poj 2046
| Time Limit: 5000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 1286 | Accepted: 592 |
Description
You have 28 cards labeled with two-digit numbers. The first digit (from 1 to 4) represents the suit of the card, and the second digit (from 1 to 7) represents the value of the card.
First, you shu2e the cards and lay them face up on the table in four rows of seven cards, leaving a space of one card at the extreme left of each row. The following shows an example of initial layout.

Next, you remove all cards of value 1, and put them in the open space at the left end of the rows: "11" to the top row, "21" to the next, and so on.
Now you have 28 cards and four spaces, called gaps, in four rows and eight columns. You start moving cards from this layout.
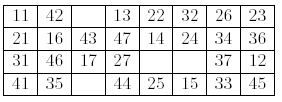
At each move, you choose one of the four gaps and fill it with the successor of the left neighbor of the gap. The successor of a card is the next card in the same suit, when it exists. For instance the successor of "42" is "43", and "27" has no successor.
In the above layout, you can move "43" to the gap at the right of "42", or "36" to the gap at the right of "35". If you move "43", a new gap is generated to the right of "16". You cannot move any card to the right of a card of value 7, nor to the right of a gap.
The goal of the game is, by choosing clever moves, to make four ascending sequences of the same suit, as follows.

Your task is to find the minimum number of moves to reach the goal layout.
Input
Each layout consists of five lines - a blank line and four lines which represent initial layouts of four rows. Each row has seven two-digit numbers which correspond to the cards.
Output
Sample Input
4 12 13 14 15 16 17 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 11 26 31 13 44 21 24 42 17 45 23 25 41 36 11 46 34 14 12 37 32 47 16 43 27 35 22 33 15 17 12 16 13 15 14 11 27 22 26 23 25 24 21 37 32 36 33 35 34 31 47 42 46 43 45 44 41 27 14 22 35 32 46 33 13 17 36 24 44 21 15 43 16 45 47 23 11 26 25 37 41 34 42 12 31
Sample Output
0 33 60 -1
Source
分析:此题貌似只有搜索了,DFS和BFS均可,BFS稍快,两者都应该记录状态+hash判重,
用DFS的话,得写个估值函数,貌似有些效果,函数f=当前不在最终位置的卡片数/2,这函数是看别人的,我想不出更好的。。。
BFS貌似只能暴力了。。。汗~~~
话说一开始hash函数写错,无限冲突啊,比没hash还惨。。。。![]()
BFS代码:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int M=1000007; struct data { char s[32],e[4],p[48]; int ans; }w[500000]; int id[M],ans; inline int BKDRHash(char *str) { int hash=0,q=0; while(++q<33)hash=hash*7+(*str++); return((hash&0x7FFFFFFF)%M); } inline void insert(char *c,int i) { int x=BKDRHash(c); while(id[x]>=0) { x+=7; if(x>=M)x%=M; } id[x]=i; } inline bool cmp(char *p,char *q) { for(int i=0;i<32;++i,++p,++q) if(*p!