,ServletActionRedirectResult,ServletRedirectResult
- result.execute(this);
- } else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode)) {
- throw new ConfigurationException("No result defined for action " + getAction().getClass().getName()
- + " and result " + getResultCode(), proxy.getConfig());
- } else {
- if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
- LOG.debug("No result returned for action "+getAction().getClass().getName()+" at "+proxy.getConfig().getLocation());
- }
- }
- } finally {
- UtilTimerStack.pop(timerKey);
- }
- }
- public Result createResult() throws Exception {
- if (explicitResult != null) {
- Result ret = explicitResult;
- explicitResult = null;;
- return ret;
- }
- ActionConfig config = proxy.getConfig();
- Map results = config.getResults();
- ResultConfig resultConfig = null;
- synchronized (config) {
- try {
- //根据result名称获得ResultConfig,resultCode就是result的name
- resultConfig = (ResultConfig) results.get(resultCode);
- } catch (NullPointerException e) {
- }
- if (resultConfig == null) {
- //如果找不到对应name的ResultConfig,则使用name为*的Result
- resultConfig = (ResultConfig) results.get("*");
- }
- }
- if (resultConfig != null) {
- try {
- //参照StrutsObjectFactory的代码
- Result result = objectFactory.buildResult(resultConfig, invocationContext.getContextMap());
- return result;
- } catch (Exception e) {
- LOG.error("There was an exception while instantiating the result of type " + resultConfig.getClassName(), e);
- throw new XWorkException(e, resultConfig);
- }
- } else if (resultCode != null && !Action.NONE.equals(resultCode) && unknownHandler != null) {
- return unknownHandler.handleUnknownResult(invocationContext, proxy.getActionName(), proxy.getConfig(), resultCode);
- }
- return null;
- }
- //StrutsObjectFactory
- public Result buildResult(ResultConfig resultConfig, Map extraContext) throws Exception {
- String resultClassName = resultConfig.getClassName();
- if (resultClassName == null)
- return null;
- //创建Result,因为Result是有状态的,所以每次请求都新建一个
- Object result = buildBean(resultClassName, extraContext);
- //这句很重要,后面将会谈到,reflectionProvider参见OgnlReflectionProvider;
- //resultConfig.getParams()就是result配置文件里所配置的参数<param></param>
- //setProperties方法最终调用的是Ognl类的setValue方法
- //这句其实就是把param名值设置到根对象result上
- reflectionProvider.setProperties(resultConfig.getParams(), result, extraContext);
- if (result instanceof Result)
- return (Result) result;
- throw new ConfigurationException(result.getClass().getName() + " does not implement Result.");
- }
这样,一个Struts2的请求流程基本上就结束了。