=*q)return 1; return 0; } inline int find(char *c) { int x=BKDRHash(c); while(id[x]>=0&&cmp(c,w[id[x]].s)) { x+=7; if(x>=M)x%=M; } return id[x]; } inline void get(char &a) { char ch=getchar(); while (ch<'0'||ch>'9')ch=getchar(); for(a=0;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar())a=a*10+ch-48; if((a==11)||(a==21)||(a==31)||(a==41))a=0; } inline void cpy(char *p,char *q,int n) { for(int i=0;i<n;++i,++p,++q)*p=*q; } inline int bfs() { int l=0,r=1,rr=2,i,k,s,p,e; do { cpy(w[rr].s,w[++l].s,32); for(i=0;i<4;++i) if(w[l].s[(e=w[l].e[i])-1]%10<7&&w[l].s[e-1]>0) { w[rr].s[e]=s=w[l].s[e-1]+1,w[rr].s[p=w[l].p[s]]=0; if((k=find(w[rr].s))<0) { ++r,++rr,cpy(w[r].e,w[l].e,4),cpy(w[r].p,w[l].p,48); w[r].e[i]=p,w[r].p[s]=e,w[r].ans=w[l].ans+1; insert(w[r].s,r); cpy(w[rr].s,w[l].s,32); } else w[rr].s[p]=s,w[rr].s[e]=0; if(!k)return w[l].ans+1; } }while(l<r); return -1; } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int n,i,j,k; for(i=0;i<25;i+=8) for(j=0;j<7;++j)w[0].s[i+j]=(i/8+1)*10+j+1; scanf("%d",&n); while(n--) { memset(id,-1,sizeof(id)); insert(w[0].s,0); for(i=0;i<25;i+=8) for(w[1].s[i]=(i/8+1)*10+1,j=1;j<8;++j)get(w[1].s[i+j]),w[1].p[w[1].s[i+j]]=i+j; if(!find(w[1].s))printf("0/n"); else { for(k=i=0;i<25;i+=8) for(j=0;j<8;++j) if(!w[1].s[i+j])w[1].e[k++]=i+j; w[1].ans=0; insert(w[1].s,1); printf("%d/n",bfs()); } } return 0; }
DFS代码:
#include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; const int M=1000007; char g[32],w[500000][32],t[500000],p[48],e[4],goat[32]={0}; int id[M],ans,tot; inline int BKDRHash(char *str) { int hash=0,q=0; while(++q<33) hash=hash*7+(*str++); return((hash&0x7FFFFFFF)%M); } inline void insert(char *c,int i) { int x=BKDRHash(c); while(id[x]) { x+=7; if(x>=M)x%=M; } id[x]=i; } inline bool cmp(char *p,char *q) { for(int i=0;i<32;++i,++p,++q) if(*p!=*q)return 1; return 0; } inline int find(char *c) { int x=BKDRHash(c); while(id[x]&&cmp(c,w[id[x]])) { x+=7; if(x>=M)x%=M; } return id[x]; } inline void get(char &a) { char ch=getchar(); while (ch<'0'||ch>'9')ch=getchar(); for(a=0;ch>='0'&&ch<='9';ch=getchar())a=a*10+ch-48; if((a==11)||(a==21)||(a==31)||(a==41))a=0; } inline int count() { int c=0; for(int i=0;i<32;++i) if(g[i]!=goat[i])++c; return c/2; } inline void cpy(char *p,char *q) { for(int i=0;i<32;++i,++p,++q)*p=*q; } void dfs(int now) { int cur; if(now+(cur=count())>=ans)return; if(!cur) { ans=now; return; } int i,j,k; for(i=0;i<4;++i) if(g[(j=e[i])-1]%10<7&&g[j-1]>0) { g[e[i]=p[g[j]=g[j-1]+1]]=0; p[g[j]]=j; if(!(k=find(g))||now+1<t[k]) { if(!k)cpy(w[++tot],g),t[tot]=now+1; else t[k]=now+1; insert(g,tot); dfs(now+1); } p[g[e[i]]=g[j]]=e[i]; g[e[i]=j]=0; } } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { int n,i,j,k; for(i=0;i<25;i+=8) for(j=0;j<7;++j)goat[i+j]=(i/8+1)*10+j+1; scanf("%d",&n); while(n--) { for(i=0;i<25;i+=8) for(g[i]=(i/8+1)*10+1,j=1;j<8;++j)get(g[i+j]),p[g[i+j]]=i+j; for(k=i=0;i<25;i+=8) for(j=0;j<8;++j) if(!g[i+j])e[k++]=i+j; cpy(w[tot=1],g); memset(id,0,sizeof(id)); insert(g,tot); ans=1000000; dfs(0); printf("%d/n",ans<1000000?ans:-1); } return 0; }